Class 5 Science - Ecosystem Interdependence in Nature - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Which of the following is a biotic component of an ecosystem?
(a) Water
(b) Air
(c) Plants
(d) Soil
Ans: (c)
Plants, along with other living things, are biotic components of an ecosystem. The types of biotic components are producers, consumers and decomposers. 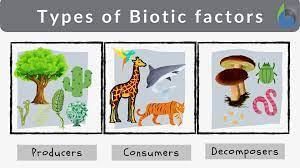
(ii) What do we call the process by which plants produce their food?
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Decomposition
(d) Transpiration
Ans: (b)
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants produce their food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.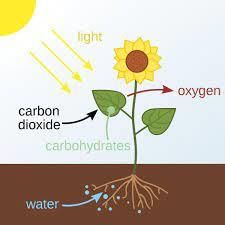
(iii) Which of the following is an example of a decomposer in an ecosystem?
(a) Deer
(b) Lion
(c) Bacteria
(d) Grass
Ans: (c)
Bacteria are decomposers in an ecosystem as they help break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil.
(iv) What is the main source of energy in an ecosystem?
(a) Wind
(b) Sun
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Ans: (b)
The sun is the main source of energy in an ecosystem, as it provides the energy needed for plants to carry out photosynthesis.
(v) What do we call the organisms that eat plants for their food?
(a) Carnivores
(b) Herbivores
(c) Omnivores
(d) Decomposers
Ans: (b)
Herbivores are organisms that eat plants for their food, such as deer, rabbits, and cows.
Q2: Fill in the Blanks.
(i) The __________ refers to all the living organisms and non-living components in a specific area.
Ans: ecosystem
An ecosystem includes all the plants, animals, and microorganisms in an area, along with the non-living factors like soil, water, and air.
(ii) __________ is the process by which green plants make their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Ans: Photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
(iii) The role of an organism in an ecosystem, including its relationships with other organisms, is called its __________.
Ans: ecological niche
An ecological niche refers to an organism's specific role and position in its environment, including its interactions with other organisms.
(iv) The place where an organism lives and finds its food is called its __________.
Ans: habitat
A habitat provides the necessary resources and conditions for an organism to survive, such as food, water, shelter, and suitable living conditions.
(v) Decomposers play a vital role in the ecosystem by __________.
Ans: breaking down dead organisms and organic matter
Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, break down dead plants, animals, and other organic materials, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Q3: True or False.
(i) All living organisms depend on each other for their survival in an ecosystem.
(ii) Photosynthesis is the process by which animals produce their food.
(iii) Decomposers help in recycling nutrients by breaking down dead organisms.
(iv) All herbivores are primary consumers in a food chain.
(v) Ecosystems remain constant and do not change over time.
Ans:
(i)True: In an ecosystem, different organisms are interconnected, and their survival depends on the availability and interactions of other organisms.
(ii) False: Photosynthesis is a process specific to plants, where they produce their food using sunlight energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
(iii) True: Decomposers play a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organisms and returning nutrients to the soil, which can be used by plants again.
(iv) True: Herbivores are animals that eat only plants, and they occupy the position of primary consumers in a food chain.
(v) False: Ecosystems are dynamic and can change over time due to natural processes or human activities.
Q4: Short Answer Questions.
(i) What are ecosystems?
Ans: Ecosystems are communities of living things interacting with each other and their surroundings. They include plants, animals, and microorganisms, and depend on each other to survive.
(ii) What is a biome?
Ans: A biome is a specialized ecosystem that exists in a specific area or climate. It is characterized by factors like temperature, rainfall, soil type, and altitude.
(iii) What are the two main types of ecosystems?
Ans: The two main types of ecosystems are aquatic and terrestrial. Aquatic ecosystems are found in water, while terrestrial ecosystems are on land.
(iv) What are decomposers, and why are they important?
Ans: Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil, which helps new plants to grow.
(v) What happens when one part of an ecosystem is damaged?
Ans: If one part of an ecosystem is damaged or disappears, it can affect all other parts of the ecosystem, disrupting the balance and health of the entire community.
|
42 videos|230 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Class 5 Science - Ecosystem Interdependence in Nature - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
| 1. What is interdependence in nature? |  |
| 2. How do ecosystems demonstrate interdependence? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of interdependent relationships in ecosystems? |  |
| 4. Why is interdependence important for biodiversity? |  |
| 5. How can human activities affect interdependence in nature? |  |
















