Worksheet Solutions: Globalisation | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Globalization refers to the movement of ____________, ____________, ____________, and ____________ among various regions of the world.
Ans: goods, services, capital, and information
Globalization involves the movement of goods, services, capital, and information across different regions, fostering international interconnectedness.
Q2: One of the causes of globalization is ____________, which enables easier global movement of people and ideas.
Ans: technological advancements
Advancements in technology have enabled easier global movement of people and ideas, contributing significantly to the process of globalization.
Q3: Economic globalization has led to increased ____________ among nations, both voluntary and compelled by international organizations.
Ans: economic interdependence
Economic globalization has led to increased economic integration among nations, both voluntarily and due to pressures from international organizations, shaping global economic landscapes.
Q4: ____________ is an international platform for those opposed to neoliberal globalization.
Ans: The World Social Forum
The World Social Forum serves as an international platform for those opposed to neoliberal globalization, providing a space for discussions on social justice, human rights, sustainable development, and democracy.
Q5: India started its economic reform program in ____________ to deregulate industries and promote trade and foreign investment.
Ans: 1991
India initiated its economic reform program in 1991, aiming to deregulate industries and promote trade and foreign investment, marking a significant shift in its economic policies.
Q6: Globalization has led to the rise of a uniform culture, also known as ____________.
Ans: cultural homogenization
Globalization has led to the rise of a uniform culture, known as cultural homogenization, where diverse cultural practices and traditions tend to converge, raising concerns about cultural diversity.
Q7: The World Social Forum focuses on issues related to ____________, ____________, ____________, and ____________.
Ans: social justice, human rights, environmental sustainability, and democracy
The World Social Forum focuses on various issues such as social justice, human rights, sustainable development, and democracy, promoting dialogue and action on these important global concerns.
Q8: Globalization reduces the ____________ of the government, leading to a more minimalist state.
Ans: role and power
Globalization reduces the role and power of the government, paving the way for a more minimalist state, where market forces play a significant role in shaping economic and social priorities.
Q9: Cultural globalization has both ____________ and ____________ effects on the world.
Ans: positive and negative
Cultural globalization has both positive, fostering cultural exchange and understanding, and negative effects, leading to cultural homogenization and potential loss of unique cultural identities.
Q10: Globalization has faced opposition from both the ____________ and the ____________ in India.
Ans: left and the right
Globalization has faced opposition from both the political left, critical of economic disparities, and the political right, concerned about preserving traditional cultural values, reflecting diverse concerns within society.
Match the Column
Q1: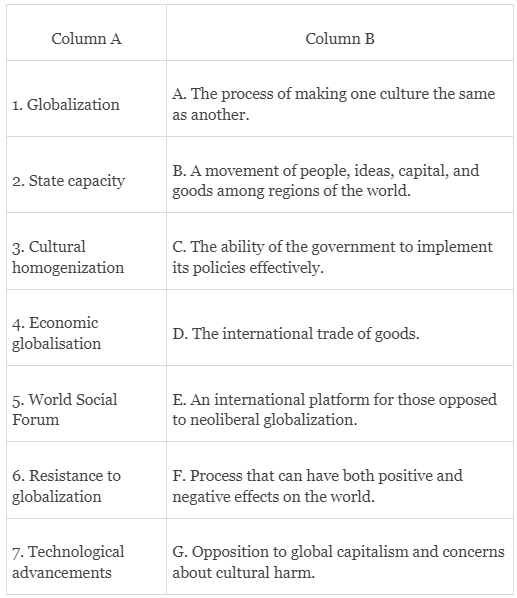 Ans: 1. Globalization (B): Globalization refers to the movement of people, ideas, capital, and goods among various regions of the world. It matches with B because it encapsulates the broad concept of global movement.
Ans: 1. Globalization (B): Globalization refers to the movement of people, ideas, capital, and goods among various regions of the world. It matches with B because it encapsulates the broad concept of global movement.
2. State capacity (C): State capacity represents the ability of the government to implement its policies effectively.
3. Cultural homogenization (A): Cultural homogenization is the process of making one culture the same as another. It aligns with A, describing the concept precisely.
4. Economic globalization (D): Economic globalization involves the international trade of goods. It corresponds with D, providing an accurate definition of economic globalization.
5. World Social Forum (E): The World Social Forum (WSF) is an international platform for those opposed to neoliberal globalization. It matches with E, providing the correct identification of the organization's purpose.
6. Resistance to globalization (G): Resistance to globalization involves opposition to global capitalism and concerns about cultural harm. It aligns with G, encompassing the varied aspects of resistance against globalization.
7. Technological advancements (F): Technological advancements have facilitated globalization by enabling easy communication and the movement of goods and ideas. It matches with F, emphasizing the positive and negative effects of technological progress on the world.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Globalization reduces state capacity.
Reason: The market takes over the role of the government in determining economic and social priorities.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
Globalization indeed reduces state capacity as the market, driven by economic forces, starts to play a more significant role in determining economic and social priorities. With increased global trade and economic integration, governments often find their policy-making capacities limited, especially in areas where international agreements and market dynamics come into play. The Reason correctly explains why the Assertion is true.
Q2: Assertion: The World Social Forum opposes neoliberal globalization and advocates for human rights and environmental issues.
Reason: The World Social Forum is a platform for promoting capitalist globalization.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The Assertion is true. The World Social Forum indeed opposes neoliberal globalization and focuses on advocating for human rights, environmental issues, social justice, and various other causes. The Reason is false; the forum is not a platform for promoting capitalist globalization but rather for challenging it.
Q3: Assertion: India started an economic reform program in 1991 to become economically self-sufficient.
Reason: Economic liberalization and trade promotion were key goals of India's reform program.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (b)
The Assertion is true; India did start an economic reform program in 1991. However, the Reason is not the correct explanation. India's economic reform program was initiated primarily to liberalize the economy, promote trade, attract foreign investment, and integrate with the global economy. The goal was not self-sufficiency but rather economic growth through globalization and liberalization.
Q4: Assertion: Cultural globalization leads to cultural homogenization.
Reason: Cultural globalization promotes diverse cultural influences.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Ans: (c)
The Assertion is true; cultural globalization indeed often leads to cultural homogenization, where diverse cultural elements merge or are replaced by a uniform global culture. The Reason is false because while there are instances of diverse cultural influences, the overall impact tends to be towards uniformity, especially in popular culture, leading to cultural homogenization.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the different dimensions of globalization?
Ans: The different dimensions of globalization include economic, political, cultural, and technological aspects.
Q2: How has technology contributed to globalization?
Ans: Technology has contributed to globalization by facilitating communication, transportation, and the exchange of information on a global scale.
Q3: What is cultural homogenization?
Ans: Cultural homogenization refers to the process of cultures becoming more similar to one another, often due to the influence of dominant cultures or globalization.
Q4: Name one international platform opposing neoliberal globalization.
Ans: One international platform opposing neoliberal globalization is the World Social Forum.
Q5: When did India initiate its economic reform program?
Ans: India initiated its economic reform program in 1991.
Q6: What is the role of the market in state capacity reduction due to globalization?
Ans: The market, driven by globalization, can lead to a reduction in the state's capacity to regulate economic activities and provide social welfare.
Q7: Give an example of a resistance movement against globalization.
Ans: The Occupy Wall Street movement can be considered as a resistance movement against globalization.
Q8: What does economic globalization involve?
Ans: Economic globalization involves the integration of economies through the free flow of goods, services, capital, and information across national borders.
Q9: How has globalization affected the role of the government?
Ans: Globalization has influenced the role of the government by challenging its ability to regulate the economy, protect domestic industries, and address social issues in the face of global competition.
Q10: Why do some people oppose globalization culturally?
Ans: Some people oppose globalization culturally because they believe it threatens their cultural identity, traditions, and local values.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of cultural homogenization and provide an example.
Ans: Cultural homogenization refers to the process in which diverse cultural elements, such as language, customs, and traditions, become more similar or even uniform across different societies. This often occurs due to the influence of dominant cultures or globalization. An example of cultural homogenization is the spread of Western fast food chains like McDonald's and Starbucks to various countries around the world, leading to a convergence in food preferences and dining experiences.
Q2: Discuss the economic consequences of globalization, highlighting both positive and negative aspects.
Ans: Globalization has both positive and negative economic consequences. On the positive side, it promotes economic growth through increased international trade, foreign direct investment, and access to a larger consumer base. It allows for specialization and economies of scale, leading to improved productivity and efficiency. However, globalization can also lead to job displacement, as companies may move production to countries with lower labor costs. It can exacerbate income inequality and create a race to the bottom in terms of labor and environmental standards.
Q3: How has technology facilitated the movement of people and ideas globally?
Ans: Technology has greatly facilitated the movement of people and ideas globally. The advent of the internet, social media, and various communication technologies has made it easier for individuals to connect and exchange information across geographical boundaries. People can now communicate and collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical location. Transportation technologies, such as airplanes and high-speed trains, have also made travel faster and more accessible, enabling easier movement of people between countries.
Q4: Describe the role of the World Social Forum in opposing globalization and promoting specific issues.
Ans: The World Social Forum (WSF) is an annual gathering of social movements, activists, and organizations that aim to challenge and oppose the negative aspects of globalization. It serves as a platform for discussions, workshops, and protests against neoliberal policies, corporate power, and social injustices resulting from globalization. The WSF promotes specific issues such as human rights, environmental sustainability, and social equality, seeking to build alliances and propose alternative models of development that prioritize people over profit.
Q5: What were the goals of India's economic reform program initiated in 1991?
Ans: The economic reform program initiated in 1991 in India aimed to liberalize and modernize the Indian economy. The goals included dismantling the License Raj system, reducing government intervention, promoting foreign investment and trade, and encouraging private sector participation. The reforms aimed to shift from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented one, with the objective of boosting economic growth, attracting foreign capital, and integrating India into the global economy.
Q6: Explain the relationship between state capacity and globalization.
Ans: State capacity refers to the ability of a government to effectively implement policies, provide public goods and services, and maintain social order. Globalization, on the other hand, refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries in terms of economic, political, and cultural aspects. State capacity can influence the extent to which a country can benefit from globalization. Strong state capacity allows a government to effectively regulate and harness the opportunities of globalization, while weak state capacity may lead to challenges in managing the negative consequences and ensuring equitable outcomes.
Q7: Discuss the reasons behind the opposition to globalization in India from both the political left and right.
Ans: The opposition to globalization in India comes from both the political left and right for different reasons. From the political left, the concerns are often focused on the impact of globalization on workers' rights, income inequality, and social justice. They argue that globalization can lead to exploitation of labor, loss of domestic industries, and increased economic disparities. From the political right, the opposition stems from concerns about the loss of cultural identity, national sovereignty, and the potential dominance of foreign companies in the domestic market. They emphasize the need to protect local industries and preserve traditional values.
Q8: How do resistance movements against globalization form international alliances?
Ans: Resistance movements against globalization form international alliances through networking, collaboration, and shared goals. They often participate in international conferences, forums, and social movements to connect with like-minded organizations and activists from different countries. These alliances can be facilitated through social media platforms, online forums, and global civil society networks. By joining forces, resistance movements can amplify their voices, share strategies, and mobilize collective action on a global scale to challenge the negative aspects of globalization.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the Political Consequences of Globalisation.
Ans: Globalisation significantly reshapes political landscapes worldwide. It diminishes the traditional notion of state sovereignty and brings forth various political consequences:
- Reduced State Autonomy: Globalisation weakens the power of individual states to control their economies. Multinational corporations and international financial institutions often influence economic policies, reducing the autonomy of national governments.
- Shift in Political Focus: Governments now prioritize attracting global investments and ensuring economic competitiveness. This shift often means economic policies prioritize market demands over social welfare programs, impacting the state's role in ensuring equitable distribution of resources.
- Emergence of Supranational Organizations: International bodies like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and International Monetary Fund (IMF) play significant roles in global trade and finance. States, especially developing ones, might find themselves adhering to policies dictated by these organizations, limiting their political choices.
- Increased Interconnectedness: Globalisation fosters diplomatic ties and international cooperation. Nations collaborate on issues like climate change, terrorism, and human rights, reflecting the interconnectedness of global politics.
Q2: Discuss the Economic Consequences of Globalisation.
Ans: Economic consequences of globalisation are multifaceted, impacting economies at various levels:
- Increased Trade and Investments: Globalisation leads to a surge in international trade and investments. Countries engage in the exchange of goods and services, boosting economic growth. However, this integration can make economies vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
- Income Inequality: While globalisation creates wealth, it often exacerbates income disparities. Skilled workers in competitive sectors benefit, while low-skilled laborers face job insecurity due to outsourcing and automation, widening the wealth gap.
- Cultural Exchange and Innovation: Economic globalisation facilitates the exchange of ideas and cultures. It promotes innovation, as companies compete globally, leading to advancements in technology and business practices.
- Dependency on Global Markets: Nations become reliant on global markets. Economic crises in one part of the world can quickly transmit to other regions, causing widespread financial instability.
Q3: Describe the Cultural Consequences of Globalisation.
Ans: Globalisation has profound effects on cultures worldwide, leading to both homogenization and diversification:
- Cultural Homogenisation: Globalisation can erode local cultures, promoting a global, uniform culture. Cultural products from dominant economies, like Hollywood movies and fast-food chains, can overshadow indigenous traditions.
- Cultural Hybridisation: Simultaneously, globalisation encourages cultural fusion. People adopt elements from different cultures, creating new, diverse cultural expressions. This blending fosters tolerance and understanding among diverse communities.
- Preservation Efforts: Aware of cultural erosion, many societies actively work to preserve their heritage. Cultural preservation initiatives, including language revitalization and traditional art promotion, counterbalance globalisation's homogenizing effects.
Q4: Explain India’s Role in Globalisation and the Resistance It Faced.
Ans: India’s engagement with globalisation has been complex, marked by economic growth and socio-cultural challenges:
- Historical Context: India, historically a trading nation, saw significant global engagement during British colonial rule, both as an exporter of raw materials and an importer of finished goods.
- Economic Reforms: Post-independence, India initially followed protectionist policies but shifted towards liberalisation in 1991. Economic reforms encouraged foreign investment and trade, leading to substantial economic growth. However, these policies faced domestic resistance from various quarters.
- Cultural Challenges: Globalisation posed cultural challenges in India. Concerns about the erosion of traditional values and cultural homogenisation prompted resistance, particularly from conservative groups.
- Global Activism: Despite domestic resistance, Indian activists engaged globally. Movements like the World Social Forum provided platforms to voice concerns about neo-liberal globalisation, promoting alternative economic models and cultural preservation efforts.
|
34 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Globalisation - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is globalization? |  |
| 2. How does globalization impact the economy? |  |
| 3. What are the cultural effects of globalization? |  |
| 4. How does globalization impact the environment? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges and criticisms of globalization? |  |















