Worksheet Solutions: How Nature Works in Harmony | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. What is a habitat?
a) Only the place where animals hunt
b) The place and conditions where an organism lives and survives
c) A community of only plants
d) Only the climate of an area
Ans: b) The place and conditions where an organism lives and survives
A habitat provides food, water, shelter, space, and suitable abiotic conditions.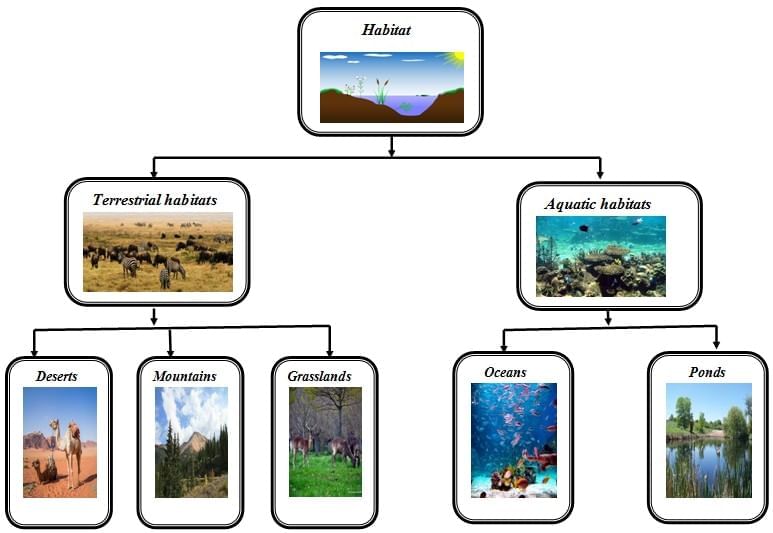
Q2. Which pair correctly shows biotic and abiotic components?
a) Soil (biotic), fish (abiotic)
b) Sunlight (biotic), bacteria (abiotic)
c) Tree (biotic), sunlight (abiotic)
d) Frog (abiotic), air (biotic)
Ans: c) Tree (biotic), sunlight (abiotic)
Living organisms are biotic; non-living factors like light, air, water are abiotic.
Q3. A population is best defined as:
a) All living and non-living things in an area
b) Different species living together
c) Members of the same species in a given area and time
d) All plants in all habitats
Ans: c) Members of the same species in a given area and time
Population counts individuals of one species in a defined space and time.
Q4. Pollination is the transfer of:
a) Seeds from fruit to soil
b) Pollen from stamen to carpel
c) Roots to shoots
d) Water to leaves
Ans: b) Pollen from stamen to carpel
Pollination enables fruit and seed formation.
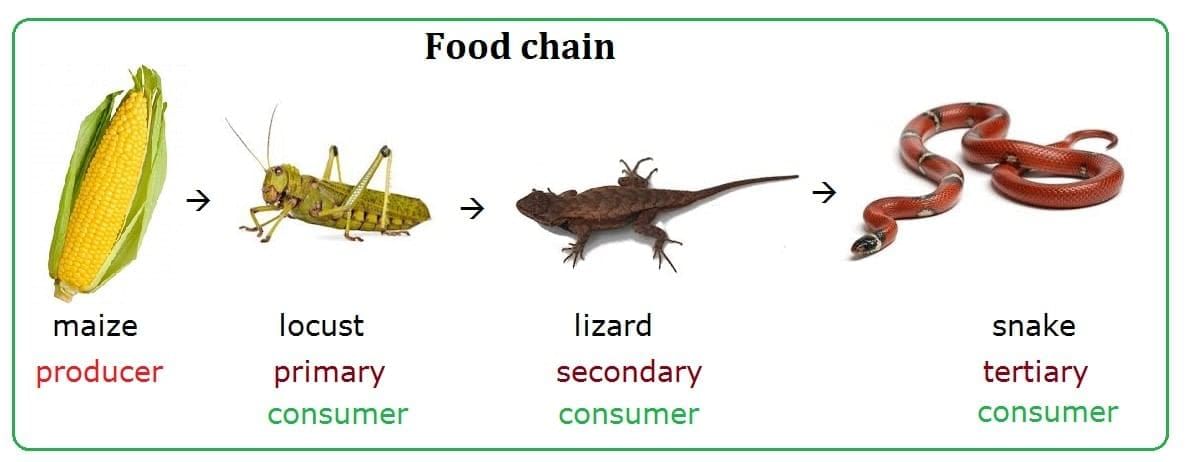
Q5. Which sequence correctly shows a food chain?
a) Snake → Eagle → Grasshopper
b) Grass → Hare → Tiger
c) Eagle → Snake → Frog → Grasshopper
d) Frog → Grass → Grasshopper
Ans: b) Grass → Hare → Tiger
Energy flows from producer to herbivore to carnivore.
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. Interconnected feeding relationships form a __________.
Ans: food web
More realistic than a single chain.
Q2. Organisms like fungi and bacteria that break down dead matter are called __________.
Ans: decomposers (saprotrophs)
They recycle nutrients back to the soil.
Q3. The position of an organism in a food chain is its __________ level.
Ans: trophic
Producers are first trophic level.
Q4. Cutting too many trees and pollution can disturb __________ balance.
Ans: ecological (ecosystem)
Large disruptions harm stability.
Q5. Areas like national parks and sanctuaries are set aside as __________ areas.
Ans: protected
They conserve habitats and wildlife.
 Entrance of a Wildlife Sanctuary
Entrance of a Wildlife Sanctuary
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. Define habitat.
Ans: The place and set of conditions where an organism lives and survives.
Q2. What is pollination?
Ans: Transfer of pollen from stamen to carpel to enable seed and fruit formation.
Q3. Name the three main consumer types.
Ans: Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
Q4. Who are decomposers? Give one example.
Ans: Organisms that break down dead matter; example: mushrooms (fungi) or bacteria.
Q5. What is one role of migratory birds?
Ans: They act as pollinators and seed dispersers linking distant habitats.
 Migrator Birds
Migrator Birds
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
Q1. How are biotic and abiotic components linked in an ecosystem?
Ans: Abiotic factors like sunlight, water, and soil enable plants to grow; plants feed animals; decomposers return nutrients to soil—forming a continuous cycle linking living and non-living parts.
Q2. Why does diversity in a habitat help maintain balance?
Ans: Many species use resources differently (time, place, food), reducing competition and stabilizing populations through food webs and checks and balances.
Q3. Explain the pond cascade when fish are removed.
Ans: Fewer fish → more dragonflies (their larvae survive) → fewer pollinators (eaten by dragonflies) → less pollination → reduced plant seed set and growth.
Q4. How do mangroves protect coasts and climate?
Ans: Their roots slow waves and storm surges, reducing floods, and their trees store carbon and support rich biodiversity.
Q5. Why can overuse of pesticides harm farms long-term?
Ans: It kills helpful soil organisms and natural predators, reduces humus and soil fertility, can create resistant pests, and harms pollinators needed for crops.
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Ans:
Producer — d) Plant making food via photosynthesis
Plants form the base of energy flow.Decomposer — e) Mushroom/bacteria recycling nutrients
They break down dead matter and return nutrients to soil.Mutualism — a) Relationship where both partners benefit (e.g., bees–flowers)
Pollinators get nectar; plants get pollinated.Trophic level — b) Position of an organism in a food chain
Indicates step in energy transfer.Protected area — c) National park/sanctuary conserving habitats
Legal protection helps biodiversity survive.
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: How Nature Works in Harmony - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What is the significance of harmony in nature? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact the harmony of nature? |  |
| 3. What role do producers, consumers, and decomposers play in maintaining ecological harmony? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of biodiversity and its importance in natural harmony? |  |
| 5. What are some ways to promote harmony with nature in our daily lives? |  |















