Worksheet Solutions: Light: Mirrors and Lenses | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. Which mirror makes objects appear smaller but gives a wider field of view?
a) Plane mirror
b) Concave mirror
c) Convex mirror
d) Two-way mirror
Ans: c) Convex mirror
Convex mirrors always form erect, diminished images and cover a wider area—used as side-view mirrors.
Q2. Looking at the inner (curved inward) side of a shiny spoon, your face appears:
a) Erect and diminished
b) Inverted (upside down)
c) Erect and same size
d) Erect and magnified at all distances
Ans: b) Inverted (upside down)
The inner side behaves like a concave mirror, forming inverted images when the object is farther.
Q3. The warning “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear” is written because a convex mirror:
a) Inverts images
b) Forms enlarged images
c) Forms diminished images
d) Does not follow reflection laws
Ans: c) Forms diminished images
Diminished (smaller) images make objects seem farther than they are.
Q4. Which statement about a concave mirror is correct?
a) Always forms erect images
b) Always forms diminished images
c) Can form enlarged erect images when object is close
d) Never focuses light
Ans: c) Can form enlarged erect images when object is close
Concave mirrors give enlarged erect images at small distances; inverted images when farther.
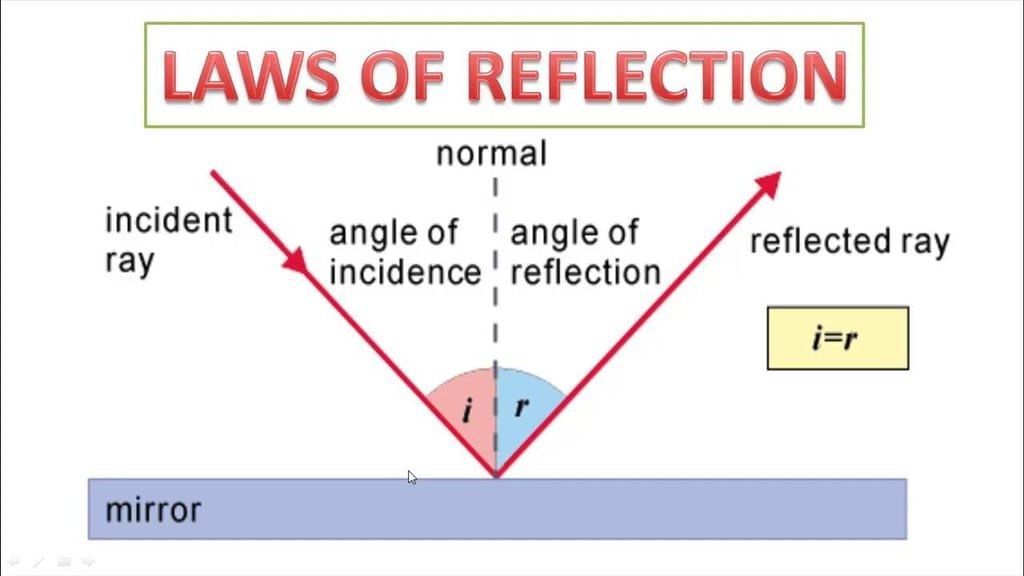
Q5. First law of reflection states:
a) i + r = 90°
b) i = r
c) i > r
d) i < r
Ans: b) i = r
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection for all mirrors.
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. A concave mirror can form an __________ image when the object is very close.
Ans: enlarged (erect)
Close objects appear bigger and upright.
Q2. A convex mirror always forms an __________ and __________ image.
Ans: erect; diminished
Hence its use in vehicle mirrors for wider view.
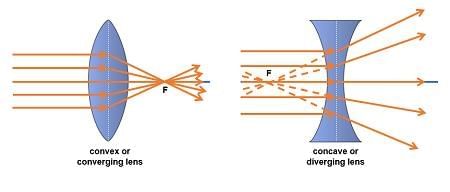
Q3. A convex lens is thicker at the __________ than at the edges.
Ans: middle
Convex lenses converge light.
Q4. A concave lens is a __________ lens because it spreads light rays apart.
Ans: diverging
Rays move away after passing through it.
Q5. The human eye contains a __________ lens that changes shape to focus.
Ans: convex
It accommodates to view near and far objects.
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. Why do vehicle side-view mirrors use convex mirrors?
Ans: They give a wider field of view and form erect, smaller images.
Q2. What is lateral inversion?
Ans: Left–right reversal seen in mirror images.
Q3. State the two laws of reflection in words.
Ans: i = r; and incident ray, normal, reflected ray lie in the same plane.
Q4. Which mirror can focus sunlight onto paper?
Ans: Concave mirror (it converges parallel rays).
Q5. Which lens always gives an erect and diminished image?
Ans: Concave lens.
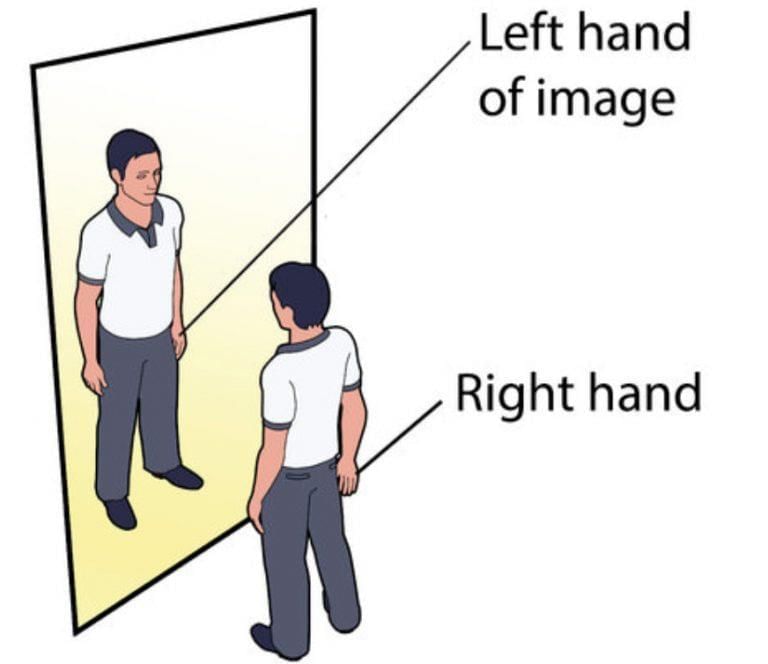 Lateral Inversion
Lateral Inversion
Q.6. What is angle of incidence?
Ans: The angle between the normal and incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i).
Q.7. What is an 'incident ray'?
Ans: The light ray, which strikes any surface, is called the incident ray.
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
Q1. How does a concave mirror’s image change as the object moves away?
Ans: Very close: image is erect and enlarged. Farther away: image becomes inverted and its size decreases with distance.
Q2. Why do convex mirrors make objects seem farther away?
Ans: They form diminished images, so objects look smaller and therefore appear farther—hence the safety warning on vehicle mirrors.
Q3. Explain why a convex lens can burn paper but a concave lens cannot.
Ans: A convex lens converges sunlight to a sharp, hot point; a concave lens diverges light and cannot focus it to ignite paper.
Q4. How do we know the laws of reflection apply to spherical mirrors?
Ans: Each incident ray still reflects with i = r and stays in the same plane; the curvature only changes the overall direction (convergence/divergence) of reflected rays.
Q5. What images do concave and convex lenses form at various distances?
Ans: Convex lens: erect enlarged when close; inverted and varying size when farther. Concave lens: always erect and diminished.
Q.6. A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 40°. What is the angle of reflection?
Ans: The angle of reflection is 40 degrees. This follows the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.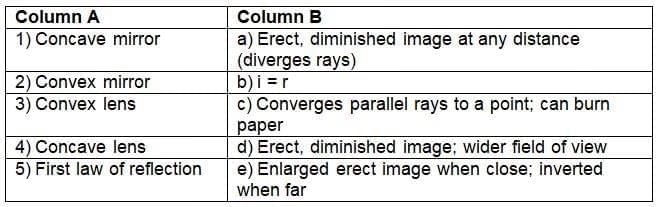
Ans:
Concave mirror — e) Enlarged erect image when close; inverted when far
Image nature depends on object distance.Convex mirror — d) Erect, diminished image; wider field of view
Hence used in vehicle mirrors and at turns.Convex lens — c) Converges parallel rays to a point; can burn paper
Acts as a converging lens focusing sunlight.Concave lens — a) Erect, diminished image at any distance (diverges rays)
Always produces smaller, upright images.First law of reflection — b) i = r
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Light: Mirrors and Lenses - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are the basic differences between concave and convex mirrors? |  |
| 2. How do lenses work in focusing light, and what are the two main types of lenses? |  |
| 3. What is the law of reflection, and how does it apply to mirrors? |  |
| 4. What are some practical applications of lenses in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How do optical instruments like microscopes and telescopes utilize mirrors and lenses? |  |















