Markets Around Us Class 7 Worksheet Civics Chapter 7
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) What is the main role of intermediaries in modern markets?
(a) To produce goods
(b) To connect producers and consumers
(c) To set market prices
(d) To eliminate competition
Ans: (b)
Intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers facilitate the exchange of goods between producers and consumers.
(ii) Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of wholesalers?
(a) Buy in large quantities
(b) Sell goods directly to consumers
(c) May provide goods on credit
(d) Deal in a limited range of items
Ans: (b)
Wholesalers typically sell to retailers and other wholesalers, not directly to consumers.
(iii) What is the primary purpose of weekly markets?
(a) To sell goods at high prices
(b) To cater to basic daily requirements
(c) To promote luxury items
(d) To provide long-term credit to consumers
Ans: (b)
Weekly markets are known for offering a variety of affordable daily necessities.
(iv) What do supermarkets offer that makes them attractive to consumers?
(a) Limited product variety
(b) Lower prices due to small scale
(c) A wide selection of products
(d) High prices for all goods
Ans: (c)
Supermarkets provide consumers with a wide range of products in one place, offering choices and convenience.
(v) What is the primary advantage of online retailers like Flipkart and Amazon?
(a) High overhead costs
(b) Lack of convenience
(c) Lower prices due to overhead savings
(d) Limited product variety
Ans: (c)
Online retailers can offer lower prices as they don't have the same overhead costs as physical stores.
Q2: Fill in the Blanks
(i) Markets serve as the connecting link between _________ and __________.
Ans: producers and consumers.
(ii) People who serve as intermediaries between producers and consumers are called _______ or _______.
Ans: sellers or traders.
(iii) When people exchange goods or services for other goods or services, it is called ___________.
Ans: bartering.
(iv) Big retail shops occasionally offer discounts to customers for the purpose of the clearance of _____________.
Ans: old stock.
(v) _________ stores sell a wide assortment of goods of the same category.
Ans: Chain.
Q3: Match the Column
 Ans:
Ans: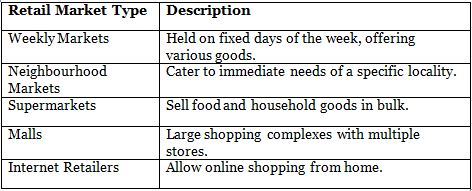
Q4: True or False
(i) Wholesalers sell goods directly to consumers.
Ans: False
Wholesalers sell goods to retailers and other wholesalers, not consumers.
(ii) Neighbourhood markets may offer home delivery services to regular customers.
Ans: True
Neighbourhood markets often provide services like home delivery to regular customers.
(iii) Supermarkets source goods in small quantities, leading to higher prices.
Ans: False
Supermarkets source goods in large quantities, allowing them to offer lower prices.
(iv) Chain stores manage multiple branches independently.
Ans: False
Chain stores are usually managed by a single management, often the manufacturers themselves.
(v) Online selling does not pose a threat to conventional shops.
Ans: False
Online selling is considered a major threat to conventional brick-and-mortar shops due to lower prices and convenience.
|
63 videos|140 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Markets Around Us Class 7 Worksheet Civics Chapter 7
| 1. What are markets and how do they function? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of markets? |  |
| 3. How do markets benefit consumers and producers? |  |
| 4. What role does the government play in regulating markets? |  |
| 5. How do market forces of demand and supply determine prices? |  |
|
63 videos|140 docs|28 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
















