Soil Erosion And Conservation - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Soil erosion is caused by
(a) Water
(b) Wind
(c) Human activities
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Soil erosion is caused by natural forces like water, wind, and human activities such as farming and construction.
(ii) Which of the following is not a method of soil conservation?
(a) Afforestation
(b) Contour plowing
(c) Deforestation
(d) Crop rotation
Ans: (c)
Deforestation leads to soil erosion as it removes the vegetation that helps hold the soil particles together. Afforestation, contour plowing, and crop rotation are all methods of soil conservation.
(iii) Which type of soil is most prone to erosion?
(a) Clay soil
(b) Sandy soil
(c) Loam soil
(d) Silt soil
Ans: (b)
Sandy soil is most prone to erosion because it has larger, loosely packed particles that can easily be washed away or blown by wind.
(iv) What is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller particles called?
(a) Weathering
(b) Erosion
(c) Deposition
(d) Dissolution
Ans: (a)
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller particles, which can then form soil.
(v) Which of the following is a negative effect of soil erosion?
(a) Increased soil fertility
(b) Loss of topsoil
(c) Improved drainage
(d) Enhanced plant growth
Ans: (b)
Soil erosion leads to the loss of topsoil, which is the most fertile part of the soil that contains essential nutrients for plant growth. This can result in reduced agricultural productivity and other negative environmental impacts.
Q2: Fill in the blanks.
(i) The removal of the top layer of soil by wind or water is known as ________.
Ans: The removal of the top layer of soil by wind or water is known as soil erosion.
(ii) ________ is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller particles called soil.
Ans: Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller particles called soil.
(iii) Planting trees along the riverbanks is a method of soil conservation called ________.
Ans: Planting trees along the riverbanks is a method of soil conservation called riparian afforestation.
(iv) Soil erosion can be prevented by practising ________ farming.
Ans: Soil erosion can be prevented by practising contour farming.
(v) The roots of plants help to hold the ________ in place, preventing erosion.
Ans: The roots of plants help to hold the soil in place, preventing erosion.
(vi) Soil erosion is the process of __________ and transporting soil particles from one place to another.
Ans: Soil erosion is the process of removing and transporting soil particles from one place to another.
(vii) __________ is the primary agent responsible for soil erosion.
Ans: Water is the primary agent responsible for soil erosion.
(viii) The wearing away of the topsoil is known as __________.
Ans: The wearing away of the topsoil is known as sheet erosion.
(ix) Terrace farming is an effective method to control soil erosion on __________ slopes.
Ans: Terrace farming is an effective method to control soil erosion on steep slopes.
(x) Planting trees along the edges of fields forms a barrier called __________, which helps prevent soil erosion.
Ans: Planting trees along the edges of fields forms a barrier called windbreak, which helps prevent soil erosion.
Q3: Match the column.
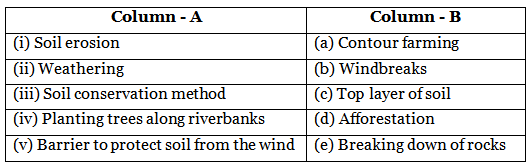
Ans: (i) Soil erosion - (c) Top layer of soil
(ii) Weathering - (e) Breaking down of rocks
(iii) Soil conservation method - (a) Contour farming
(iv) Planting trees along riverbanks - (d) Afforestation
(v) Barrier to protect soil from the wind - (b) Windbreaks
Q4: True or False.
(i) Soil erosion is beneficial for agricultural activities.
Ans: False
Soil erosion is detrimental to agricultural activities because it removes the fertile topsoil that is necessary for plant growth and nutrient cycling.
(ii) Wind and water are the main agents of soil erosion.
Ans: True
Wind and water are the main agents of soil erosion, as they can carry away the loose topsoil and cause it to be deposited elsewhere.
(iii) Deforestation leads to increased soil erosion.
Ans: True
Deforestation leads to increased soil erosion because it removes the protective cover of vegetation, exposing the soil to the erosive forces of wind and water.
(iv) Terrace farming is a method of soil conservation.
Ans: True
Terrace farming is a method of soil conservation that involves creating level steps on sloping land, which helps to slow down the flow of water and prevent soil erosion.
(v) Soil erosion only occurs in desert areas.
Ans: False
Soil erosion occurs in various environments, including deserts, forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas. It is influenced by factors such as climate, topography, soil type, and land use practices.
(vi) Soil erosion can have detrimental effects on agriculture and the environment.
Ans: True
Soil erosion can lead to the loss of fertile topsoil, reducing crop productivity and causing sedimentation in water bodies, harming aquatic ecosystems.
(vii) Wind erosion is more common in wet and humid regions.
Ans: False
Wind erosion is more prevalent in dry and arid regions where there is little vegetation to anchor the soil.
(viii) Deforestation can exacerbate the problem of soil erosion.
Ans: True
Deforestation removes the protective vegetation cover, increasing the risk of soil erosion by water and wind.
(ix) Contour plowing is a farming practice that can reduce soil erosion.
Ans: True
Contour plowing involves plowing across the slope rather than up and down, which helps to slow down the flow of water and prevent erosion.
(x) Soil erosion only affects the surface layer of the soil.
Ans: False
Soil erosion can affect both the surface layer and deeper layers of the soil, depending on the intensity and duration of erosion.
Q5: Define the Following.
(i) Soil Conservation
Ans: Soil conservation refers to the methods and strategies used to protect and preserve soil from erosion, degradation, and depletion.
(ii) Erosion Control
Ans: Erosion control involves implementing measures to prevent or reduce the detachment and transport of soil particles caused by agents like water, wind, or gravity.
(iii) Sedimentation
Ans: Sedimentation is the process of soil particles settling out of water and accumulating in bodies of water, causing siltation and reducing water quality.
(iv) Contour Farming
Ans: Contour farming is a farming practice where crops are planted along the contour lines of a slope to reduce water runoff and soil erosion.
(v) Desertification
Ans: Desertification is the process of fertile land turning into desert-like conditions due to factors like deforestation, overgrazing, and soil erosion.
Q6: Arrange in Correct Way.
Arrange the following steps in the correct order to demonstrate a method of preventing soil erosion.
(a) Mulch the soil surface
(b) Plant trees and grasses
(c) Construct terraces on steep slopes
(d) Use contour plowing
(e) Avoid overgrazing
Ans: Correct order to demonstrate a method of preventing soil erosion:
(b) Plant trees and grasses (To establish vegetation cover)
(e) Avoid overgrazing (To prevent excessive soil compaction and erosion)
(a) Mulch the soil surface (To protect the soil from direct impact of raindrops and reduce surface runoff)
(d) Use contour ploughing (To slow down the flow of water on slopes)
(c) Construct terraces on steep slopes (To create level surfaces for farming and prevent soil runoff)
The correct sequence of steps ensures that soil erosion is minimized. Planting trees and grasses establishes protective vegetation cover, avoiding overgrazing maintains soil structure, mulching shields the soil from raindrop impact, contour ploughing slows water flow, and terraces on steep slopes create flat areas to prevent soil runoff.
Q7: Short Answer Questions.
(i) What is soil erosion?
Ans: Soil erosion is the process by which the topsoil is removed from the land surface by natural forces such as water, wind, or human activities.
(ii) List two factors that contribute to soil erosion.
Ans: Two factors that contribute to soil erosion are deforestation (removal of vegetation) and poor agricultural practices (e.g., overgrazing, excessive ploughing).
(iii) Describe one method of soil conservation.
Ans: One method of soil conservation is contour ploughing, which involves ploughing along the natural contours of the land. This helps to slow down water runoff and prevent soil erosion.
(iv) How does contour ploughing help in conserving soil?
Ans: Contour ploughing helps in conserving soil by slowing down water runoff and reducing the chances of soil being washed away. By ploughing along the natural contours of the land, the flow of water is interrupted, allowing it to infiltrate the soil instead of flowing over it and causing erosion.
(v) Why is soil conservation important?
Ans: Soil conservation is important because it helps maintain the fertility and productivity of the soil, ensuring that it can support plant growth and agriculture. Conserving soil also helps prevent negative environmental impacts such as water pollution, loss of biodiversity, and increased greenhouse gas emissions due to soil erosion.
|
42 videos|230 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Soil Erosion And Conservation - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is soil erosion and why is it a problem? |  |
| 2. What are the main causes of soil erosion? |  |
| 3. How can we prevent soil erosion? |  |
| 4. What role do plants play in preventing soil erosion? |  |
| 5. What are some benefits of soil conservation? |  |
















