Solids, Liquids and Gases - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Which state of matter has a definite shape and volume?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) Plasma
Ans: (a)
Solids have a definite shape and volume. This is because their particles are closely packed together, which restricts their movement and keeps them in a fixed position.

(ii) Which state of matter takes the shape of the container it is in?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) Plasma
Ans: (b)
Liquids take the shape of the container they are in because their particles are not as tightly packed as in solids, allowing them to move and flow freely.
(iii) Which state of matter has particles that move the fastest?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) Plasma
Ans: (c)
Gas particles move the fastest among the states of matter because they possess more energy and are not as tightly packed as the particles found in solids or liquids.
(iv) The process of a solid changing into a liquid is called:
(a) Melting
(b) Freezing
(c) Evaporation
(d) Condensation
Ans: (a)
Melting is the process in which a solid changes into a liquid. This occurs when the temperature increases, causing the particles of the solid to gain energy and move more freely.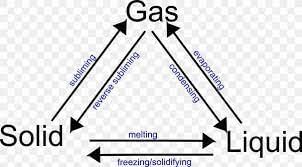
(v) The process of a gas changing into a liquid is called:
(a) Melting
(b) Freezing
(c) Evaporation
(d) Condensation
Ans: (d)
Condensation is the process by which a gas changes into a liquid. This occurs when the temperature decreases, causing the particles in the gas to lose energy and become more tightly packed together.
Q2: Fill in the blanks.
(i) The three states of matter are _______, _______, and _______.
Ans: The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
(ii) Particles in a solid are packed closely together, making it _______.
Ans: Particles in a solid are packed closely together, making it incompressible.
(iii) Liquids do not have a fixed shape, instead, they take the shape of the _______.
Ans: Liquids do not have a fixed shape, instead, they take the shape of the container.
(iv) Gases have no fixed shape or volume and can be compressed or _______.
Ans: Gases have no fixed shape or volume and can be compressed or expanded.
(v) The change of a solid into a liquid is called _______.
Ans: The change of a solid into a liquid is called melting.
Q3: Match the column.
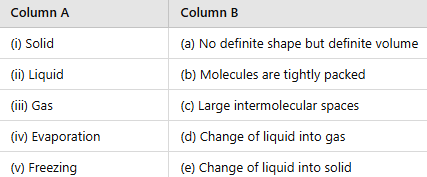
Ans:
(i) Solid → (b) Molecules are tightly packed
(ii) Liquid → (a) No definite shape but definite volume
(iii) Gas → (c) Large intermolecular spaces
(iv) Evaporation → (d) Change of liquid into gas
(v) Freezing → (e) Change of liquid into solid
Q4: True or False.
(i) Solids have a fixed shape.
Ans: True
Solids have a fixed shape, which distinguishes them from liquids and gases. This characteristic means that solids maintain their form and do not flow or change shape easily under normal conditions.
(ii) Particles in a gas are loosely packed.
Ans: True
The statement that particles in a gas are loosely packed is accurate. In gases, the particles are not tightly bound, allowing them to move freely and occupy a larger volume compared to solids and liquids.
(iii) The process of a liquid turning into a solid is called evaporation.
Ans: False
The process of a liquid turning into a solid is called freezing or solidification.
(iv) The particles in a liquid are more tightly packed than in a solid.
Ans: False
The particles in a liquid are less tightly packed than in a solid.
(v) The particles in a gas have more energy than those in a solid or liquid.
Ans: True
The particles in a gas indeed have more energy than those in a solid or liquid. This is due to the greater kinetic energy of gas particles, which allows them to move freely and rapidly compared to the more tightly bound particles in solids and liquids.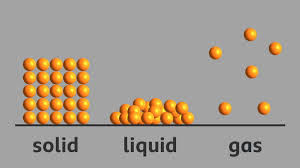
Q5: Short Answer Questions.
(i) What are the three main states of matter?
Ans: The three main states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
(ii) How do the particles in a solid, liquid, and gas differ from each other?
Ans: In a solid, particles are closely packed together and cannot move freely. In a liquid, particles are less tightly packed and can move and flow. In a gas, particles are not tightly packed at all and move quickly and freely.
(iii) What is the process called when a liquid changes into a gas?
Ans: The process of a liquid changing into a gas is called evaporation.
(iv) What happens to the particles of a substance when it is heated?
Ans: When a substance is heated, its particles gain energy and move faster. This increased movement can cause the substance to change state, such as from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas.
(v) What is the process called when a liquid changes into a solid?
Ans: The process of a liquid changing into a solid is called freezing.
|
42 videos|230 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Solids, Liquids and Gases - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the main properties that differentiate solids, liquids, and gases? |  |
| 2. How do temperature and pressure affect the state of matter? |  |
| 3. What is the process of sublimation, and can you provide an example? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of each state of matter? |  |
| 5. How do changes in states of matter relate to energy changes? |  |





















