The Making of National Movement : 1870s-1947 Class 8 Worksheet History Chapter 8
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Columns |

|
| True/False |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: Which political association was not formed in the 1870s or 1880s?
a) Poona Sarvajanik Sabha
b) Indian Association
c) Madras Mahajan Sabha
d) All India Muslim League
Ans: d) All India Muslim League
The All India Muslim League was formed in 1906, later than the other associations.
Q2: What was the primary aim of the early Indian National Congress?
a) Immediate independence from British rule
b) Greater representation for Indians in government
c) Establishment of a separate Muslim state
d) Formation of an Indian army
Ans: b) Greater representation for Indians in government
The Congress initially sought more representation in government, not immediate independence.
Q3: Which three leaders were collectively known as 'Lal, Bal, Pal'?
a) Tilak, Gokhale, Tagore
b) Tilak, Pal, Rai
c) Naoroji, Mehta, Banerji
d) Gandhi, Nehru, Patel
Ans: b) Tilak, Pal, Rai
Lal (Lala Lajpat Rai), Bal (Bal Gangadhar Tilak), and Pal (Bipin Chandra Pal) were known for their radical approach against British policies.
Q4: In which year was the Indian National Congress established?
a) 1885
b) 1905
c) 1915
d) 1947
Ans: a) 1885
The Indian National Congress was established in 1885, playing a crucial role in the freedom struggle.
Q5: The Rowlatt Act of 1919 led to which significant event?
a) Partition of Bengal
b) Jallianwala Bagh massacre
c) Formation of the Muslim League
d) Dandi March
Ans: b) Jallianwala Bagh massacre
The Rowlatt Act led to the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, a significant and tragic event in Indian history.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The ______ allowed the British government to confiscate the assets of newspapers that published 'objectionable' content.
Ans: Vernacular Press Act
Q2: _______ was the leader who declared, "Freedom is my birthright, and I shall have it!"
Ans: Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Q3: The _______ Act of 1919 allowed the British government to arrest any person without a warrant.
Ans: Rowlatt
Q4: The partition of _______ in 1905 by Viceroy Curzon caused widespread anger and led to the Swadeshi movement.
Ans: Bengal
Q5: The treaty imposed on the Turkish Sultan in 1920 led to the _______ Movement.
Ans: Khilafat
Match the Columns
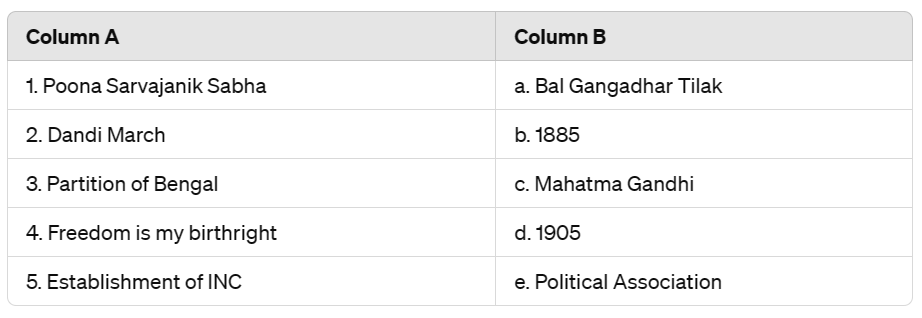
Ans:
1 - e) Political Association
2 - c) Mahatma Gandhi
3 - d) 1905
4 - a) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
5 - b) 1885
True/False
Q1: The Vernacular Press Act was introduced to promote freedom of the press in India.
Ans: False.
It was introduced to censor the Indian press.
Q2: The Indian National Congress was divided into extremists and moderates in 1907.
Ans: True
Q3: The Ilbert Bill sought to prevent Indian judges from trying British individuals.
Ans: False.
It sought to allow Indian judges to try British individuals.
Q4: The Lucknow Pact was an agreement between the Indian National Congress and the British government.
Ans: False.
It was an agreement between the Indian National Congress and the All-India Muslim League.
Q5: The Chauri Chaura incident led to the continuation of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
Ans: False.
It led to the suspension of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Name the newspaper edited by Balgangadhar Tilak.
Ans: Kesari, a Marathi newspaper, was edited by Balgangadhar Tilak.
Q2: When was the Muslim League formed?
Ans: The All-India Muslim League was formed at Dacca in 1906.
Q3: When did the Congress split and reunite?
Ans: The Congress split in 1907 and reunited in December 1915.
Q4: What was the Swadeshi Movement known as in deltaic Andhra?
Ans: It was known as the Vandemataram Movement in the deltaic Andhra.
Q5: Who were the leaders of the Khilafat agitation?
Ans: The leaders of the Khilafat agitation were Mohammad Ali and Shaukat Ali.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What was the purpose of the Ilbert Bill introduced in 1883?
Ans: The Ilbert Bill, introduced by Lord Ripon's Law Member Sir Courtenay Ilbert, aimed to allow Indian judges to try British or European individuals, seeking equality between British and Indian judges.
Q2: Why was the Vernacular Press Act significant?
Ans: The Vernacular Press Act was significant because it aimed to censor the Indian press by allowing the British government to confiscate the assets of newspapers that published 'objectionable' content, thus controlling the flow of information and suppressing dissent.
Q3: What was the impact of the Arms Act of 1878 on the Indian population?
Ans: The Arms Act of 1878 disallowed Indians from possessing arms, which was an attempt by the British to disarm the Indian population and prevent them from revolting against British rule.
Q4: Explain the significance of the Lucknow Pact of 1916.
Ans: The Lucknow Pact of 1916 was significant because it marked an agreement between the Indian National Congress and the All-India Muslim League to work together for representative government in India, showcasing Hindu-Muslim unity in the national movement.
Q5: What was the Khilafat Movement, and how was it connected to the Non-Cooperation Movement?
Ans: The Khilafat Movement, led by Mohammad Ali and Shaukat Ali, aimed to support the Turkish Caliphate against British impositions. It joined forces with Gandhiji's Non-Cooperation Movement, both movements seeking self-rule and protesting against British policies.
|
66 videos|428 docs|46 tests
|





















