Worksheet: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. Which of the following forms a true (clear) solution with water?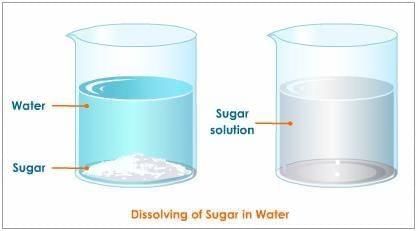 a) Sand
a) Sand
b) Sawdust
c) Sugar
d) Chalk powder
Q2. In a salt-water solution, which is the solvent?
a) Salt
b) Water
c) Both are solvents
d) Neither is solvent
Q3. Air is a gaseous solution in which the major component (solvent) is:
a) Oxygen
b) Nitrogen
c) Carbon dioxide
d) Argon
Q4. As more salt is added to a fixed amount of water, undissolved salt starts settling. The solution has become: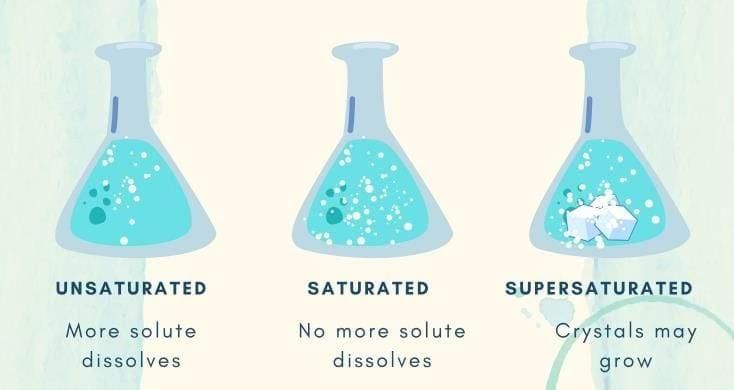 a) Dilute
a) Dilute
b) Unsaturated
c) Saturated
d) Concentrated but unsaturated
Q5. Which statement about dilute vs. concentrated is correct?
a) They are absolute, fixed terms
b) They are comparative terms for amount of solute
c) They depend only on solvent type
d) They only apply to gases
Q6. For most solid solutes in water, increasing temperature generally:
a) Decreases solubility
b) Increases solubility
c) Has no effect
d) Makes solution non-uniform
Q7. The solubility of gases in water generally:
a) Increases with temperature
b) Is highest at boiling point
c) Is unaffected by temperature
d) Decreases with temperature
Q8. If in a syrup (chashni) sugar amount is more than water, the solvent is still:
a) Sugar, because it is more
b) Water, because it is liquid and determines state
c) Both are solvents
d) Neither is solvent
Q9. Density is defined as:
a) Volume per unit mass
b) Mass per unit volume
c) Weight per unit mass
d) Weight per unit volume
Q10. Which statement explains why ice floats on water?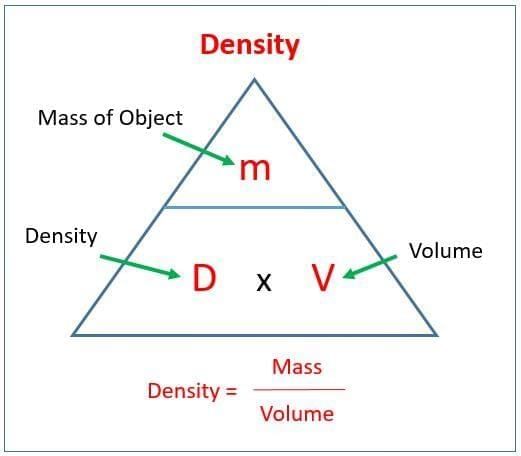 a) Ice has more mass
a) Ice has more mass
b) Ice has higher density
c) Ice has lower density than liquid water
d) Ice has no mass
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. A solution is a __________ mixture in which components are evenly distributed.
Q2. In a solid–liquid solution, the solid is the __________ and the liquid is the __________.
Q3. When no more solute can dissolve at a given temperature, the solution is __________.
Q4. The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a fixed quantity of solvent at a given temperature is called __________.
Q5. Oxygen dissolves only in __________ quantities in water, yet it is vital for aquatic life.
Q6. For gases, solubility generally __________ with increase in temperature.
Q7. Density = __________ / __________.
Q8. The SI unit of density is __________.
Q9. When temperature increases, volume tends to increase and density tends to __________ (if mass stays same).
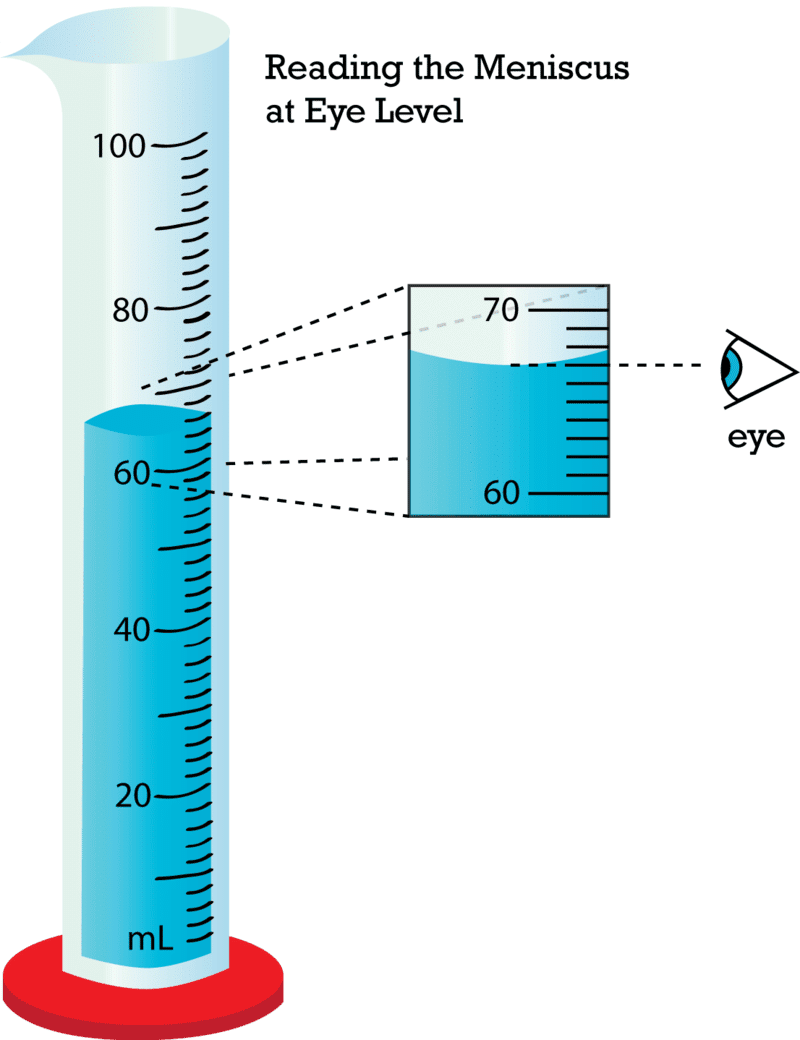
Q10. Reading liquids in a measuring cylinder is done at the bottom of the __________ for water and colorless liquids.
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. Define solute and solvent with an example.
Q2. What happens when a saturated salt solution is heated?
Q3. Name the major component of air that acts as the solvent.
Q4. State the formula for density.
Q5. Which has higher dissolved oxygen: cold water or warm water?
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
Q1. Why does sugar dissolve in water but sand does not form a solution?
Q2. Explain dilute vs. concentrated solutions with an example.
Q3. How does temperature affect solubility of solids vs. gases in water?
Q4. How do you measure the volume of an irregular solid using a measuring cylinder?
Q5. Why does ice float on water and why is this important for aquatic life?
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

FAQs on Worksheet: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What is the definition of solutes, solvents, and solutions? |  |
| 2. What are some common examples of solutes and solvents in everyday life? |  |
| 3. How does temperature affect the solubility of a solute in a solvent? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a saturated solution and an unsaturated solution? |  |
| 5. What role do solutes and solvents play in biological systems? |  |




















