Wren and Martin Summary: Tenses | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What Are Tenses? |

|
| Forms of Tenses |

|
| Uses of Present and Past Tenses |

|
| The Future |

|
What Are Tenses?
- Definition: A tense is a form of a verb that indicates the time (present, past, or future) and the state (complete, ongoing, or habitual) of an action or event.
- Key Idea: Tenses show when an action happens and how it is performed (e.g., completed, ongoing, or repeated).
- Examples:
- Present: "I write a letter." (Happening now)
- Past: "I wrote a letter." (Happened before now)
- Future: "I shall write a letter." (Will happen later)
Three Main Tenses
- Present Tense: Refers to actions in the present time.
- Example: "I love music." (Current action or state)
- Past Tense: Refers to actions completed in the past.
- Example: "I loved the concert." (Action happened before now)
- Future Tense: Refers to actions that will happen in the future.
- Example: "I shall love the new album." (Action will happen later)
Note: The word "tense" comes from the Latin word tempus, meaning time.
Special Cases
Sometimes, tenses may not strictly align with time:
- Past Tense for Present Time: "I wish I knew the answer." (Expresses a present regret using past tense)
- Present Tense for Future Time: "Let’s wait till he comes." (Refers to a future event using present tense)
Forms of Tenses
Each tense has four forms that describe the state of the action:
- Simple: Describes an action simply, without details about its completion.
- Continuous: Shows an action that is ongoing or incomplete.
- Perfect: Indicates an action that is completed or finished.
- Perfect Continuous: Describes an action that started in the past and is still ongoing or was ongoing for a period.
Present Tense Forms (Verb: to love)
- Simple Present: I love, you love, he loves, we love, they love.
- Example: "I love chocolates." (Habit or fact)
- Present Continuous: I am loving, you are loving, he is loving, etc.
- Example: "I am loving this book." (Ongoing action)
- Present Perfect: I have loved, you have loved, he has loved, etc.
- Example: "I have loved this song since childhood." (Completed action with present relevance)
- Present Perfect Continuous: I have been loving, you have been loving, etc.
- Example: "I have been loving this series for weeks." (Ongoing action up to now)
Past Tense Forms (Verb: to love)
- Simple Past: I loved, you loved, he loved, etc.
- Example: "I loved the movie." (Completed action)
- Past Continuous: I was loving, you were loving, he was loving, etc.
- Example: "I was loving the party when it started raining." (Ongoing past action)
- Past Perfect: I had loved, you had loved, he had loved, etc.
- Example: "I had loved the book before I saw the movie." (Action completed before another past action)
- Past Perfect Continuous: I had been loving, you had been loving, etc.
- Example: "I had been loving the game until I got tired." (Ongoing action up to a past point)
Future Tense Forms (Verb: to love)
- Simple Future: I shall/will love, you will love, he will love, etc.
- Example: "I will love the new cafe." (Future action)
- Future Continuous: I shall/will be loving, you will be loving, etc.
- Example: "I will be loving my vacation next week." (Ongoing future action)
- Future Perfect: I shall/will have loved, you will have loved, etc.
- Example: "I will have loved this book by tomorrow." (Completed future action)
- Future Perfect Continuous: I shall/will have been loving, you will have been loving, etc.
- Example: "I will have been loving this game for a year by next month." (Ongoing action up to a future point)
Verb Agreement
A verb must agree with its subject in number (singular/plural) and person (1st, 2nd, 3rd).
Example:
- Singular: "He speaks." (3rd person singular)
- Plural: "They speak." (3rd person plural)
Mood and Tense Identification
Mood: Indicates the manner of the verb (e.g., Indicative for facts, Imperative for commands).
Exercise Examples:
- "The river flows under the bridge."
- Verb: flows
- Mood: Indicative (states a fact)
- Tense: Simple Present
- "I shall answer the letter tonight."
- Verb: shall answer
- Mood: Indicative
- Tense: Simple Future
- "Be good, sweet maid."
- Verb: be
- Mood: Imperative (command)
- Tense: Present
Uses of Present and Past Tenses
1. Simple Present Tense
Uses:
- Habitual Actions: For regular or repeated actions.
- Example: "She drinks tea every morning."
- General Truths: For facts that are always or generally true.
- Example: "The sun rises in the east."
- Exclamatory Sentences: To describe something happening now with "here" or "there."
- Example: "Here comes the bus!"
- Vivid Narrative: To describe past events dramatically, as if happening now.
- Example: "Sohrab rushes forward and strikes Rustam."
- Fixed Timetables: For scheduled events.
- Example: "The train leaves at 5:20."
- Quotations: To introduce quotes.
- Example: "Keats says, ‘A thing of beauty is a joy forever.’"
- Time/Condition Clauses: Instead of future tense in clauses with "if," "when," etc.
- Example: "I’ll wait till she arrives."
- Sports Commentaries: To describe rapid actions in progress.
- Example: "He kicks the ball and scores!"
Note: Verbs of perception (see, hear), emotion (love, hate), thinking (think, believe), or possession (have, own) are usually not used in continuous form.
- Example: "I have a car." (Correct) vs. "I am having a car." (Incorrect)
2. Present Continuous Tense
Uses:
- Action Happening Now: For actions occurring at the moment of speaking.
- Example: "She is singing now."
- Temporary Actions: For actions happening around now, not necessarily at the exact moment.
- Example: "I am reading a novel." (Even if not reading right now)
- Planned Future Actions: For fixed personal plans.
- Example: "I am going to the cinema tonight."
- Persistent Habits: With adverbs like "always" or "constantly" for annoying habits.
- Example: "He is always losing his keys."
Note: Avoid using continuous forms with verbs like "see," "love," or "think" unless they have a different meaning.
- Example: "I am thinking of you." (Considering, not believing)
3. Present Perfect Tense
Uses:
- Immediate Past: For actions just completed (often with "just").
- Example: "He has just left."
- Unspecified Time: For past actions without a specific time.
- Example: "I have visited Paris."
- Present Relevance: For past actions affecting the present.
- Example: "I have lost my keys." (I don’t have them now)
- Ongoing Action: For actions starting in the past and continuing now (with "since" or "for").
- Example: "I have lived here for five years."
- Adverbs Used: never, ever, so far, till now, yet, already, today, etc.
Note: Do not use present perfect with specific past time adverbs (e.g., "yesterday").
- Incorrect: "I have gone yesterday."
- Correct: "I went yesterday."
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Use: For actions that started in the past and are still continuing or emphasise ongoing effort.
- Example: "She has been studying for three hours." (Still studying)
- Special Case: Can describe a recently finished action to explain a situation.
- Example: "My clothes are wet because I have been watering the garden."
- Adverbs Used: for, since, all day, etc.
5. Simple Past Tense
Uses:
- Completed Actions: For actions finished in the past, often with time adverbs.
- Example: "She visited London last year."
- Implied Time: For past actions, where time is understood from context.
- Example: "I met her in Paris." (Implies a past event)
- Past Habits: For regular actions in the past.
- Example: "He played football every weekend."
Adverbs Used: yesterday, last week, ago, etc.
6. Past Continuous Tense
Uses:
- Ongoing Past Actions: For actions happening at a specific past time.
- Example: "They were watching TV all evening."
- Interrupted Actions: Used with simple past to show a longer action interrupted by a shorter one.
- Example: "I was reading when the phone rang."
- Persistent Habits: With "always" or "continually" for annoying past habits.
- Example: "He was always complaining."
Note: Often used with simple past to show sequence (e.g., ongoing action + new action).
7. Past Perfect Tense
Use: For actions completed before another past action.
- Example: "I had finished my homework before the movie started."
Structure: Used in one clause with simple past in another to show which happened first.
- Example: "When I arrived, the train had left."
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Use: For actions that were ongoing up to a certain point in the past.
- Example: "She had been working for hours before she took a break."
Emphasis: Highlights duration before a past moment.
- Example: "By 1995, he had been teaching for ten years."
The Future
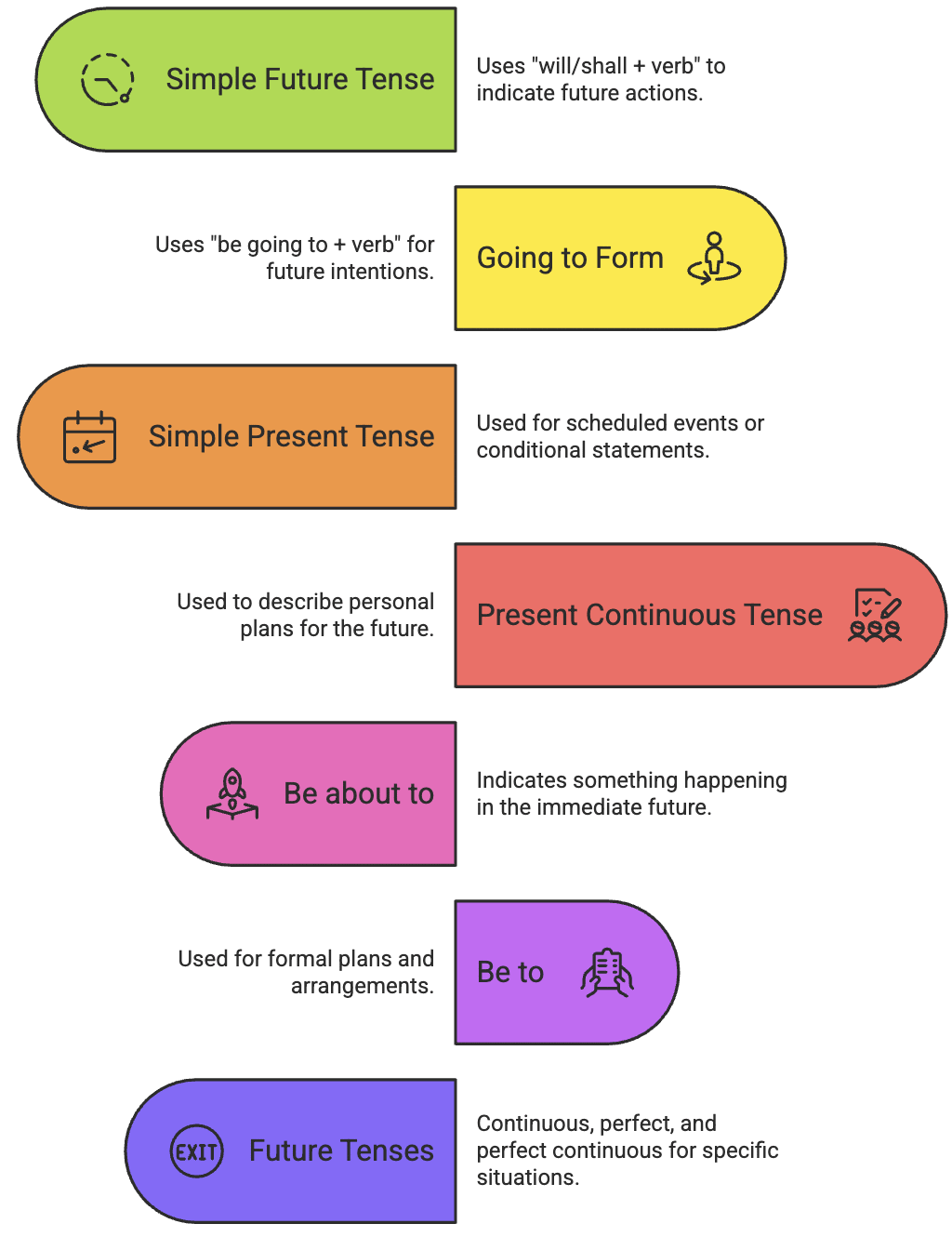
1. Ways to Express the Future
English uses multiple structures to talk about the future:
- Simple Future Tense: Will/shall + verb
- Going to Form: Be going to + verb
- Simple Present Tense: For schedules or conditions
- Present Continuous Tense: For personal plans
- Be about to: For the immediate future
- Be to: For formal plans
- Future Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous: For specific future situations
2. Simple Future Tense
Uses:
- Future Facts: For things we cannot control.
- Example: "I will be 20 next week."
- Predictions/Beliefs: For what we think will happen.
- Example: "I think she will win the race."
- Instant Decisions: For decisions made at the moment of speaking.
- Example: "It’s raining. I’ll take an umbrella."
Common Phrases: Used with "I think," "I’m sure," "I expect," etc.
3. Going to Form
Uses:
- Planned Actions: For decisions made before speaking.
- Example: "I’m going to buy a new phone."
- Likely Events: When there’s evidence in the present.
- Example: "Look at those clouds. It’s going to rain."
- Imminent Actions: For actions about to happen.
- Example: "The train is going to leave!"
Note: Use "going to" for planned actions, not simple future.
4. Simple Present Tense for Future
Use: For fixed schedules or official timetables.
- Example: "The movie starts at 7:00 PM."
Time/Condition Clauses: Used with "if," "when," "until," etc.
- Example: "I’ll call you when I arrive."
5. Present Continuous for Future
Use: For personal plans already arranged.
- Example: "I’m meeting my friend tonight."
Note: Preferred over simple present for personal arrangements.
6. Future Continuous Tense
Uses:
- Ongoing Future Actions: For actions happening at a specific future time.
- Example: "This time tomorrow, I’ll be flying to Paris."
- Planned/Expected Actions: For actions in the normal course of events.
- Example: "The postman will be coming soon."
7. Be to Form
Use: For formal plans or official arrangements, often in news reports.
- Example: "The President is to visit Japan next month."
Note: Common in formal writing; "be" may be omitted in headlines.
8. Future Perfect Tense
Use: For actions that will be completed by a specific future time.
- Example: "I will have finished my homework by 8 PM."
9. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Use: For actions ongoing up to a future point, emphasising duration.
- Example: "By next year, I will have been working here for a decade."
Note: Rarely used but emphasises long duration.
|
112 videos|451 docs|90 tests
|
FAQs on Wren and Martin Summary: Tenses - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What are the different forms of tenses in English? |  |
| 2. How do I identify the tense of a sentence? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of tenses in communication? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of future tense forms? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my understanding and use of tenses? |  |















