Mnemonics : Structure of the Atom | Science Class 9 PDF Download
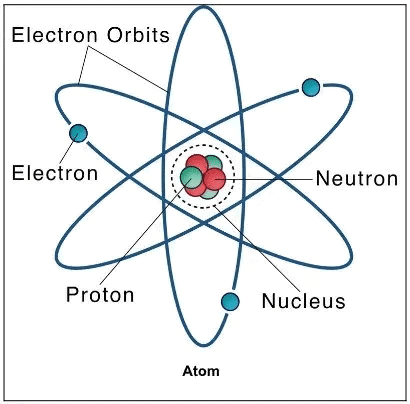
1. Subatomic Particles
Mnemonic: PEN
Sentence: “A PEN writes the story of an atom.”
Mnemonic Explanation:
P = Proton → +ve charge → in nucleus
E = Electron → –ve charge → orbits around
N = Neutron → 0 charge → in nucleus
2. Scientists and Subatomic Particles Discoveries
Mnemonic: “Thomson's Electron Gold's Proton Bohr's Shell James Neutron”
Mnemonic Explanation:
Thomson (1897) → Electron
Goldstein (1886) → Canal Rays/Proton
Bohr (1913) → Electron shells
James Chadwick (1932) → Neutron
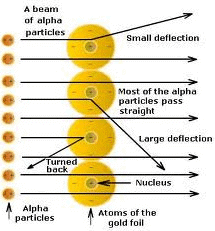
3. Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment
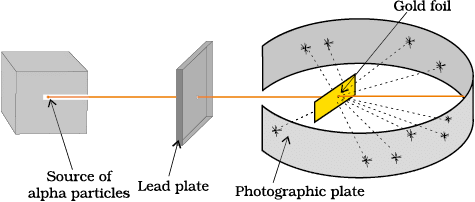
Mnemonic: “Most Passed, Few Deflected, One Reflected”
Mnemonic Explanation:
Most α-particles passed → atom is mostly empty
Some deflected → positive center (nucleus)
One bounced back → dense nucleus
4. Valency
Mnemonic: “VALENCE = Value of Electrons in Chemical Reactions"
Mnemonic Explanation: Valency = number of electrons gained, lost, or shared to complete octet
5. First 20 Elements of Periodic Table
Mnemonic For First 10 Elements: “Hi Hello Listen B B C News On Friday Night "
Mnemonic For 11-20 Atomic No. Elements : " Naa Maango Allah Se Pepsi Soda Cola Aur Kaju Catli"
Mnemonic Explanation
H– Hydrogen (1)
He – Helium (2)
Li – Lithium (3)
Be – Beryllium (4)
B – Boron (5)
C – Carbon (6)
N – Nitrogen (7)
O – Oxygen (8)
F – Fluorine (9)
Ne – Neon (10)
Na – Sodium (11)
Mg – Magnesium (12)
Al – Aluminium (13)
Si – Silicon (14)
P – Phosphorus (15)
S – Sulfur (16)
Cl – Chlorine (17)
Ar – Argon (18)
K – Potassium (19)
Ca – Calcium (20)
6. Isotopes vs. Isobars vs. Isotones
Mnemonic: “Top-Bar-Tone”
Mnemonic Explanation:
ISOtopes → Same Atomic Number (Z)
“TOP = same top (Z), different bottoms (mass)”ISObars → Same Mass Number (A)
“BAR = balanced mass bars, different Z”ISOtones → Same Number of Neutrons
“TONE = same NEUTRONS”
Examples:
Isotopes: ¹H, ²H, ³H
Isobars: ⁴⁰Ar (Z=18), ⁴⁰Ca (Z=20)
Isotones: ¹²C₆ and ¹⁶O₈ → both have 8 neutrons
|
84 videos|543 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics : Structure of the Atom - Science Class 9
| 1. What are subatomic particles and what roles do they play in an atom? |  |
| 2. Who were the key scientists involved in the discovery of subatomic particles? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment? |  |
| 4. What is valency and how is it determined? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between isotopes, isobars, and isotones? |  |
















