RMS & Average Power | Network Theory (Electric Circuits) - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| RMS Power |

|
| Average Power |

|
| Comparison: RMS Power vs. Average Power |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Power calculations are fundamental in electrical engineering, especially when dealing with alternating current (AC) signals like sinusoids. Two terms often come up in this context: RMS (Root Mean Square) power and average power. While they may sound similar, they serve different purposes and have distinct implications when analyzing or specifying power in a system. Understanding their differences is key to applying them correctly in practical scenarios.
RMS Power
RMS power refers to the root mean square value of the instantaneous power waveform over time. For example, when a 1 V RMS sinusoidal voltage is applied across a 1 Ω resistor, the instantaneous power varies between 0 W and 2 W, with an offset of 1 W. Calculating the RMS value of this power waveform yields approximately 1.225 W. This is derived using the formula:

However, this value—while mathematically calculable—lacks clear physical significance in most electrical contexts. It does not directly correspond to the energy dissipated or the useful power delivered to a load, making it less practical for real-world applications.
Average Power
Average power, on the other hand, represents the mean value of the instantaneous power over one complete cycle of an AC signal. For the same 1 V RMS sinusoidal voltage across a 1 Ω resistor, the average power is calculated using the RMS voltage and resistance:
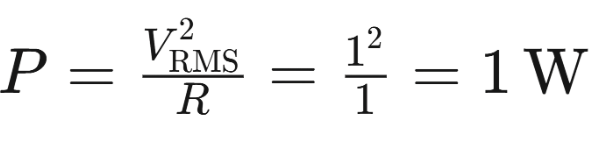
This 1 W matches the physical reality of power dissipation, as it reflects the actual energy transferred to the resistor over time. Average power is a well-established metric with tangible meaning, widely used to describe the power delivered by AC signals, such as noise, RF signals, or oscillators.
 |
Download the notes
RMS & Average Power
|
Download as PDF |
Comparison: RMS Power vs. Average Power
- Definition: RMS power is the root mean square of the instantaneous power waveform, while average power is the time-averaged value of that waveform.
- Calculation: RMS power involves squaring the instantaneous power, averaging it, and taking the square root (e.g., 1.225 W for the example above). Average power uses RMS voltage or current directly (e.g., P=VRMS2/R, yielding 1 W).
- Physical Meaning: Average power corresponds to the real, measurable energy dissipated or delivered, making it physically significant. RMS power, as defined here, lacks a direct practical interpretation and is rarely used in engineering contexts.
- Application: Average power is the standard for specifying power in AC systems, while RMS power is more of a theoretical exercise without obvious utility.
Conclusion
When specifying or analyzing power in an AC system, average power is the preferred metric due to its physical relevance and practical utility. RMS power, while an interesting mathematical construct, does not provide meaningful insight into energy dissipation or system performance. For accurate and useful results, engineers should rely on RMS values of voltage and current to compute average power, ensuring their calculations align with real-world electrical behavior.
|
73 videos|102 docs|62 tests
|















