Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Fractional distillation is suitable for separation of miscible liquids with a boiling point difference of about 25 K or less. What part of fractional distillation apparatus makes it efficient and possess an advantage over a simple distillation process. Explain using a diagram.
Answer:
The apparatus used for fractional distillation includes a fractionating column. This column is designed to enhance the separation of liquids with similar boiling points. Here’s how it works:
- The fractionating column contains glass beads that increase the surface area.
- As vapours rise, they encounter these beads, allowing them to cool and condense more effectively.
- This process occurs in multiple cycles, improving the separation of components.
In contrast, a simple distillation lacks this feature, making it less efficient for separating miscible liquids with small boiling point differences.
Q2. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
Answer: When constituent particles of a combination of two or more element or compound retains their properties, then it is called mixture. In an alloy the constituent particles, hence alloys are classified as mixture. For example; steel is an alloy of carbon and iron.
(b) A solution is always a liquid. Comment.
Answer: Since, a solution is the homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, thus it is not necessary that a solution would always a liquid.A solution can be in all the three states of matter. A solution is a homogeneous mixture and can be in all the three states of matter.
Example:
Solution of alcohol in water is a liquid.
Air is a solution of different gas.
Alloy is a solution which is in the form of solid.
(c) Can a solution be heterogeneous?
Answer: Solution is defined as the homogeneous mixture, hence a solution cannot be heterogeneous. But when a mixture becomes heterogeneous, it cannot be fall under the definition of solution.
Q3. Iron filings and sulphur were mixed together and divided into two parts, ‘A’ and ‘B’. Part ‘A’ was heated strongly while Part ‘B’ was not heated. Dilute hydrochloric acid was added to both the Parts and evolution of gas was seen in both the cases. How will you identify the gases evolved?
Answer: When iron filings and sulphur are mixed, Part B (unheated) reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas (Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2), while Part A (heated to form iron sulphide, FeS) reacts to produce hydrogen sulphide gas (FeS + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2S). The gases can be identified by simple tests: hydrogen from Part B gives a pop sound with a burning splinter, whereas hydrogen sulphide from Part A turns moist lead acetate paper black. This confirms that heating transforms the mixture into a compound, changing the nature of the gas evolved.
Q4. A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of in 36. A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in Fig. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.
(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
Answer: Streaks of different colours can be seen on the filter paper.
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
Answer: Chromatography
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique.
Answer: Chromatography is used for separating pigments from colours, for the separation drugs from blood sample, etc.
Q5. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the lig37. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the Fig. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was Fig.illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it?
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.
Answer: Since, milk is a colloid and when light scattered from the particles of colloids, it is illuminated, thus light was illuminated when passed through the milk. This is known as Tyndall Effect.
(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.
Answer: For scattering of light the size of particles should be large enough. Since the particles of solution are not enough to scattered the beam of light, hence same result were not observed.
(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution?
Answer: Soap bubbles and fog are the colloids, hence same effect, i.e. scattering of light is shown by these. This is known as Tyndall effect.
Q6. Classify each of the following, as a physical or a chemical change. Give reasons.
(a) Drying of a shirt in the sun.
Answer: Drying of shirt in the sun is a Physical change. Since in this change no new substance is formed.
(b) Rising of hot air over a radiator.
Answer: Since, in rising of hot air over a radiator no new substance is formed, hence it is a Physical change.
(c) Burning of kerosene in a lantern.
Answer: While burning of kerosene in a lantern carbon dioxide, and water vapour is formed, hence it is a Chemical change.
(d) Change in the colour of black tea on adding lemon juice to it.
Answer: In this change a new substance is formed, hence it is a Chemical change.
(e) Churning of milk cream to get butter.
Answer: While churning of milk cream to get butter, no new substance is formed, hence it is a Physical change.
Q7. During an experiment the students were asked to prepare a 10% (Mass/Mass) solution of sugar in water. Ramesh dissolved 10g of sugar in 100g of water while Sarika prepared it by dissolving 10g of sugar in water to make 100g of the solution.
(a) Are the two solutions of the same concentration
Answer: No, the two solutions have different concentrations.
(b) Compare the mass % of the two solutions.
Answer: We know;
For first solution:
Mass of solute = 10 gram
Mass of solution = 100 gram + 10 gram = 110 gram
Hence;
Mass % of solution = 10/110 x 100 = 9.09 %
For second solution:
Mass of solute = 10 gram
Mass of solution = 100 gram
Hence;
Mass percent of first solution: Mass percent of second solution = 9.09 : 10
Q8. You are provided with a mixture containing sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Describe the procedures you would use to separate these constituents from the mixture?
Answer:
The given mixture can be separated using the following methods:
- Magnetic Separation: Use a magnet to attract the iron filings from the mixture. The iron filings will stick to the magnet, allowing for easy separation.
- Sublimation: After removing the iron filings, heat the remaining mixture. Ammonium chloride will sublimate, turning into vapour without becoming liquid. This vapour will condense on the inner wall of a funnel, leaving sodium chloride and sand behind.
- Filtration: Mix the remaining sand and sodium chloride with water. Stir the mixture; the sodium chloride will dissolve. Use filter paper to separate the undissolved sand from the solution.
- Vapourisation: Heat the solution obtained from filtration to evaporate the water. This will leave behind sodium chloride crystals.
In summary, the components of the mixture—sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride, and sodium chloride—can be effectively separated using magnetic separation, sublimation, filtration, and vapourisation.
Q9. Arun has prepared 0.01% (by mass) solution of sodium chloride in water. Which of the following correctly represents the composition of the solutions?
(a) 1.00 g of NaCl + 100g of water
(b) 0.11g of NaCl + 100g of water
(c) 0.01 g of NaCl + 99.99g of water
(d) 0.10 g of NaCl + 99.90g of water
Answer: (c) 0.01 g of NaCl + 99.99 g of water
The correct composition for a 0.01% (by mass) NaCl solution is 0.01 g of NaCl in 99.99 g of water. The other options either miscalculate the mass of NaCl or the water, making them incorrect.
Q10. Calculate the mass of sodium sulphate required to prepare its 20% (mass percent) solution in 100g of water?
Answer: In a 20% solution containing 100 g water; the mass percentage of water = 100 – 20 = 80%
∴ 80% of solution is 100 gm
∴ 100% of solution is 100/80 gm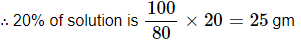
Hence; to prepare 20% (w/w) solution in 100 gram of water 25 gram of sodium sulphate is needed.
|
84 videos|543 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Is Matter Around Us Pure?
| 1. What is the definition of pure matter? |  |
| 2. How can we distinguish between pure and impure matter? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of impurities found in matter? |  |
| 4. How can impurities be removed from matter? |  |
| 5. Can impure matter be converted into pure matter? |  |

















