NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Pollution of Air and Water
Q 1: What are the different ways in which water gets contaminated?
Answer: The different ways in which water gets contaminated are as follows:
(i) Many industries discharge harmful chemicals into rivers and streams. Examples are oil refineries, paper factories, textile and sugar mills, etc.
(ii) The pesticides and weedicides used for the protection of crops get dissolved in water and are washed into water bodies from the fields.
(iii) Many times untreated sewage is thrown directly into rivers.
(iv) Faecal matters of mammals get added into water bodies.
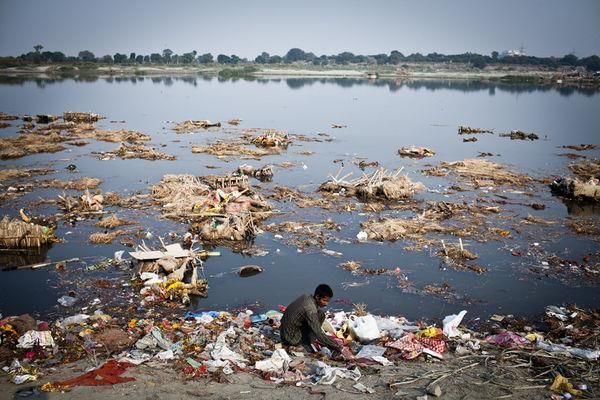 Fig: Contaminated water
Fig: Contaminated water
Q 2: At an individual level, how can you help reduce air pollution?
Answer: An individual can reduce air pollution by:
(i) Avoiding the use of cars as much as possible and by using public transport whenever possible.
(ii) By not using vehicles for short distances.
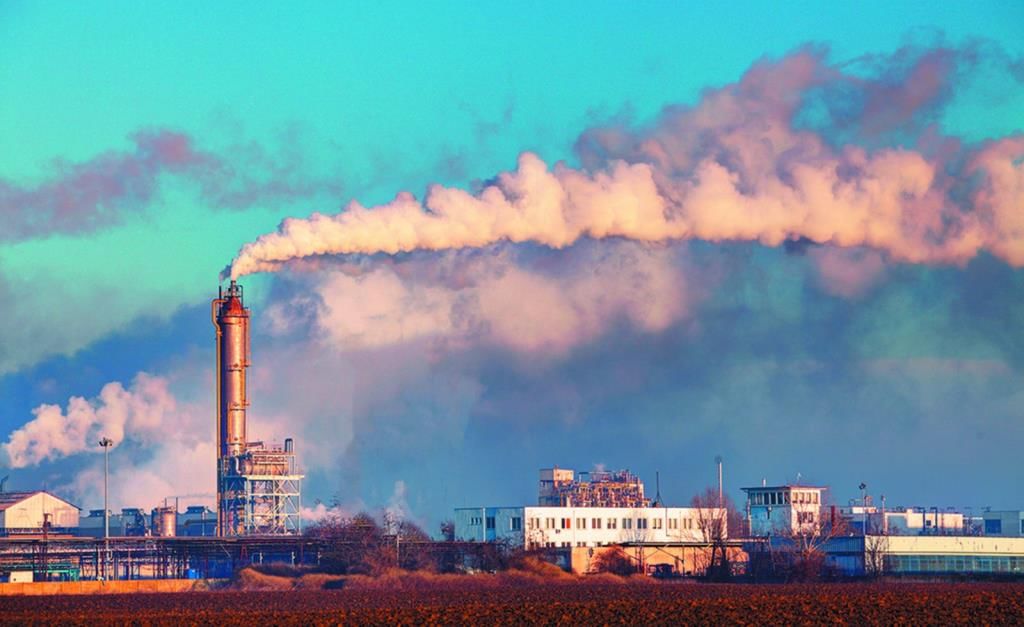 Fig: Air pollution(iii) By using clean fuels such as LPG and CNG instead of diesel and petrol.
Fig: Air pollution(iii) By using clean fuels such as LPG and CNG instead of diesel and petrol.
(iv) Always disposing the garbage properly and not burning it.
(v) Controlling the emissions from vehicles and household chimneys.
Q 3: Clear, transparent water is always fit for drinking. Comment.
Answer: Clear and transparent water is not always fit for drinking. Water might appear clean, but it may contain some disease causing micro-organisms and other dissolved impurities. Hence, it is advised to purify water before drinking. Purification can be done by water purifying systems or by boiling the water.
Q 4: You are a member of the municipal body of your town. Make a list of measures that would help your town to ensure the supply of clean water to all its residents.
Answer: To ensure the supply of clean water to all residents the following steps must be taken:
(i) Implementation of strict laws for industrial units so that the polluted water is not disposed off directly into rivers and lakes. Because it is same water we receive at our home.
(ii) Treatment of water must be done to make it free from harmful germs, chemicals and impurities.
(iii) The water supply pipes must be properly maintained to avoid any corrosion, breakage and leakage.
(vi) Campaigns and awareness programmes should be organized to keep water resources clean and educate people to save water.
Q 5: Explain the differences between pure air and polluted air.
Answer: Pure air contains around 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 0.03% carbon dioxide. Other gases such as argon, methane, ozone, and water vapours are also present in small quantities.
When this composition of air is altered by the addition of harmful substances or gases such as nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter, then the air is said to be polluted.
Q 6: Explain circumstances leading to acid rain. How does acid rain affect us?
Answer: Burning of fossil fuels such as coal and diesel releases a variety of pollutants such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide into the atmosphere. These pollutants react with water vapours present in the atmosphere to form sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively. These acids come down with the rain, thereby resulting in acid rain.
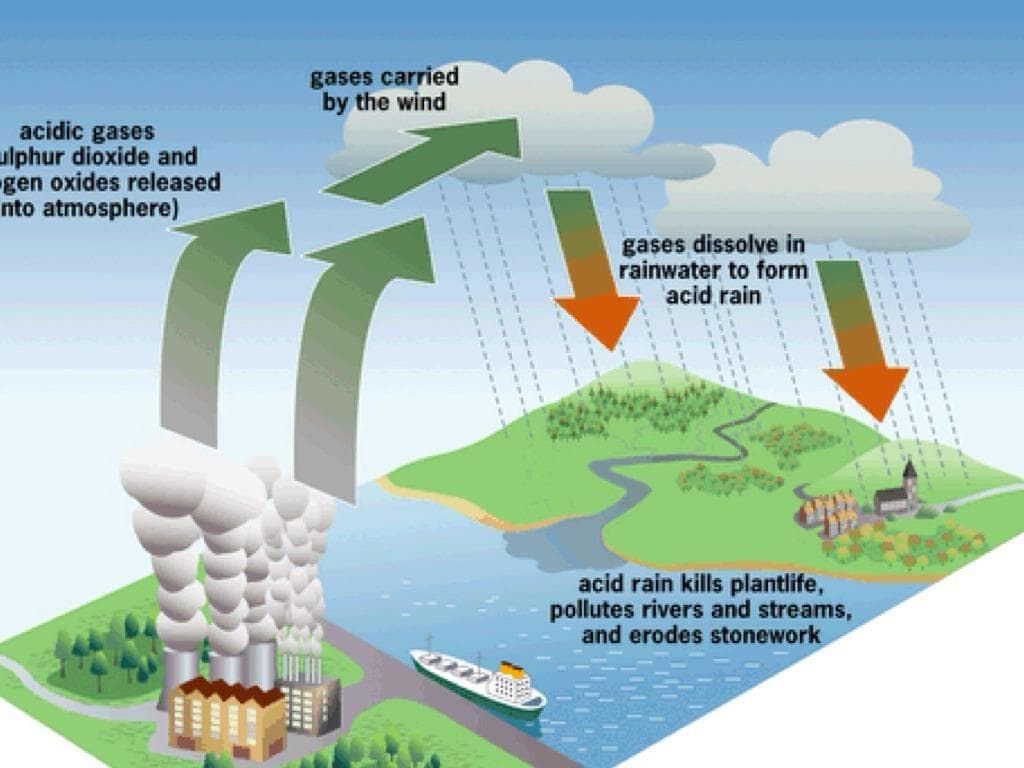 Fig: Acid rain
Fig: Acid rain
Following is list which shows how acid rain affect us:
(i) It can cause skin irritation.
(ii) It removes nutrients like calcium from the soil.
(iii) It causes corrosion to bridges, building and other metallic objects.
(iv) It can destroy plants and aquatic life.
Q 7: Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Methane
(d) Nitrogen
Answer: (d) Nitrogen
Q 8: Describe the 'Greenhouse Effect' in your own words.
Answer: ‘Green House Effect’ is the trapping of radiations inside the earth’s atmosphere. Along with other gases, CO2 also gets trapped in the atmosphere which is mainly responsible for Greenhouse Effect. Because of human activities the amount of CO2 level has increased in the atmosphere which traps heat and does not allow heat to escape into space. As a result, the average temperature of the earth’s atmosphere is gradually increasing. This is called global warming.
Q 9: Prepare a brief speech on global warming. You have to deliver the speech in your class.
Answer: Global warming is an increase in the average temperature of the Earth's surface. It occurs as a result of an increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour. These gases trap solar radiations released back by the Earth. This helps in keeping our planet warm and thus, helps in human survival. However, an increase in the amount of greenhouse gases can lead to an increase in the Earth's temperature leading to global warming.
Q 10: Describe the threat to the beauty of the Taj Mahal.
Answer: Acid rain is a major threat to the beauty of the Taj Mahal. When acid rains fall on the monument (that is completely made of marble), they react with marble to form a powder-like substance that is then washed away by the rain. This phenomenon is known as marble cancer. Also, the soot particles emitted from the Mathura oil refinery located near Agra is leading to the yellowing of the marble.
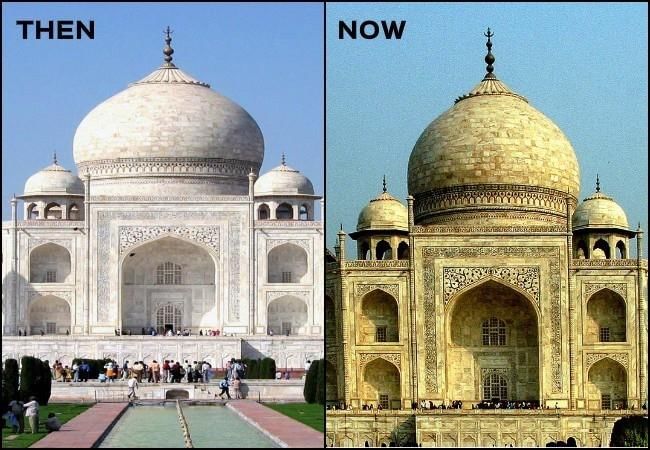 Fig: Yellowing of the marbleQ 11 :Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Fig: Yellowing of the marbleQ 11 :Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms?
Answer: An increase in the level of nutrients in a water body leads to an excessive increase in the population of algae in the water body.
When these algae die, they serve as food for decomposers. A lot of oxygen is utilised in this process, consequently leading to a decrease in the level of oxygen dissolved in the water body. This in turn causes fishes and other aquatic organisms to die.
|
114 videos|534 docs|217 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Pollution of Air and Water
| 1. What are the major causes of air pollution? |  |
| 2. How does air pollution affect human health? |  |
| 3. What are the main sources of water pollution? |  |
| 4. How does water pollution affect aquatic life? |  |
| 5. What are the measures to control air and water pollution? |  |






















