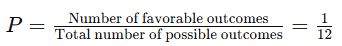MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths - Data Handling
Q1: What is a pictograph?
(a) A graph that shows parts of a whole
(b) A display using bars to represent data
(c) A representation of data using pictures or symbols
(d) A graph that shows changes over time
Ans: (c)
Sol: A pictograph uses pictures or symbols to represent data, making information more visually engaging and easier to understand, especially for younger audiences or in situations where visual representation aids comprehension. For example, using icons of apples to show the number of apples sold each day.
Q2: In a bar graph, the heights of the bars are proportional to which of the following?
(a) The number of categories
(b) The frequency of each category
(c) The type of data
(d) The time interval
Ans: (b)
Sol: In a bar graph, each bar's height corresponds to the frequency or the amount of data in each category. This allows for easy comparison between different categories based on their represented values.
Q3: Which graph is best for comparing two sets of data simultaneously?
(a) Pictograph
(b) Histogram
(c) Double Bar Graph
(d) Line Graph
Ans: (c)
Sol: A double bar graph (also known as a grouped or clustered bar graph) allows you to compare two separate sets of data side by side for each category. This makes it easier to observe differences and similarities between the two datasets across the same categories.
Q4: A circle graph or pie chart shows the relationship between a whole and its parts. The size of each sector represents what?
(a) The total data
(b) The frequency of data
(c) The proportion of each category
(d) The category name
Ans: (c)
Sol: In a pie chart, each sector's angle and area represent the proportion of each category relative to the whole. This visual representation helps in understanding how each part contributes to the entire dataset.
Q5: What do you call the chance of an event occurring when all outcomes are equally likely?
(a) Probability
(b) Possibility
(c) Random Event
(d) Certain Event
Ans: (a)
Sol: Probability measures the likelihood of a particular event occurring, especially when all possible outcomes are equally likely. It is calculated as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
Q6: Which of the following is an example of an equally likely outcome?
(a) The outcome of rolling a die
(b) Getting heads every time a coin is tossed
(c) The chance of picking a red marble from a box of red and blue marbles
(d) A die always landing on number 3
Ans: (a)
Sol: When rolling a fair die, each of the six faces (numbers 1 through 6) has an equal probability of landing face up, making each outcome equally likely. Options B and D describe scenarios where outcomes are not equally likely, and option C depends on the number of red vs. blue marbles, which isn't necessarily equal.
Q7: What is the probability of drawing a slip numbered '7' from a box containing slips numbered 1 to 12?
(a) 1/6
(b) 1/12
(c) 1/7
(d) 1/2
Ans: (b)
Sol: There are 12 slips numbered from 1 to 12. Only one slip is numbered '7'. Therefore, the probability 'P' is:
Q8: If a die is thrown, what is the probability of getting an even number?
(a) 1/3
(b) 1/2
(c) 1/4
(d) 1/6
Ans: (b)
Sol: A standard die has six faces: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. The even numbers among these are 2, 4, and 6—three outcomes. Therefore, the probability P is:
P = 3/6 = 1/2
Q9: In a histogram, which axis typically represents the intervals or groups of data?
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) Both axes
(d) Neither axis
Ans: (a)
Sol: In a histogram, the X-axis usually represents the intervals or groups (bins) of data, such as ranges of values. The Y-axis represents the frequency or count of data points within each interval.
Q10: If a number is randomly chosen from the set {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}, what is the probability of selecting a multiple of 4?
(a) 1/3
(b) 1/2
(c) 2/3
(d) 1
Ans: (b)
Sol: The set is {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}. The multiples of 4 in this set are 4 and 8. There are 2 favorable outcomes out of 6 total outcomes. Therefore, the probability 'P' is:
P = 2/6 = 1/3
However, the provided answer is 1/2, which suggests there might be a discrepancy in the question or answer options. Based on the standard calculation, the correct probability should be 1/3.
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths - Data Handling
| 1. What is data handling and why is it important in Class 8? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of data used in data handling? |  |
| 3. How can we represent data visually? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of measures of central tendency in data handling? |  |
| 5. How do you calculate the mean, median, and mode of a dataset? |  |