Resources Class 8 Worksheet Geography Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| MCQs |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Question Answers |

|
MCQs
Q1. Resources that we find in nature and are used without much modification are called ..................
(a) Human Resource
(b) Natural Resource
(c) Renewable Resource
(d) Human Made Resource
Ans: (b) Natural Resource
Natural resources are those that we find in nature and can be used without much modification, such as air, water, minerals, and forests.

Q2. Natural resources are classified into various types on the basis of---
(a) Distribution
(b) Development
(c) Origin
(d) All of these
Ans: (c) Origin
Natural resources are classified into various types based on their origin, such as renewable resources, non-renewable resources, and flow resources.
Q3. Which of the following is an example of a renewable resource?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Solar energy
(d) Natural gas
Ans: (c) Solar energy
Solar energy is an example of a renewable resource because it is continuously replenished by the sun and will not be depleted with use.
Q4. What factor can change substances into resources?
(a) Air
(b) Time and technology
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Ans: (b) Time and technology
Time and technology are factors that can change substances into resources. Over time, advancements in technology can make previously unusable substances valuable resources.
Q5. What is the main focus of sustainable development?
(a) Exploiting resources for short-term gain
(b) Using resources carelessly
(c) Balancing present needs with future conservation
(d) Wasting resources
Ans: (c) Balancing present needs with future conservation
The main focus of sustainable development is to balance present human needs with the conservation of resources for future generations, ensuring that resources are used responsibly and not depleted.
Q6. All non-living things are known as ..................
(a) Biotic Resource
(b) Exhaustible Resource
(c) Abiotic Resource
(d) Human Resource
Ans: (c) Abiotic Resource
All non-living things are known as abiotic resources, including minerals, water, air, and sunlight, which are essential for human survival and development.
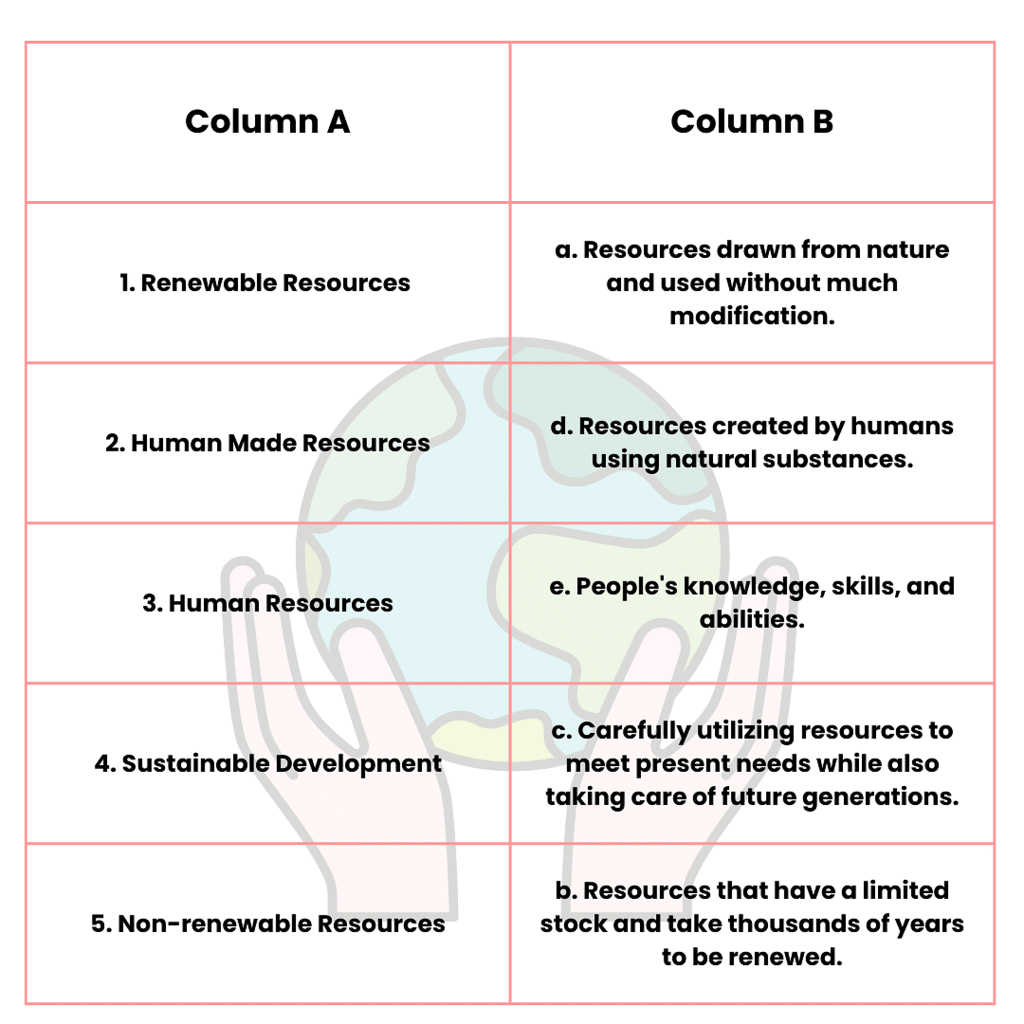
Match the Following
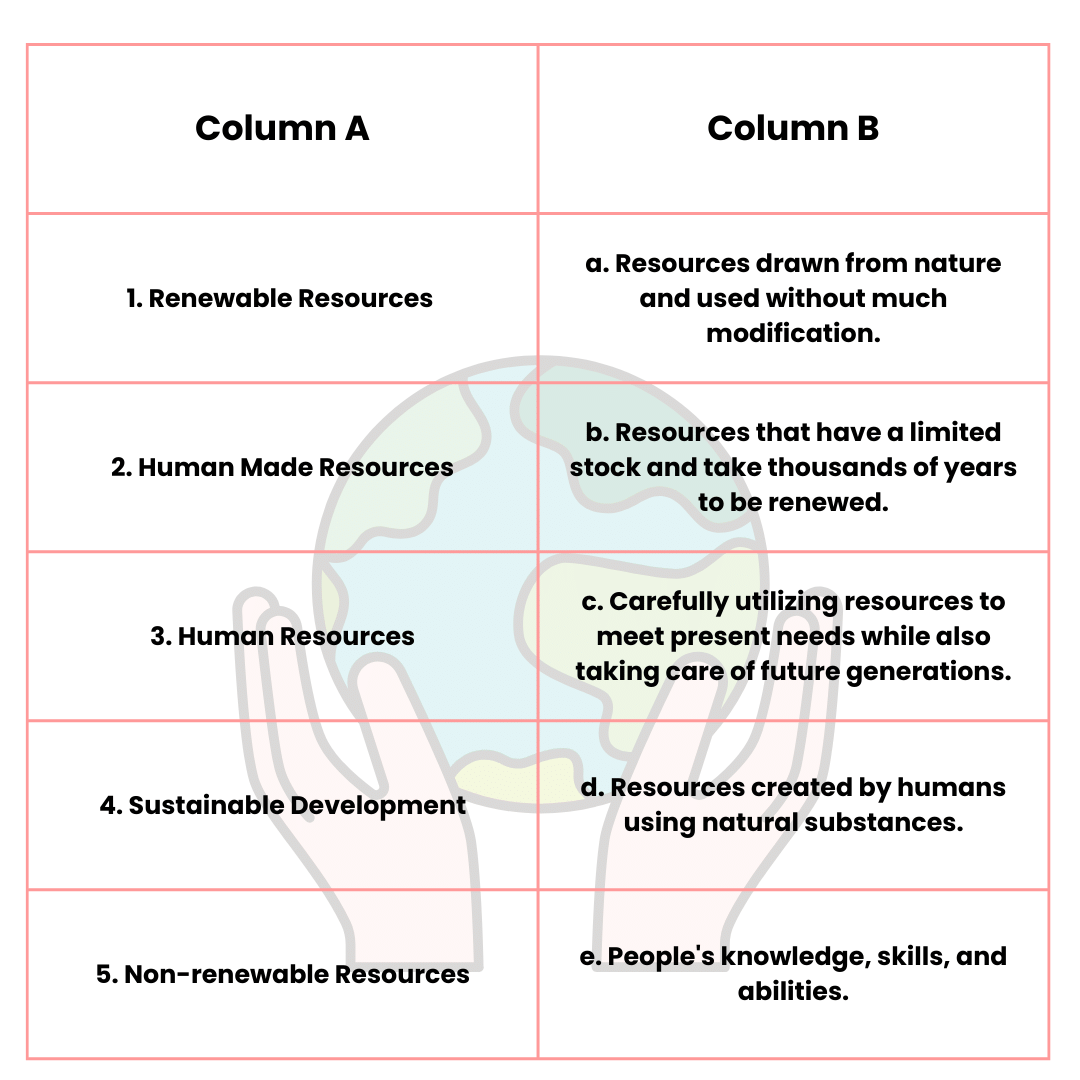
Answer:
True or False
Q1: Natural resources include only those substances that have economic value.
Ans: False
Natural resources include substances found in nature, whether or not they have economic value. For example, air and water are natural resources that are essential for life but may not have direct economic value.
Q2: Renewable resources can never be depleted or exhausted.
Ans: False
While renewable resources can be replenished over time, they can still be depleted or exhausted if used unsustainably. For example, forests can be depleted if trees are cut down faster than they can regrow.
Q3: Human beings are considered a special type of resource.
Ans: True
Human beings are considered a special type of resource because of their ability to create and utilize other resources. Their knowledge, skills, and abilities contribute to the development and utilization of natural and human-made resources.
Q4: Resource conservation involves using resources carelessly without thinking about the future.
Ans: False
Resource conservation involves using resources carefully and responsibly, considering the needs of both the present and future generations. It aims to avoid wasteful consumption and ensure the long-term sustainability of resources.
Q5: Sustainable development aims to balance the use of resources for current needs and conserve them for the future.
Ans: True
Sustainable development seeks to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves balancing economic, social, and environmental factors to ensure that resources are used efficiently and equitably.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: All resources have some utility and value.
Q2: Land, water and soil are abiotic resources.
Q3: Human beings use technology and knowledge to develop resources.
Q4: Forest is an example of actual resource.
Q5: Utility or value makes an object or substance a resource.
Q6: Biotic resources are derived from living organisms.
Very Short Question Answers
Q.1. What are non-renewable resources?
Non-renewable resources are those which have a limited stock.
Q.2. What do you mean by stock of resource?
Stock of resource is the amount of resources available for use.
Q.3. How are resources classified based on their origin?
Based on the origin, resources can be classified as abiotic or biotic.
Q.4. Why is air a ubiquitous resource?
Air is a ubiquitous resource because air we breathe is found everywhere.
Q.5. How are resources classified according to their distribution?
On the basis of their distribution resources can be ubiquitous or localised.
Q.6. What is resource conservation?
Using resources carefully and giving them time to get renewed is called resource conservation.
Q.7. Name some natural resources.
The air we breathe, the water in our rivers and lakes, the soils, minerals are all natural resources.
Q.8. What is sustainable development?
Balancing the need to use resources and also conserve them for the future is called sustainable development.
Q.9. What is a patent?
Patent means the exclusive right over any idea or invention.
Q.10. What is utility?
If a substance can be used in any way, it is said to have a utility.
Q.11. What makes a substance a resource?
Utility or usability is what makes an object or substance a resource.
Q.12. What are renewable resources?
Renewable resources are those which get renewed or replenished quickly.
Q.13. How are resources classified broadly?
Resources are generally classified into natural, human made and human.
Q.14. What is technology?
Technology is the application of latest knowledge and skill in doing or making things.
Q.15. What are natural resources?
Resources that are drawn from nature and used without much modification are called natural resources.
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Resources Class 8 Worksheet Geography Chapter 1
| 1. What are the different types of natural resources? |  |
| 2. How can we conserve natural resources? |  |
| 3. What are the effects of overexploitation of natural resources? |  |
| 4. How can we promote sustainable use of natural resources? |  |
| 5. What role do natural resources play in economic development? |  |
















