Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Practice Question Answers - Gravitation
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Newton’s law of gravitation is valid
(a) on the earth only
(b) on the moon only
(c) in the laboratory only
(d) everywhere
Ans: (d)
Newton’s law of gravitation is valid everywhere in the universe.
Q2: Newton’s law of gravitation is valid
(a) in laboratory
(b) only on the earth
(c) only in our solar system
(d) everywhere
Ans: (d)
Newton’s law of gravitation is a universal law
Q3: When a body is thrown up, the force of gravity is
(a) in the upward direction
(b) in the downward direction
(c) zero
(d) in the horizontal direction
Ans: (b)
The acceleration due to gravity is always directed downwards towards the centre of the Earth for a freely falling body.
Q4: When an object is thrown upward, the force of gravity is
(a) opposite to the direction of motion
(b) in the same direction as the direction of motion
(c) becomes zero at the highest point
(d) increases as it rises up
Ans : (a)
When an object is thrown upwards, the force of gravity acts in the direction opposite to that of motion.
Q5: What happens to the acceleration due to gravity with the increase in altitude from the surface of the earth?
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) First decreases and then increases
(d) Remains same
Ans : (b)
Acceleration due to gravity decreases with the increase in altitude.
Q6: The acceleration due to gravity
(a) has the same value everywhere in space
(b) has the same value everywhere on the earth
(c) varies with the latitude on the earth
(d) is greater on the moon due to its smaller diameter
Ans : (c)
The acceleration due to gravity varies with latitude on the earth.
Q7: Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Mass of an object is the measure of its inertia.
2. Heavier the object smaller is the inertia.
3. The mass of an object is variable.
(a) Only 1
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 2
Ans : (a)
Heavier the object, greater is the inertia. The mass of an object is constant.
Q8: The mass of a body is measured to be 12 kg on the earth. If it is taken to the moon, its mass will be
(a) 12 kg
(b) 6 kg
(c) 2 kg
(d) 72 kg
Ans : (a)
Mass of the body is constant and does not change from place of place.
Q9: Which of the following is correct?
(a) Weight is a scalar quantity.
(b) Weight is not a fundamental quantity.
(c) Weight does not depend on acceleration due to gravity.
(d) None of these
Ans : (b)
If the value of g changes the weight of the body changes.
Q10: Gravitational force is a
(a) repulsive force
(b) attractive force
(c) neither (a) nor (b)
(d) both (a) and (b)
Ans : (b)
Gravitational force is an attractive force.
Fill in the blanks.
Q11: Acceleration due to gravity is ........... proportional to the density of the planet.
Ans : directly
The acceleration due to gravity is directly proportional to the density of the planet. This means that as the density of the planet increases, the acceleration due to gravity also increases. Density is the mass per unit volume of an object and a planet with higher density will have a greater gravitational pull, hence higher acceleration due to gravity.
Q12: The force of gravity between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the ...........
Ans : distance between them
The force of gravity between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This means that as the distance between the two objects increases, the force of gravity between them decreases. This is according to Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Q13: The force of ........... is the centripetal force on the moon.
Ans : gravity
The force of gravity is the centripetal force on the moon. Centripetal force is the force that keeps a body moving in a circular path. It is always directed towards the centre of the circle. In the case of the moon, the force of gravity from the Earth pulls it towards the Earth and keeps it moving in its circular orbit.
Q14: The orbit of a geostationary orbit is called ..........
Ans : parking orbit.
The orbit of a geostationary satellite is called a parking orbit. This is because the satellite appears to be stationary from the surface of the Earth as it moves in the same direction and at the same speed as the rotation of the Earth. This makes it seem as though the satellite is "parked" in space.
Q15: The value of g will become 10% of its value at the earth’s surface at a height ........... above the surface of earth. Take radius of earth as 6400 km.
Ans : 57,600
The value of g (acceleration due to gravity) will become 10% of its value at the earth’s surface at a height 57,600 km above the surface of earth. At this height, the gravitational pull from the Earth is significantly weaker, hence the value of g is just 10% of its value at the Earth's surface. This is based on the formula for gravitational force which states that the force decreases with the square of the distance from the center of the Earth.
True/False
Direction: Read the following statements and write your answer as true or false.
Q16: The orbit speed of a satellite is inversely proportional to radius of its orbit.
Ans : False
The answer is false because the orbital speed of a satellite is not inversely proportional to the radius of its orbit. In fact, the speed is determined by the gravitational force of the planet and the mass of the satellite, not the radius of the orbit.
Q17: For a spherically symmetric earth, the acceleration due to gravity should be same at the equator and at the poles
Ans : False
The answer is false because the acceleration due to gravity is not the same at the equator and at the poles. The earth is not a perfect sphere but an oblate spheroid, i.e., slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. Hence, the gravitational pull is slightly lesser at the equator than at the poles.
Q18: An object in a satellite experiences weightlessness.
Ans : True
The answer is true. When an object is in a satellite orbiting the earth, it is in a state of continuous free fall towards the earth. This gives the sensation of weightlessness as the object and the satellite are falling towards the earth at the same rate.
Q19: If earth suddenly stops rotating about its axis, then the value of g will be same at all the places.
Ans : True
The answer is true because if the earth suddenly stops rotating about its axis, the centrifugal force, which is responsible for the slight decrease in gravity at the equator, would cease. This would mean the value of g (acceleration due to gravity) would be the same at all places.
Q20: Weightlessness experienced while orbiting the earth in a spaceship is the result of zero gravity.
Ans : True
The answer is true as the sensation of weightlessness experienced while orbiting the earth in a spaceship is due to the continuous free fall of the spaceship towards the earth, which gives the impression of zero gravity. However, gravity is still present and is what keeps the spaceship in orbit.
Matching Questions
Direction: In the section, each question has two matching lists. Choices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q21: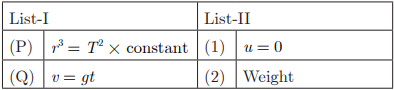
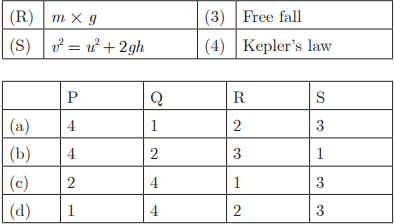 Ans : (a) P-4, Q-1, R-2, S-3
Ans : (a) P-4, Q-1, R-2, S-3
Q22: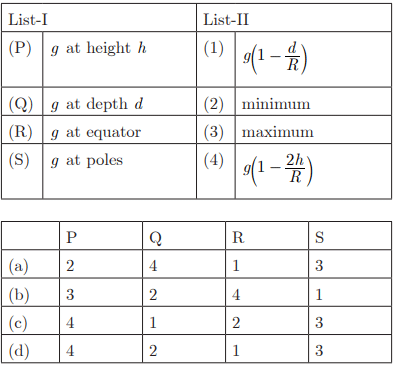
Ans : (c) P-4, Q-1, R-2, S-3
Q23: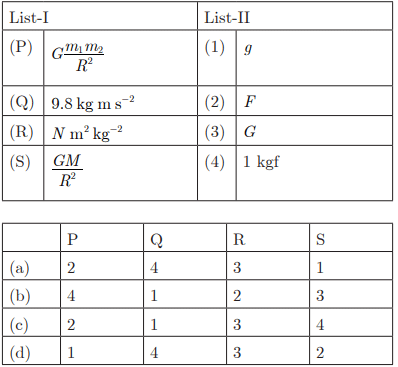 Ans : (a) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-1
Ans : (a) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-1
Q24:
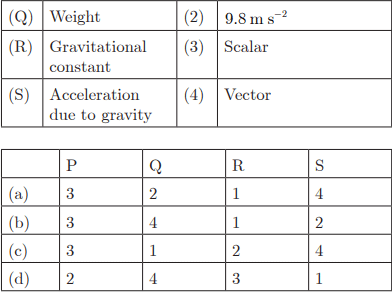
Ans : (b) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
















