Class 6 History Chapter 1 Notes - What, Where, How and When?
| Table of contents |

|
| What is History? |

|
| Where did People Live? |

|
| Names of the Land |

|
| What do Dates Mean? |

|
| Finding Out About the Past |

|
| One Past or Many? |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
What is History?
History is the study of past events in the order they occurred. It helps us understand how people lived, worked, and interacted with each other across different time periods.

Finding Out What Happened
Yesterday: We can learn about recent events by listening to the radio, watching television, or reading newspapers. These sources provide timely information about current happenings.
Last Year: For events from the past, such as those from last year, we rely on people’s memories or written records to gain insights.
Long Ago: But how do we learn about events that happened long, long ago? Let us explore the methods used to uncover these distant pasts.
What Can We Learn About the Past?
Daily Life: History reveals what people ate, the clothes they wore, and the types of homes they lived in. This information helps us understand their daily routines and lifestyles.
Occupations: By studying history, we learn about the roles of different groups, including hunters, herders, farmers, rulers, merchants, priests, craftspersons, artists, musicians, and scientists. Each occupation contributed to shaping society.
Leisure and Culture: History also uncovers the games children played, the stories shared, the performances enjoyed, and the songs sung. These cultural aspects provide a clearer picture of people’s values and ways of life.
Where did People Live?
People majorly lived near river valleys. This was because rivers provided water for all purposes.
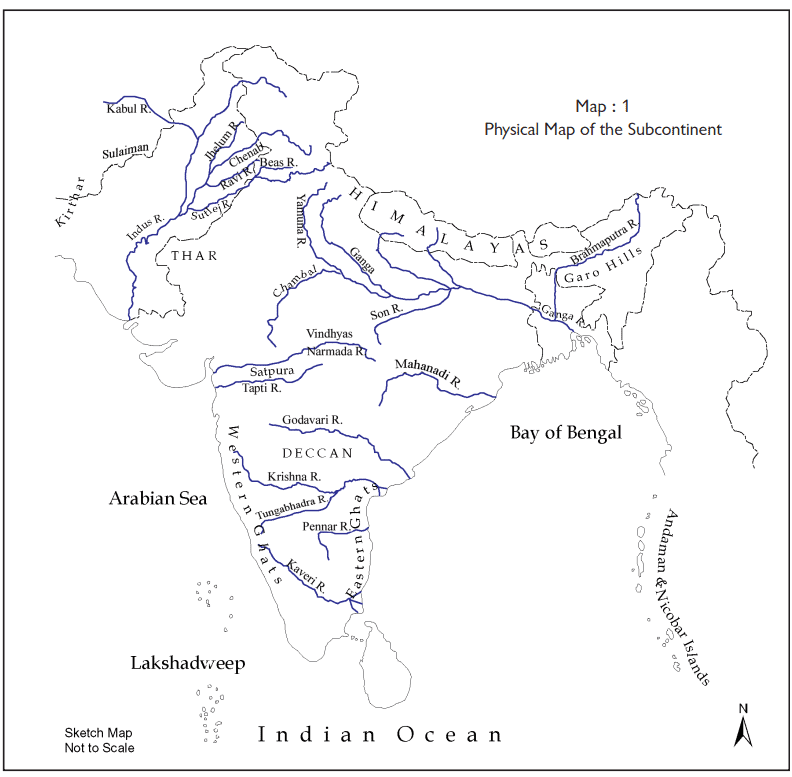 Rivers of India
Rivers of India
Living Along the Narmada River:
- For thousands of years, people have lived along the Narmada River.
- These early people were skilled gatherers, meaning they knew how to find food from nature.
- They collected roots, fruits, and other plants from forests and also hunted animals for food.
The First Farmers and Herders - Sulaiman and Kirthar Hills:
- About 8000 years ago, people began farming in the Sulaiman and Kirthar hills (northwest).
- They grew crops like wheat and barley and started raising animals such as sheep, goats, and cattle.
- This was when people began settling in villages instead of constantly moving.
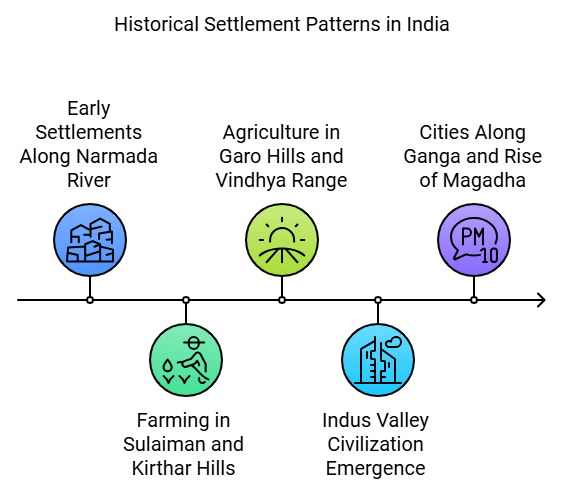
Agriculture in Garo Hills and Vindhya Range:
- People in the Garo hills (northeast) and the Vindhya range (central India) also started farming.
- In these areas, rice was one of the first crops grown, especially north of the Vindhyas.
Indus Valley Civilization:
- Around 4700 years ago, some of the world’s first cities appeared along the Indus River and its smaller rivers (tributaries).
- These cities were very advanced for their time, with well-planned buildings and a strong community.
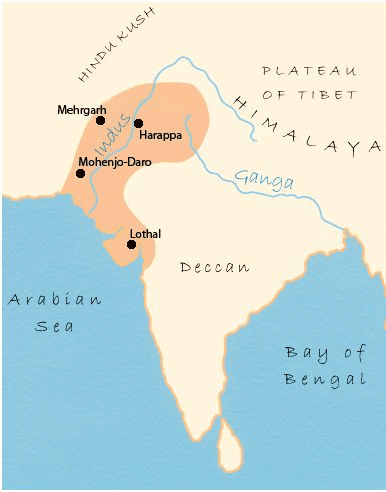 Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
Cities Along the Ganga and the Rise of Magadha:
- About 2500 years ago, new cities began to grow along the Ganga River and its smaller rivers.
- In the area south of the Ganga, a powerful kingdom named Magadha rose, located in present-day Bihar.
Why Did People Move Around?
- For Work and Safety: People often moved to find jobs or to escape dangers like floods or droughts.
- Conquests and Armies: Sometimes, armies traveled to conquer other lands.
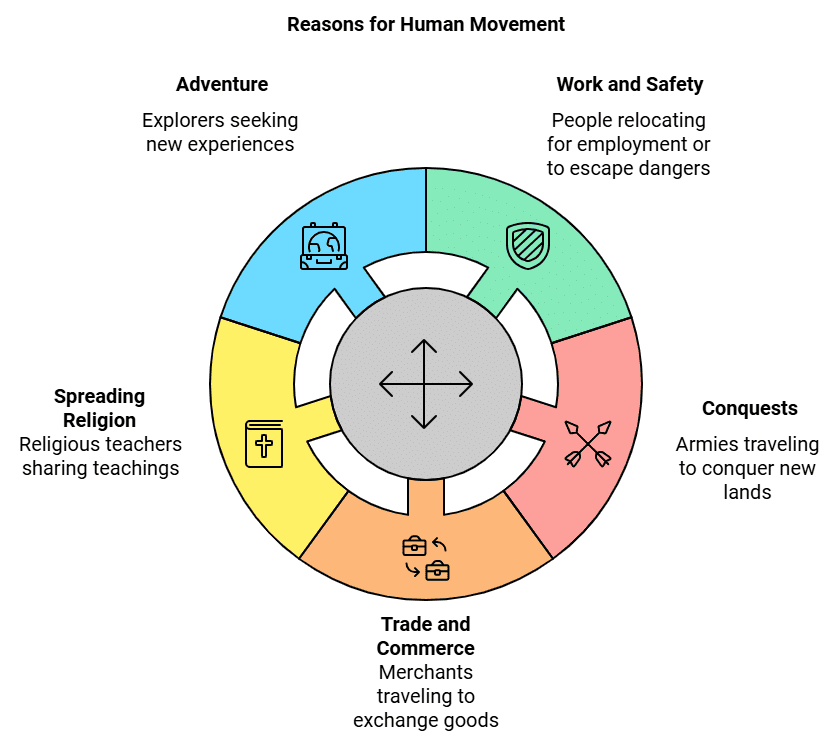
- Trade and Commerce: Merchants, or traders, traveled in groups (caravans) or by ship, bringing valuable goods from one place to another.
- Spreading Religion and Knowledge: Religious teachers traveled from village to village to share teachings and advice.
- For Adventure: Some people moved to explore new places and discover exciting things.
- Moving around helped people share ideas, knowledge, and cultural traditions, making communities more connected.
Why do people travel nowadays?
- South Asia is bordered by high mountains, seas, and deserts, making it challenging to cross, but not impossible.
- People traveled over mountains and across seas to reach new places, bringing their skills, music, foods, and ideas with them.
- This movement of people over time helped enrich the cultural traditions in the region.
Names of the Land
The two common names we use for our country are India and Bharat.
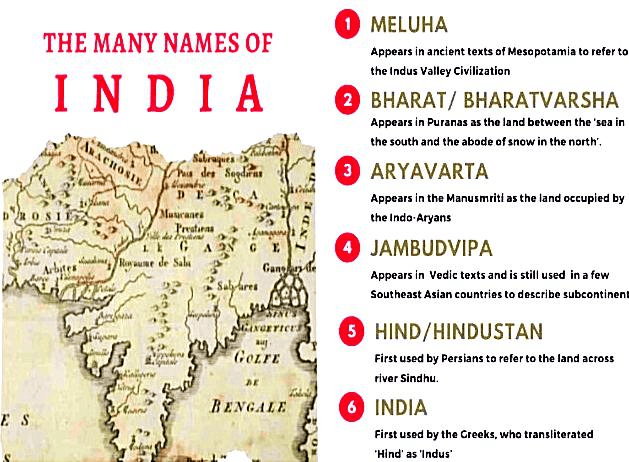 The Many Names of India
The Many Names of India
Origin of the Name India:
- The name India comes from the Indus River, which is called Sindhu in Sanskrit.
- Ancient Iranians and Greeks referred to the Indus as Hindos or Indos and named the land east of the river India.
Origin of the Name Bharat:
- The name Bharat was originally used to describe a group of people living in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent.
- This group is mentioned in the Rigveda, the earliest known Sanskrit text, which dates back to about 3500 years ago.
What do Dates Mean?
When asked for a date, we typically provide the day, month, and year (e.g., "2000 and something").
- Reference Point for Dates: Dates are generally counted from the birth of Jesus Christ, who is recognized as the founder of Christianity. This event is taken as year zero.
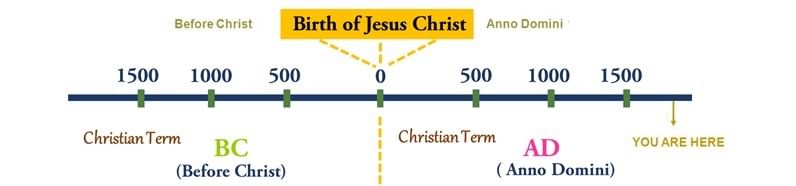 Reference Point for Dates
Reference Point for Dates
- Chronological Sequence: Historians use a chronological sequence to better understand historical events.
Events that occurred before the birth of Christ are labeled as BC (Before Christ), while events after His birth are denoted as AD (Anno Domini), which translates to "in the year of our Lord." - Divisions of Historical Timeline: The timeline of history is divided into three main stages:
- Prehistory: The period before written records.
- Protohistory: The transitional period when early writing began but is not well-documented.
- History: The period after written records became more common and documented.
What letters are used to represent dates that occurred before the birth of Christ?
Finding Out About the Past
Archaeologists and historians study various sources to learn about the past. These sources can be categorized into two main types: archaeological and literary.
1. Archaeology
Archaeology involves studying human history and prehistory through the excavation of sites and the analysis of physical remains.
Inscriptions: These are writings carved on hard surfaces such as stone or metal. Kings used inscriptions to make their orders visible so that people could read and follow them. Inscriptions also document significant events, such as battles and royal decrees.
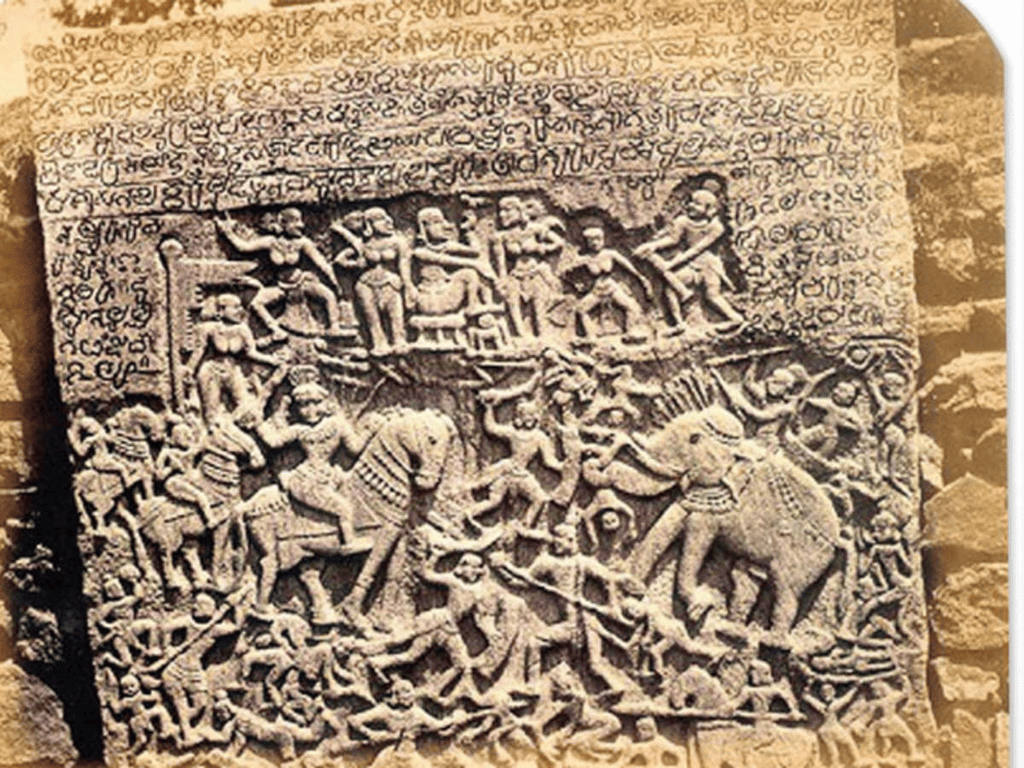 Stone Inscriptions
Stone InscriptionsSources Used by Archaeologists:
Monuments: Large structures that provide insight into the architectural styles and cultural practices of past societies.
Artifacts: Objects created or used by humans, including tools, pottery, and everyday items, which reveal information about daily life.
Inscriptions: Provide direct evidence of historical events, beliefs, and practices.
Coins: Used for trade, coins can indicate economic conditions and cultural influences.
Animal and Plant Remains: Archaeologists examine bones of animals, birds, and fish to learn about diets and lifestyles. They also analyze plant remains, though these are less frequently preserved, and may find charred seeds or wood.
2. Literary Sources
Any handwritten or recorded material from the past is called a literary source.
 Palm Leaf Manuscripts
Palm Leaf Manuscripts
Types of Literature:
- Religious Literature: Texts that deal with religious beliefs, practices, and rituals.
- Secular Literature: Non-religious texts, including historical records, poetry, and literature that reflects everyday life.
- Manuscripts: Books written long ago by hand, often on palm leaves or specially prepared birch bark from trees in the Himalayas.
Manuscripts cover various subjects, including:
Religious Beliefs and Practices: Insights into the spiritual life of people.
The Lives of Kings: Historical accounts of rulers and their reigns.
Medicine and Science: Early medical texts and scientific observations that reveal knowledge and practices of the time. Literary Works: Epics, poems, and plays that reflect cultural values and storytelling traditions
One Past or Many?
Class 6 History Book is titled Our Pasts to emphasize that there isn't a single past; instead, there are multiple pasts, each reflecting the experiences of different groups of people.
Diverse Lifestyles:
- Different Occupations: The lives of various groups such as herders, farmers, kings and queens, merchants, and craftspersons were distinct from one another.
- Regional Practices: People followed different customs and practices based on their geographical location. For instance, people in the Andaman Islands rely on fishing, hunting, and gathering forest produce, while those in urban areas depend on others for their food supply.
Recording History:
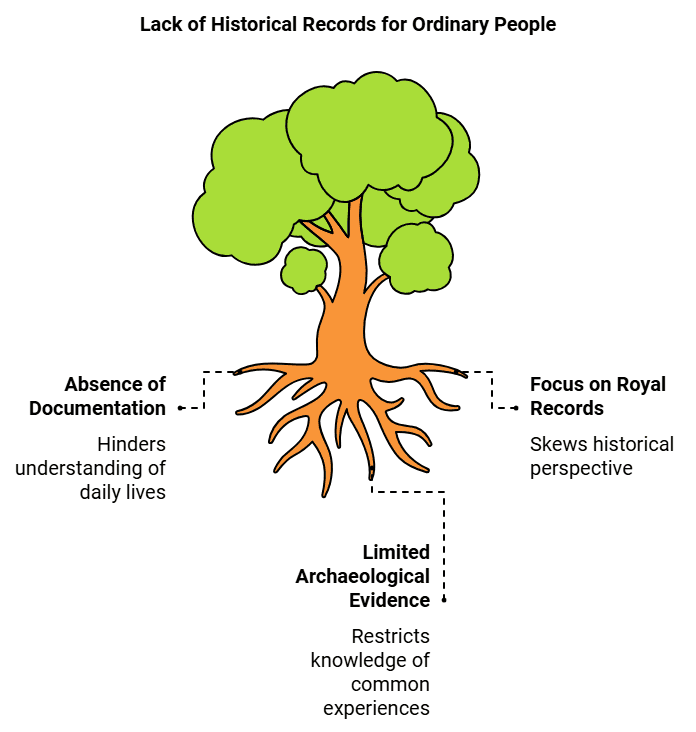
- Royal Records: We have abundant information about kings and their battles because they documented their victories and significant events.
- Lack of Records for Ordinary People: In contrast, common people such as hunters, gatherers, farmers, and herders typically did not keep records of their daily lives. This leads to gaps in our understanding of their experiences.
- Role of Archaeology: Archaeology plays a crucial role in uncovering the lives of ordinary people by examining artifacts and remains, but much of their history remains unknown due to the absence of written records.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 They study the remains of buildings made of stone and brick, paintings, and sculptures. They explore to find tools, weapons, ornaments, and coins. Who are they?
Ans: There were many things that were made and used in the past. Those who study these objects are called archaeologists. They study the remains of buildings made of stone and brick, paintings, and sculptures. They also explore and excavate (dig under the surface of the earth) to find tools, weapons, pots, pans, ornaments, and coins.
Q.2. Name two main groups (or categories) of historical sources.
Ans: The two main groups (or categories) of historical sources are :
- Archaeological sources include physical remains inscriptions, coins, etc.
- Literary sources include religious books, manuscripts, foreign, travelers’ accounts etc.
Q.3. Explain the term BC.
Ans:
- The letter BC means Before Christ.
- Dates are generally counted (i.e., the day, the month, and the years) or assigned to the birth of Jesus Christ, the founder of Christianity.
- So 2000 BC means 2000 years before the birth of Jesus Christ.
- All dates before the birth of Jesus Christ are counted backward and generally have the letter BC (Before Christ) added on.
FAQs on Class 6 History Chapter 1 Notes - What, Where, How and When?
| 1. What is history and why is it important? |  |
| 2. Where did early humans live? |  |
| 3. How do historians determine the names of places in the past? |  |
| 4. What do dates signify in historical context? |  |
| 5. Can there be multiple interpretations of historical events? |  |





















