Parts and Wholes Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Fraction? |

|
| What Makes a Whole? |

|
| Dividing Shapes into Equal Parts |

|
| Fraction of a Group |

|
| Comparing Fractions: Greater Than, Less Than, and Equal |

|
| Shopping with Fractions |

|
What is a Fraction?
Fraction is a part of a whole or a part of a collection.
- A fraction is a way to show a part of something.
- Imagine you have a pizza, and you want to share it with your friend.
- If you cut the pizza into 4 equal pieces and take 1 piece, you can write this as a fraction. The fraction would look like this: 1/4.
- A fraction has two parts:
1. Numerator
2. Denominator
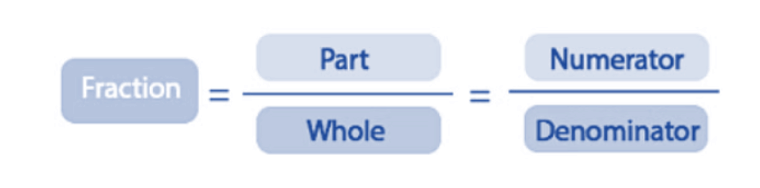
- So, 1/4 means you have 1 out of 4 equal pieces of the pizza.
- Fractions help us show parts of a whole, like pieces of a pizza, parts of a chocolate bar, or even parts of time (like half an hour).
- They are useful for telling how much of something we have.
Some common fractions:
- Half is written as 1/2
- One-sixth is written as 1/6
- One-fourth or Quarter is written as 1/4
- One-eight is written as 1/8
What Makes a Whole?
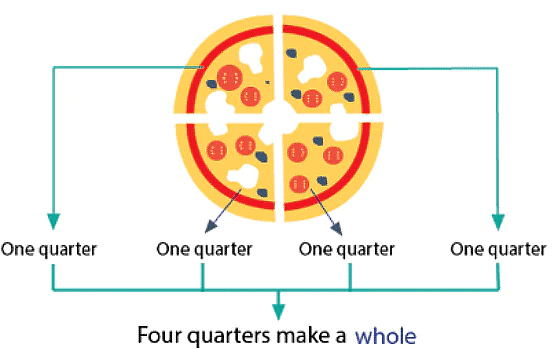
- A whole means you have all the parts of something, nothing is missing.
- For example, think of a chocolate bar that is divided into 4 equal pieces. If you have all 4 pieces, you have the whole chocolate bar. We can write this as a fraction:
4/4 means you have 4 out of 4 pieces, which is the whole thing. - In fractions, when the numerator (top number) and denominator (bottom number) are the same, like 3/3, 5/5, or 10/10, that means you have a whole.
- Another way to think about it is if you cut something into parts, like slices of pizza, and then you gather all the parts back together, you make a whole again. So, when all the parts are there, you have the whole!
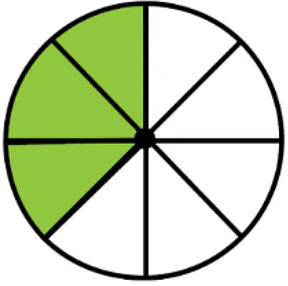
Example: Find the fraction of the coloured part in the shape.
(a) 4/8
(b) 5/8
(c) 3/8
(d) 6/8
Correct answer is option (c)
There is a total of 8 parts so the denominator of fraction = 8.
We want to find the fraction of the coloured parts.
There is a total of 3 coloured parts so the numerator of fraction = 3.
So the required fraction = 3/8.
Therefore, Option (C) is correct.
Dividing Shapes into Equal Parts
- When we divide a shape into equal parts, it means we are splitting the shape into sections that are exactly the same size.
- Each part has the same area, so no part is bigger or smaller than the others.
- By dividing shapes equally, we can understand concepts like halves, thirds, quarters, and more.
- This helps us share or compare parts of a whole in a fair and equal way.
Examples:
Circle Divided into Equal Parts: Imagine cutting a pizza into slices. If you cut the pizza into 4 equal slices, each slice represents 1/4 of the pizza. All the slices are exactly the same size.
Square Divided into Equal Parts: If you draw a square and divide it into 4 smaller squares, each small square is 1/4 of the original large square. All 4 squares are identical in size.
Rectangle Divided into Equal Parts: Think of a chocolate bar shaped like a rectangle. If it is divided into 6 equal pieces, each piece represents 1/6 of the chocolate bar.
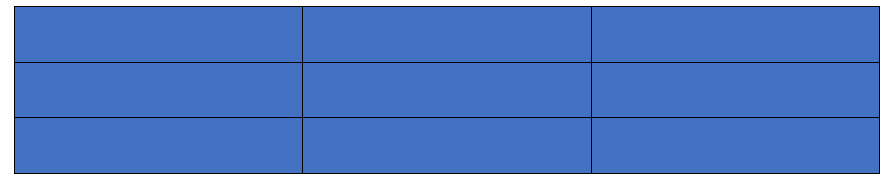
Example: Divide the rectangle into nine equal parts:

Sol:
Fraction of a Group
- The fraction of a group is written as fraction x total number of items in the group.
Example: A farmer grows the following vegetables by dividing his field into 9 equal parts.
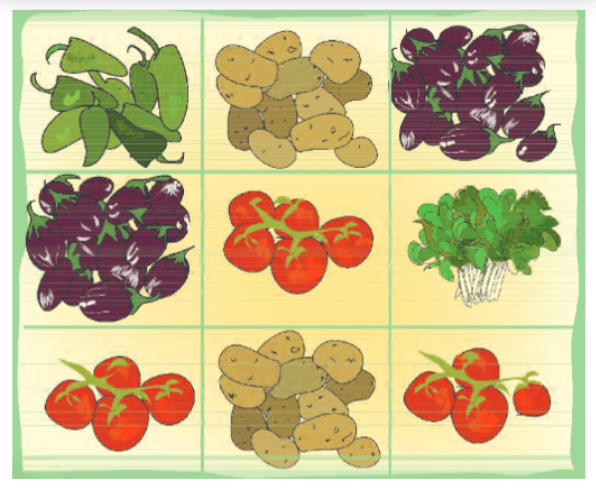
- Which vegetables take up 1/3 of the field?
- What fraction of the field is used to grow potatoes?
- Is the part of the field used for spinach bigger or smaller than the part used for brinjals?
Sol:
1. There are two vegetables that take up 1/3 of the field, namely, spinach and peppers.
2. Potatoes are grown on 2 parts out of the 9 parts of the field, i.e., 2/9.
3. Spinach is grown on 1/9 of the field, while brinjal is grown on 2 parts or 2/9 of the field. Therefore, the part of the field used for spinach is smaller than the part used for brinjals.
Comparing Fractions: Greater Than, Less Than, and Equal
When comparing fractions, we look at the size of the parts to determine which fraction is greater, less, or if the two fractions are equal.
- A fraction is greater than another if it represents a larger part of the whole.
- A fraction is less than another if it represents a smaller part of the whole.
- Two fractions are equal if they represent the same size of the whole, even if they look different.
Some examples:
- 1/2 is greater than 1/3 because half of something is bigger than one-third.
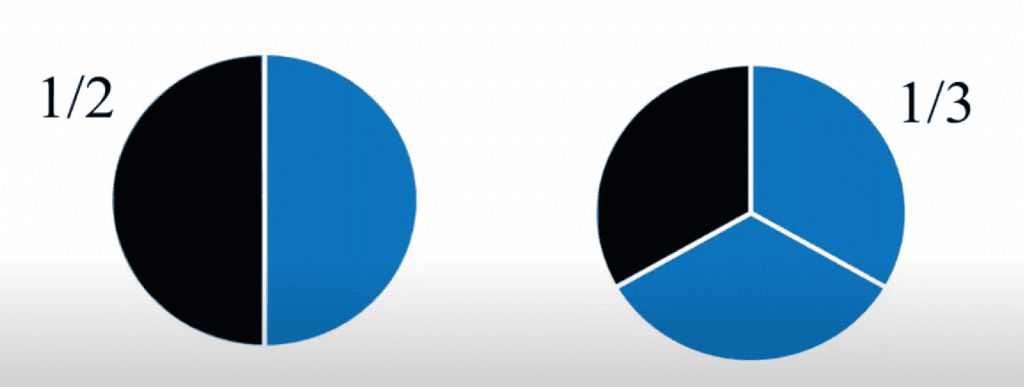
Similarly,
- 1/4 is less than 1/2 because one-fourth is smaller than one-half.
- 2/4 is equal to 1/2 because both represent the same part of the whole, even though they look different.
By comparing fractions, we can understand their size and how they relate to one another.
Shopping with Fractions
- When we go shopping, we often buy items in different amounts, like vegetables or fruits by weight. Sometimes, we need to calculate the cost for a certain amount of items, even if we buy only a fraction or part of the total amount.
- In this section, we will use fractions and multiplication to calculate the cost of items from a price list. This will help you understand how to apply fractions in real-life situations, like shopping!
- Let's understand with the help of an example.
Example: Look at the price list below.
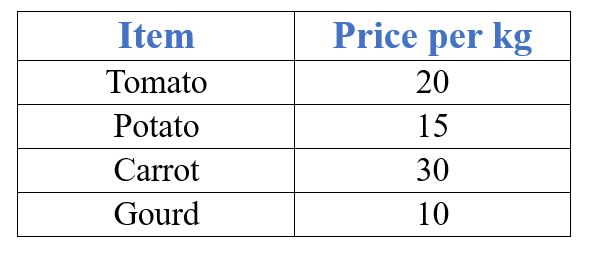
Answer the following questions:
a) How much does 1/2 kg of tomato cost?
b) How much does 1/4 kg of potato cost?
c) Kiran wants 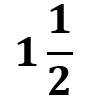 kg of tomato. How much will it cost?
kg of tomato. How much will it cost?
d) How much does 3/4 kg of potato cost?
e) What is the cost of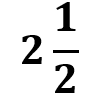 kg of carrots?
kg of carrots?
f) He bought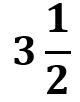 kg of gourd. How much will it cost?
kg of gourd. How much will it cost?
Sol:
a) The price for 1 kg of tomato is ₹20, so for 1/2 kg:
1/2 x 20 = 10
Cost of 1/2 kg of tomato = ₹10.
b) The price for 1 kg of potato is ₹15, so for 1/4 kg:
1/4 x 15 = 3.75
Cost of 1/4 kg of potato = ₹3.75.
c) The price for 1 kg of tomato is ₹20, so for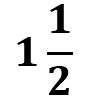 kg:
kg:
3/2 x 20 = 3 x 10 = 30
Cost of 1 1/2 kg of tomato = ₹30.
d) The price for 1 kg of potato is ₹15, so for 3/4 kg:
3/4 x 15 = 11.25
Cost of 3/4 kg of potato = ₹11.25.
e) The price for 1 kg of carrot is ₹30, so for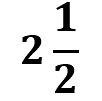 kg:
kg:
5/2 x 30 = 5 x 15 = 75
Cost of 2 1/2 kg of carrot = ₹75.
f) The price for 1 kg of gourd is ₹10, so for 3 1/2 kg:
31/2 x 10 = 3.5 x 10 = 35
Cost of 3 1/2 kg of gourd = ₹35.
|
31 videos|192 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Parts and Wholes Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What is a fraction and how is it represented? |  |
| 2. How can we determine what makes a whole in fractions? |  |
| 3. How do we divide shapes into equal parts to create fractions? |  |
| 4. What is meant by the fraction of a group, and how do we calculate it? |  |
| 5. How can we compare fractions to determine which is greater, less, or equal? |  |




















