NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths - Cubes and Cube Roots - 2 (Exercise 6.2)
Exercise 6.2
Q1: Find the cube root of each of the following numbers by prime factorisation method.
(i) 64
Sol: 64 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 64 = (2 × 2 × 2) x (2 × 2 × 2)
Here, 64 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 64 = (2 x 2)3 = 43
Hence, 4 is the cube root of 64.
(ii) 512
Sol: 512 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 512 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2)
Here, 512 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 512 = (2 × 2 × 2)3 = 83
Hence, 8 is the cube root of 512.
(iii) 10648
Sol: 10648 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 11 × 11 × 11
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 10648 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (11 × 11 × 11)
Here, 10648 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 10648 = (2 × 2 x 2) x (11 x 11 x 11) = 23 x 113 = (2 x 11)3 = (22)3
Hence, 22 is the cube root of 10648.
(iv) 27000
Sol: 27000 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 5
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 27000 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (3 × 3 × 3) × (5 × 5 × 5)
Here, 27000 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 27000 = (2 × 3 × 5)3 = 303
Hence, 30 is the cube root of 27000.
(v) 15625
Sol: 15625 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 15625 = (5 × 5 × 5) × (5 × 5 × 5)
Here, 15625 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 15625 = (5 × 5)3 = 253
Hence, 25 is the cube root of 15625.
(vi) 13824
Sol: 13824 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors,
13824 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (3 × 3 × 3)Here, 13824 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 13824 = (2 × 2 × 2 × 3)3 = 243
Hence, 24 is the cube root of 13824.
(vii) 110592
Sol: 110592 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors,
110592 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (3 × 3 × 3)Here, 110592 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 110592 = (2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3)3 = 483
Hence, 48 is the cube root of 110592.
(viii) 46656
Sol: 46656 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors,
46656 = (2 × 2 × 2) × (2 × 2 × 2) × (3 × 3 × 3) × (3 × 3 × 3)Here, 46656 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 46656 = (2 × 2 × 3 × 3)3 = 363
Hence, 36 is the cube root of 46656.
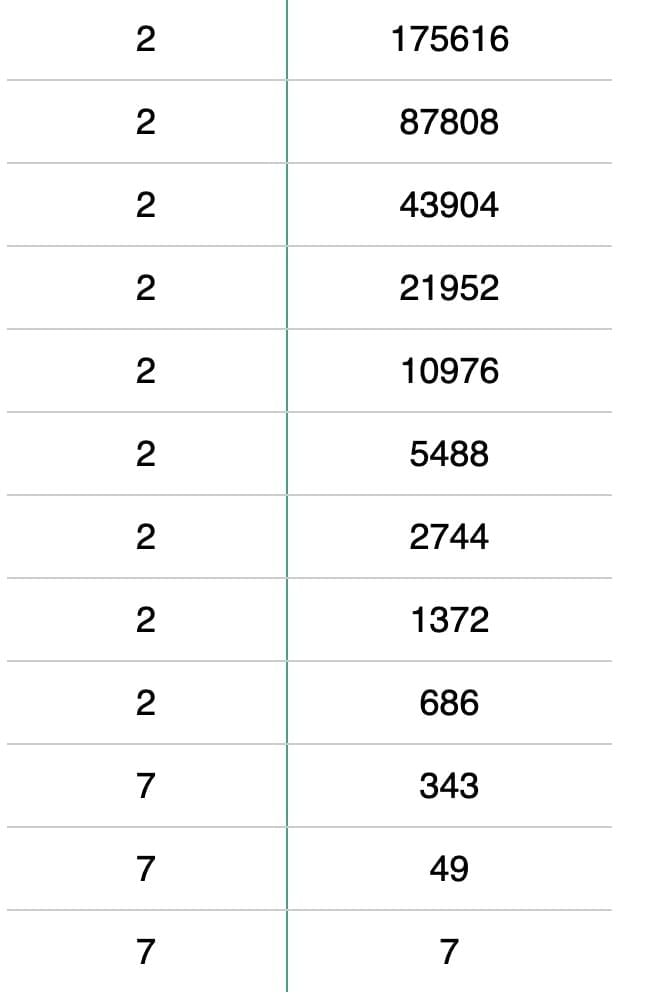
(ix) 175616
Sol: 175616 = 2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×7×7×7
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors,
175616 = (2×2×2)×(2×2×2)×(2×2×2)×(7×7×7)Here, 175616 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 175616 = (2×2×2×7)3 = 563
Hence, 56 is the cube root of 175616.
(x) 91125
Sol: 91125 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 5
By grouping the factors in triplets of equal factors, 91125 = (3 × 3 × 3) × (3 × 3 × 3) × (5 × 5 × 5)
Here, 91125 can be grouped into triplets of equal factors.
∴ 91125 = (3 × 3 × 5)3 = 453
Hence, 45 is the cube root of 91125.
Q2: State True or False
(i) The cube of any odd number is even.
Ans: False
Cube of any odd number is always odd, e.g., (7)3 = 343
(ii) A perfect cube does not end with two zeros.
Ans: True
A perfect cube cannot end with exactly two zeros (it would have to end with three zeros because of the factorization of 10³).
(iii) If the square of a number ends with 5, then its cube ends with 25.
Ans: False
Example given uses 5: 5² = 25 (ends with 5), 5³ = 125 (not 25, ends with 125).
Similarly, 15² = 225 (ends with 5), 15³ = 3375 (ends with 375).
(iv) There is no perfect cube which ends with 8.
Ans: False
(12)3 = 1728 (ends with 8)
(v) The cube of a two-digit number may be a three-digit number.
Ans: False
(10)3 = 1000 (4-digit number)
(vi) The cube of a two-digit number may have seven or more digits.
Ans: False
(99)3 = 970299 (6-digit number)
(vii) The cube of a single-digit number may be a single-digit number.
Ans: True
(2)3 = 8 (1-digit number)
|
94 videos|549 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths - Cubes and Cube Roots - 2 (Exercise 6.2)
| 1. What is a cube and what are its properties? |  |
| 2. How to calculate the volume of a cube? |  |
| 3. What is a cube root and how to find it? |  |
| 4. How to find the surface area of a cube? |  |
| 5. How are cubes used in real-life applications? |  |