NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 51 |

|
| Page No. 53 |

|
| Page No. 55 |

|
| Page No. 57 |

|
| Page No. 59 |

|
Page No. 51
Q1. Who discovered cells and how?
Ans:
- The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He examined thin slices of cork under a self-made microscope and saw a multitude of tiny hollow spaces that he remarked looked like the walled compartments of a honeycomb.
- He termed these spaces as ‘cell’ meaning ‘small room’ in Latin.
 Microscope and Cork cells
Microscope and Cork cells
Q2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Ans:
- All living organisms are made up of cells. This shows that the cell is the structural unit of life.
- Each living cell can perform certain basic functions that are characteristic of all living forms.
Example:
(i) Phagocytic cells eat or kill unwanted or foreign particles inside the body (e.g., WBCs).
(ii) Some cells secrete enzymes and hormones, e.g., pancreatic cells, small intestinal cells, and liver cells.
Page No. 53
Q1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Ans: CO2 moves by diffusion – This cellular waste accumulates in high concentrations in the cell, whereas the concentration of CO2 in the external surroundings is comparatively lower. This difference in the concentration level inside and outside of the cell causes the CO2 to diffuse from a higher (within the cell) region to a lower concentration.
H2O diffuses by osmosis through the cell membrane. It moves from a region of higher concentration to a lower concentrated region through a selectively permeable membrane until equilibrium is reached.
Q2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Ans: The plasma membrane allows or permits the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell and prevents the movement of some other materials through it. Hence, it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Page No. 55
Q1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.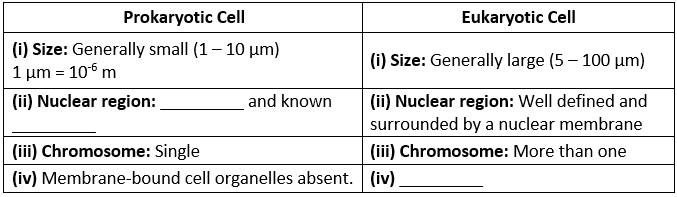
Ans: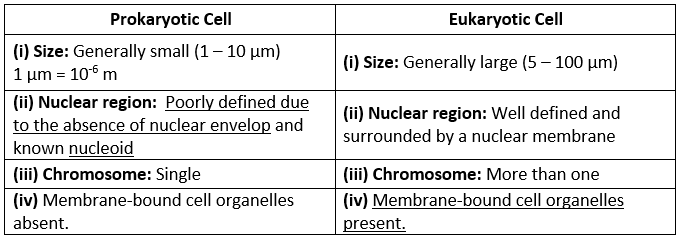
Page No. 57
Q1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their genetic material?
Ans: Two organelles that contain their genetic material are Mitochondria and Plastids. Mitochondria help in respiration in the cell, while plastids are responsible for the process of photosynthesis in leaves.
Q2. If the organization of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Ans:
- Cell organelles are responsible for the organization and proper functioning of a cell, as each of them performs some specific functions.
- Naturally, if any of these organelles are destroyed, the cell will not be able to perform many basic functions like photosynthesis, respiration, nutrition, etc., and may also result in the stopping of all life activities in the cell. Due to the cell damage, the lysosome bursts, and their enzymes digest such cells.
Q3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Ans:
- Lysosomes are the cell organelles involved in the digestion of any foreign material that enters the cell, as they contain digestive enzymes.
- In case any cell is dead or damaged, the lysosome bursts to release the digestive enzymes to digest its cell.
- Thus, these are known as ‘suicide bags’.
Q4. Where are proteins synthesized inside the cell?
Ans:
- Proteins are the building blocks of the body that are made up of various amino acids. They are synthesized inside the ribosomes, are the small structures present in the cytoplasm, or might be attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum due to the presence of ribosomes on its surface.
- In simpler words, proteins are the body's building blocks, made of amino acids. They are created inside ribosomes, which are small structures found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. When ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, it’s called the rough endoplasmic reticulum because the ribosomes give it a rough surface.
Page No. 59
Q1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Ans:
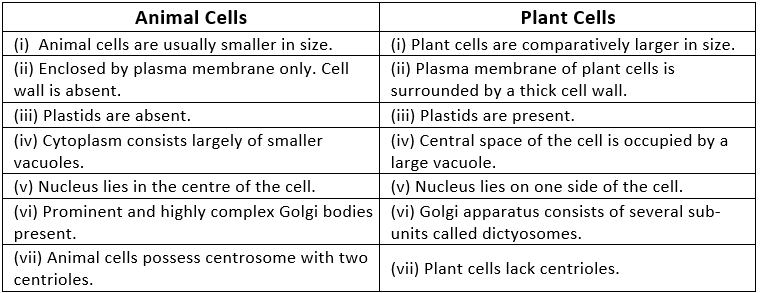
Q2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Ans: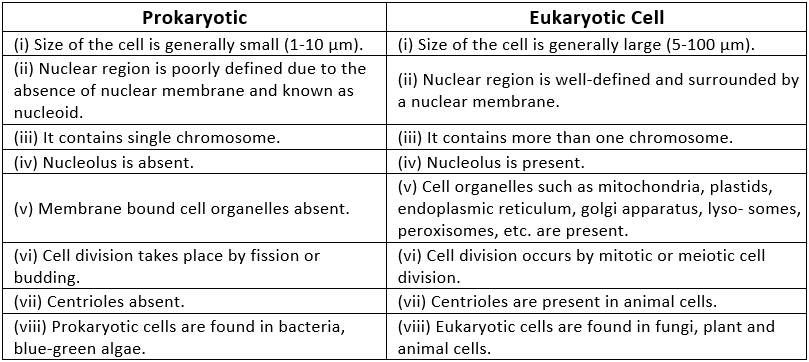
Q3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Ans:
- The plasma membrane is the selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and allows the entry and exit of selected materials of the cell.
- If it ruptures, the contents of the cell will come in direct contact with the surrounding medium, and not only unwanted material will be able to enter freely into the cell, but useful material will also find its way out of the cell easily.
- This will seriously disrupt the various metabolic activities of the cell and will result in its imminent death.
Q4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Ans:
- If there were no Golgi apparatus, the material synthesized by the endoplasmic reticulum would not be carried to the various parts inside and outside of the cell.
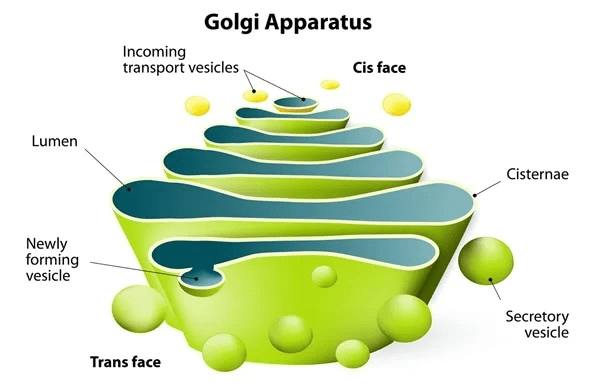
- Also, as the Golgi apparatus performs the function of storage and modification of the material synthesized in the cell, these materials would not be stored and modified further.
- Moreover, there will be no production of lysosomes, which will cause the accumulation of waste material, viz., worn out and dead cell organelles within the cell, which will ultimately lead to cell death.
Q5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why
Ans:
- Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because these are the sites of cellular respiration.
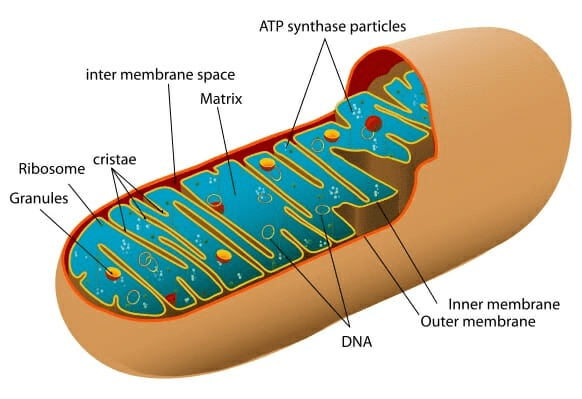 Mitochondria
Mitochondria - The energy that is released by the mitochondria is in the form of ATP molecules and is required for various chemical activities needed for.
- The energy stored in ATP is used by the body to make new chemical compounds and to perform mechanical work.
- Thus, mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of cells.
Q6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesized?
Ans:
- Lipids and proteins are the essential parts of the plasma membrane, which are synthesized through the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is found to be of two types based on the substances they synthesize.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the synthesis of lipids, while the rough endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the synthesis of proteins.
Q7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Ans:
- Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface, which fuse over the food particle, forming a food vacuole as shown in the figure.
- Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones, which then diffuse into the cytoplasm.
- The remaining undigested material is moved to the surface of the cell and thrown out.
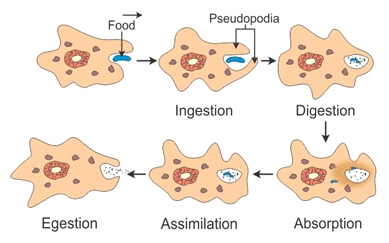 Nutrition in Amoeba
Nutrition in Amoeba
Q8. What is osmosis?
Ans: It is the passage of solvent from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Q9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty.
(b) Put one teaspoon of sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon of sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D.
Ans:
(i)
- Water gathers in the hollowed portion of cups B and C because of the process of endosmosis (moving in of the solvent). The potato wall acts as a semi-permeable membrane.
- As cups B and C are filled with sugar and salt, respectively, and their outer part is in contact with the water, the concentration of water outside the cups is higher than inside the cups.
- So, water moves from its higher concentration towards the lower concentration, i.e., inside the cup.
(ii) Potato A is necessary for this experiment because:
- Potato A acts as a control of the experiment. It is very necessary to compare the results of the experiment.
- It shows that if the concentration of water is the same on both sides, there will be no movement of water.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D because:
- Water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A as it does not contain a hypertonic solution, so there is no concentration difference and hence no movement of solvent.
- Water does not gather in cup D as the cells of the boiled potato are dead, and the potato wall is no longer semi-permeable. Hence, no osmosis occurs.
Q10. Which type of cell division is required for the growth and repair of the body and which type is involved in the formation of gametes?
Ans:
- For growth and repair, mitotic division (mitosis) is involved as this type of division keeps the chromosome number constant.
- For gamete formation, meiosis is involved as a reduction of chromosome number is necessary for this case.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life
| 1. What is the basic structural and functional unit of life? |  |
| 2. What are the main components of a plant cell that differentiate it from an animal cell? |  |
| 3. How does the cell membrane regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell? |  |
| 4. What is the role of mitochondria in the cell? |  |
| 5. Why is the study of cells important in biology? |  |
















