NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Coordination Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
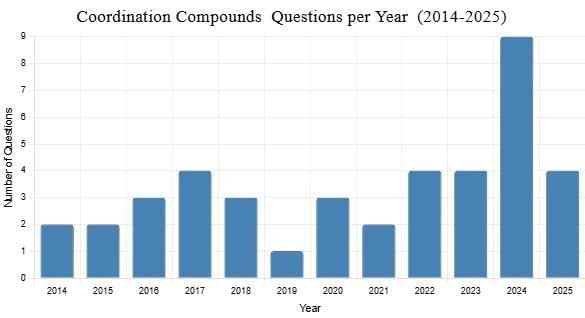
From 2014 to 2025, 41 questions were asked on Coordination Compounds. Typically, one to four questions appeared in the exam (2014–2023, 2025), with a peak of 9 in 2024, and none with zero questions. The questions focused on coordination compounds, ligands (e.g., EDTA, ambidentate), magnetic properties (paramagnetic, diamagnetic), and isomerism (solvate, geometrical), with no specific difficulty distribution provided in the data.
2025
Q1: Out of the following complex compounds, which of the compounds will be having the minimum conductance in solution? (NEET 2025)
(a) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
(b) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl
(c) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
(d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]
Ans: (c)
- [Co(NH₃)₃Cl₃]: This is a neutral complex where all three chlorides are coordinated to cobalt. It does not dissociate into ions. Hence, conductance is minimum.
- [Co(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl: This is a 1:2 electrolyte. It dissociates as:[Co(NH₃)₄Cl₂]Cl → [Co(NH₃)₄Cl2]+ + Cl-
Producing 2 ions in solution. - [Co(NH₃)₆]Cl₃:This is a 1:3 electrolyte. It dissociates as:
[Co(NH₃)₆]Cl₃ → [Co(NH₃)₆]3+ + 3Cl-
Producing 4 ions in solution. [Co(NH₃)₅Cl]Cl: This is a 1:2 electrolyte. It dissociates as:[Co(NH₃)₅Cl]Cl → [Co(NH₃)₅Cl]+ + Cl-
Producing 2 ions in solution.
So, [Co(NH₃)₃Cl₃] produces no ions in solution and will have the minimum conductance.
Therefore, the compound with minimum conductance in solution is [Co(NH₃)₃Cl₃].
Q2: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2025)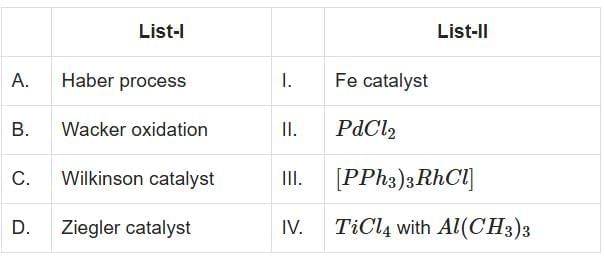 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-IV, C-III, P-II
(c) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(d) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
Ans: (a)
In the given problem, we need to match the catalysts in List-I with their corresponding reactions or components in List-II:
- A. Haber Process: This is the industrial process to synthesize ammonia (NH₃) from nitrogen (N₂) and hydrogen (H₂). The catalyst used is iron (Fe). Hence, A matches with I.
- B. Wacker Oxidation: This process involves the oxidation of alkenes (e.g., ethylene) to aldehydes or ketones using palladium chloride (PdCl₂) as the catalyst. Hence, B matches with II.
- C. Wilkinson Catalyst: This is a homogeneous catalyst [(PPh₃)₃RhCl] used for hydrogenation reactions in organic chemistry. Hence, C matches with III.
- D. Ziegler Catalyst: This catalyst (a combination of TiCl₄ and Al(CH₃)₃) is used for polymerization of alkenes to produce polyethylene. Hence, D matches with IV.
Correct Answer: Option A) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Q3: Which of the following are paramagnetic? (NEET 2025)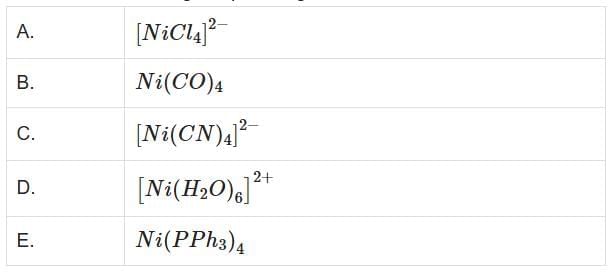
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and D only
(b) A, D and E only
(c) A and C only
(d) B and E only
Ans: (a)
Q4: The correct order of the wavelength of light absorbed by the following complexes is.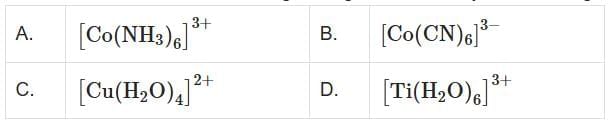 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (NEET 2025)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (NEET 2025)
(a) C<D<A<B
(b) C<A<D<B
(c) B<D<A<C
(d) B<A<D<C
Ans: (d)
In the given complexes:
- [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺: NH₃ is a moderate field ligand and causes moderate splitting of d-orbitals.
- [Co(CN)₆]³⁻: CN⁻ is a strong field ligand and causes large splitting of d-orbitals, resulting in absorption of shorter wavelengths.
- [Cu(H₂O)₄]²⁺: H₂O is a weak field ligand and causes small splitting of d-orbitals, resulting in absorption of longer wavelengths.
- [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺: H₂O is also a weak field ligand, but the metal ion Ti³⁺ has a smaller splitting than Cu²⁺.
Considering the ligand field strengths and resulting d-orbital splitting:
- [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ absorbs the shortest wavelength due to CN⁻ (strong field ligand).
- [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ absorbs a shorter wavelength than [Ti(H₂O)₆]³⁺ due to NH₃ (moderate field ligand).
- [Cu(H₂O)₄]²⁺ absorbs the longest wavelength due to H₂O (weak field ligand) and Cu²⁺ having a higher splitting than Ti³⁺.
So, the correct order is B < A < D < C.
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II.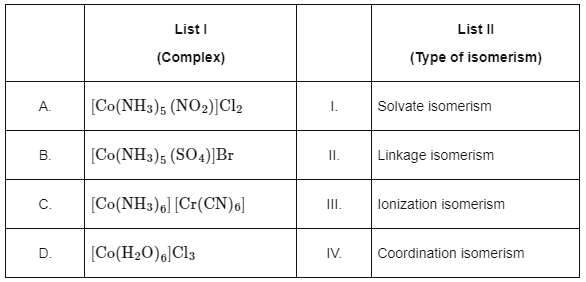 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:(a) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
Q2: Given below are two statements :
Statement I : [Co(NH3)6]3+ is a homoleptic complex whereas [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ is a heteroleptic complex.
Statement II : Complex [Co(NH3)6]3+ has only one kind of ligand but [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ has more than one kind of ligand.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
To determine the correctness of these statements and choose the correct option, we need to understand the concepts of homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes:
Homoleptic Complex: A complex in which a central atom is surrounded by only one kind of donor atom or identical ligands is known as a homoleptic complex. An example would be [Co(NH3)6]3+, where all the ligands are ammonia (NH3).
Heteroleptic Complex: A complex in which a central atom is surrounded by more than one kind of donor atom or different ligands is known as a heteroleptic complex, such as [Co(NH3)4Cl]+ which contains two different types of ligands, ammonia (NH3) and chloride (Cl−).
Statement I: [Co(NH3)6]3+ is a homoleptic complex whereas [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ is a heteroleptic complex.
This statement is accurate because [Co(NH3)6]3+ indeed is a homoleptic complex as it consists only of ammonia ligands. Conversely,
[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ is a heteroleptic complex, containing both ammonia and chloride ligands.
Statement II: Complex [Co(NH3)6]3+ has only one kind of ligand but [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ has more than one kind of ligand.
This statement is also true. As explained, in [Co(NH3)6]3+, there is only one type of ligand (ammonia), and in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+, there are two different types of ligands (ammonia and chloride), which is consistent with the definition provided.
Conclusion: Both Statement I and Statement II are true. Therefore, the correct choice is:
Option A: Both Statement I and Statement II are true
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Both [Co(NH3)6]³+ and [CoF6]³- complexes are octahedral but differ in their magnetic behaviour.
Statement II: [Co(NH3)6]³+ is diamagnetic, whereas [CoF6]³- is paramagnetic.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
(b) Statement I is True and Statement II is False.
(c) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(d) Both
Statement I and Statement II are True.
Ans: (d)
Statement I: It is true that both [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ and [CoF₆]³⁻ complexes are octahedral in shape, as the central metal ion (Co³⁺) is surrounded by six ligands in both cases. However, their magnetic behavior differs, which will be discussed below.
Statement II: The [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ complex is diamagnetic because NH₃ is a weak field ligand, leading to pairing of electrons in the d orbitals of the Co³⁺ ion, making the complex diamagnetic (no unpaired electrons).
In contrast, [CoF₆]³⁻ is paramagnetic because F⁻ is a weak field ligand, and it does not cause pairing of the d electrons in Co³⁺. Therefore, the [CoF₆]³⁻ complex has unpaired electrons and is paramagnetic.
Thus, both statements are true.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
Q4: The correct 'spin only' magnetic moments for the given complexes are: [CoF6]³- and [Co(C2O4)3]³- respectively are:
(a) 0 BM and 4.9 BM
(b) 0 BM and 0 BM
(c) 4.9 BM and 0 BM
(d) 4.9 BM and 4.9 BM (NEET 2024)
Ans: (c)
[CoF6]³-: Co³+ has a 3d⁶ electron configuration. Since fluoride is a weak field ligand, it doesn't cause pairing of electrons, and thus the complex is paramagnetic with a magnetic moment of 4.9 BM (due to 2 unpaired electrons).
[Co(C2O4)3]³-: The oxalate is a stronger field ligand, and it causes pairing of electrons. As a result, Co³+ in this complex has no unpaired electrons, and the complex is diamagnetic with a magnetic moment of 0 BM.
Q5: Match the complex ions in List-I with their corresponding hybridization in List-II. (NEET 2024)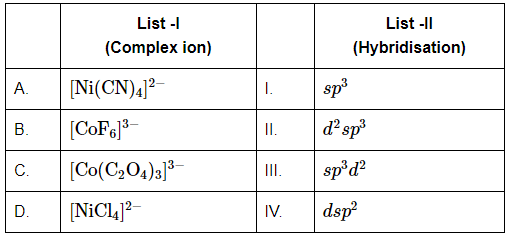 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: (a)
- A. [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻: This is a tetrahedral complex. The nickel ion has 2+ charge and is coordinated with four cyanide ions (CN⁻). Since CN⁻ is a strong field ligand, it causes pairing of electrons. For tetrahedral complexes, the hybridization of the metal ion is sp³. Thus, the hybridization for [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻ is sp³ (Option IV).
- B. [CoF₆]³⁻: This is an octahedral complex with a 3- charge. The cobalt ion here undergoes d²sp³ hybridization to accommodate six fluoride ions. The hybridization involves two d orbitals, one s orbital, and three p orbitals. Therefore, the hybridization is d²sp³ (Option III).
- C. [Co(C₂O₄)₃]³⁻: This complex is octahedral as well, where cobalt is coordinated with three oxalate ions (C₂O₄²⁻). The hybridization is sp³d² because cobalt uses sp³ and d² orbitals to form the bonds. Therefore, the hybridization is sp³d² (Option II).
- D. [NiCl₄]²⁻: This is a tetrahedral complex, where the nickel ion is coordinated with four chloride ions. As a result, the hybridization of the metal is sp³ (Option I).
Thus, the correct matching of the complex ions with their respective hybridizations is: A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I.
Therefore, the correct answer is (a).
Q6: The crystal field stabilisation energy (CFSE) and the 'spin-only' magnetic moment of [FeF6]³- ion respectively, are:
(a) 0 Δ and 5.9 BM
(b) 0 Δ and 1.73 BM
(c) 2.0 Δ and 5.9 BM
(d) 2.0 Δ and 1.73 BM (NEET 2024)
Ans: (a)
For the complex [FeF₆]³⁻:
Oxidation State of Fe: In [FeF₆]³⁻, iron is in the +3 oxidation state. The electronic configuration of Fe³⁺ is d⁵ (since Fe has an atomic number of 26, so Fe³⁺ has 23 electrons, and the electron configuration is [Ar] 3d⁵).
Geometry: The complex has an octahedral geometry due to the six fluoride ligands (F⁻).
Crystal Field Splitting: For octahedral complexes, the d-orbitals split into two energy levels: eg (higher energy) and t₂g (lower energy). The d⁵ configuration of Fe³⁺ results in high spin because fluoride is a weak field ligand (does not induce pairing of electrons).
Therefore, in an octahedral field:
- 5 d-electrons will occupy the t₂g and eg orbitals in a high-spin configuration, leading to five unpaired electrons.
- Crystal Field Stabilisation Energy (CFSE): For high-spin complexes, the CFSE is 0 because the electrons are distributed equally in both the eg and t₂g orbitals, and no extra stabilization occurs due to pairing of electrons.
- Magnetic Moment: The magnetic moment is calculated using the formula:
μ = √(n(n + 2)) BM, where n is the number of unpaired electrons.
For 5 unpaired electrons:
μ = √(5(5 + 2)) = √35 ≈ 5.92 BM.
Thus, the CFSE is 0 Δ, and the magnetic moment is approximately 5.9 BM.Therefore, the correct answer is (a).
Q7: Ethylene diaminetetraacetate ion is a/an: (NEET 2024)
(a) Hexadentate ligand
(b) Ambidentate ligand
(c) Monodentate ligand
(d) Bidentate ligand
Ans: (a)
Ethylene diamine tetraacetate (EDTA) is a hexadentate ligand, meaning it can form six bonds with a central metal ion. It has four acetate groups (each with two oxygen atoms that can donate electrons) and two amine groups (each nitrogen atom can donate electrons), making a total of six donor sites. Therefore, EDTA forms six bonds with a metal ion, making it a hexadentate ligand.
Q8: Which of the following is not an ambidentate ligand? (NEET 2024)
(a) C2O4²-
(b) SCN-
(c) NO2-
(d) CN-
Ans: (a)
Ambidentate ligands are ligands that can coordinate to a metal through two different atoms.
- C₂O₄²⁻ (Oxalate): The oxalate ion can act as a bidentate ligand, meaning it can coordinate through both oxygen atoms. It does not have two different types of donor atoms, so it is not ambidentate.
- SCN⁻ (Thiocyanate): This is an ambidentate ligand because it can coordinate through either the sulfur (S) atom or the nitrogen (N) atom, giving two different donor sites.
- NO₂⁻ (Nitrite): This is also an ambidentate ligand because it can coordinate through either the nitrogen (N) atom or the oxygen (O) atom.
- CN⁻ (Cyanide): Cyanide is typically considered a monodentate ligand, coordinating through the carbon (C) atom, but it is sometimes considered ambidentate in certain cases where it can bind through both C and N. However, in most contexts, it is treated as a monodentate ligand.
Therefore, C₂O₄²⁻ (oxalate) is not an ambidentate ligand, as it only coordinates through oxygen atoms. Hence, the correct answer is (a).
Q9: Identify the structural features common to [Mn₂(CO)₁₀] and [Co₂(CO)₈]: (NEET 2024)
A. Presence of a metal-metal bond
B. Presence of terminal carbonyl groups
C. Presence of bridging carbonyl groups
D. Metals in the zero oxidation state
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A, B and C
(b) Only B, C and D
(c) Only A, C and D
(d) Only A, B and D
Ans: (d)
- A. Presence of a metal-metal bond: Both [Mn₂(CO)₁₀] and [Co₂(CO)₈] contain a metal-metal bond. In these complexes, the metal atoms are connected by a direct bond. This is a common feature of such dimetallic carbonyl complexes.
- B. Presence of terminal carbonyl groups: Both complexes also feature terminal CO groups, which are directly bonded to the metal atoms. This is a characteristic of carbonyl complexes.
- C. Presence of bridging carbonyl groups: This is not true for both complexes. While [Co₂(CO)₈] does have bridging carbonyl groups, [Mn₂(CO)₁₀] does not; instead, it only contains terminal CO groups.
- D. Metals in the zero oxidation state: In both [Mn₂(CO)₁₀] and [Co₂(CO)₈], the metals are in the zero oxidation state. This is typical for many metal carbonyl complexes.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Only A, B and D.
2023
Q1: Homoleptic complex from the following complexes is (NEET 2023)
(a) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(b) Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
(c) Pentaamminecarbonatocobalt (III) chloride
(d) Triamminetriaquachromium (III) chloride
Ans: (a)
- Complexes in which a metal is bound to only one kind of donor groups are called as homoleptic complexes
- Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
K3[Al(ox)3]
It is a homoleptic complex
Q2: Which complex compound is most stable? (NEET 2023)
(a) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Br]NO3)2
(b) [Co(NH3)3(NO3)3]
(c) [CoCl2(en)2]NO3
(d) [Co(NH3)6] 2(SO4)3
Ans: (c)
Chelating ligands in general form more stable complexes than their monodentate analogs
∴ The most stable complex is
[CoCl2(en)2]NO3
Q3: Which of the following sets represents a complex and a double salt, respectively? (NEET 2023)
(a) CuSO₄·5H₂O and CuCl₂·4NH₃
(b) PtCl₂·2NH₃ and PtCl₄·2HCl
(c) K₂PtCl₂·2NH₃ and KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O
(d) NiCl₂·6H₂O and NiCl₂(H₂O)₄
Ans: (c)
Complex: A complex consists of a central metal ion bonded to surrounding ligands (ions or molecules). The metal ion typically has coordination bonds with the ligands, and the bonding can be strong and involve more than one ion or molecule.
K₂PtCl₆·2NH₃ is a complex because Pt²⁺ is surrounded by Cl⁻ and NH₃ ligands, forming a coordination complex.
Double Salt: A double salt is a solid that contains two different salts which are crystallized together. In a double salt, the ions remain in their original ionic form and do not form coordination bonds as in a complex.
KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O is a double salt (commonly known as potash alum) because it consists of potassium and aluminum salts crystallized together with water of hydration.
Thus, (c) K₂PtCl₆·2NH₃ is a complex, and KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O is a double salt. Therefore, (c) is the correct answer.
Q4: Type of isomerism exhibited by compounds (NEET 2023)
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3, [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O,
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O and the value of coordination number (CN) of central metal ion in all these compounds, respectively, is:
(a) Geometrical isomerism, CN = 2
(b) Optical isomerism, CN = 4
(c) Ionisation isomerism, CN = 4
(d) Solvate isomerism, CN = 6
Ans: (d)
Coordination Number (CN): The coordination number refers to the number of bonds formed between the central metal ion and the ligands.
In all of the given compounds:
- [Cr(H₂O)₆]Cl₃: The central metal ion Cr³⁺ is coordinated with six H₂O molecules, so the coordination number (CN) is 6.
- [Cr(H₂O)₅Cl]Cl₂·H₂O: The central metal ion Cr³⁺ is coordinated with five H₂O molecules and one Cl ion, giving a coordination number of 6.
- [Cr(H₂O)₄Cl₂]Cl·2H₂O: The central metal ion Cr³⁺ is coordinated with four H₂O molecules and two Cl ions, again resulting in a coordination number of 6.
Therefore, the coordination number in all these complexes is 6.
Type of Isomerism:
The given compounds exhibit solvate isomerism. Solvate isomerism occurs when the solvent molecules in the crystal structure can be exchanged or replaced by other solvent molecules (such as water in this case). For example, in [Cr(H₂O)₅Cl]Cl₂·H₂O, water molecules are present as both ligands and crystallization water, and different arrangements of the water molecules lead to different isomers.
Thus, these compounds exhibit solvate isomerism with a coordination number of 6.
Hence, the correct answer is (d) Solvate isomerism, CN = 6.
2022
Q1: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
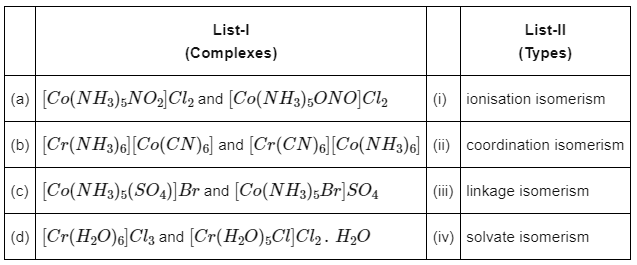
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (a)-(iv), (b)-(iii), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i)
(b) (a)-(iii), (b)-(i), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iv)
(c) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
(d) (a)-(iii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iv)
Ans: (d)
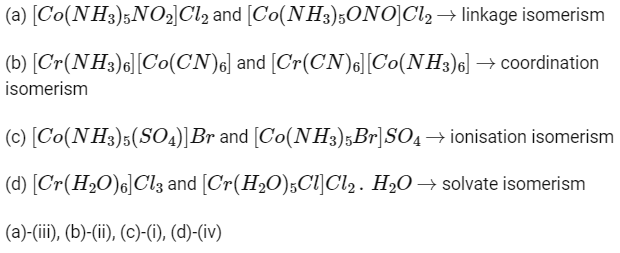
Q2: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : The metal carbon bond in metal carbonyls possesses both σ and π character.
Reason (R) : The ligand to metal bond is a π bond and metal to ligand bond is a σ bond.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (d)
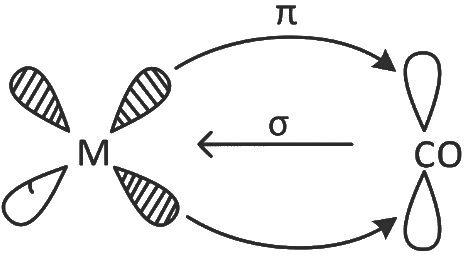
In case of metal carbonyls, the bonding has both σ and π nature, where ligand to metal bond is 'σ ' (coordinate) bond and metal to ligand bond is 'π' (synergic) bond.
Q3: The IUPAC name of the complex- [Ag(H2O)2][Ag(CN)2] is: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) dicyanidosilver(I) diaquaargentate(I)
(b) diaquasilver(I) dicyanidoargentate(I)
(c) dicyanidosilver(II) diaquaargentate(II)
(d) diaquasilver(II) dicyanidoargentate(II)
Ans: (b)
[Ag(H2O)2][Ag(CN)2]
IUPAC name : diaquasilver(I) dicyanidoargentate(I)
Q4: The order of energy absorbed which is responsible for the color of complexes (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(A) [Ni(H2O)2(en)2]2+
(B) [Ni(H2O)4(en)2]2+
(C) [Ni(en)3]2+
(a) (C) > (A) > (B)
(b) (B) > (A) > (C)
(c) (A) > (B) > (C)
(d) (C) > (B) > (A)
Ans: (a)
Stronger the field strength of ligand, higher will be the energy absorbed by the complex.
'en' has a stronger field strength than 'H2O' according to spectrochemical series
Correct order of energy absorbed will be :
[Ni(en)3]2+ > [Ni(H2O)2(en)2]2+ > [Ni(H2O)4(en)]2+
i.e. (C) > (A) > (B)
2021
Q1: Ethylene diaminetetraacetate (EDTA) ion is: (NEET 2021)
(a) Bidentate ligand with two "N" donor atoms
(b) Tridentate ligand with three "N" donor
(c) Hexadentate ligand with four "O" and two atoms "N'' donor atoms
(d) Unidentate ligand
Ans: (c)
Ethylene diaminetetraacetate (EDTA) ion is a hexadentate ligand having four donor oxygen atoms and two donor nitrogen atoms
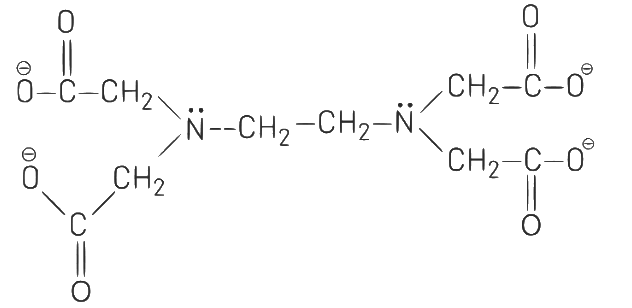
Q2: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2021)

Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (a)-(iv), (b)-(i), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iii)
(b) (a)-(iv), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
(c) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(iii), (d)-(i)
(d) (a)-(i), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(ii)
Ans: (c)
Magnetic moment, 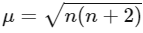 BM (where n = number of unpaired electrons)
BM (where n = number of unpaired electrons)
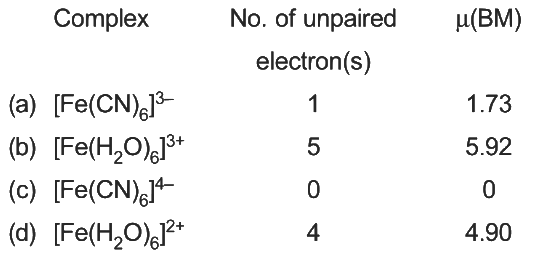
2020
Q1: The calculated spin only magnetic moment of Cr2+ ion is? (NEET 2020)
(a) 4.90 BM
(b) 5.92 BM
(c) 2.84 BM
(d) 3.87 BM
Ans: (a)
Electronic configuration of 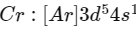
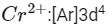
No. of unpaired electrons = 4
Spin only magnetic moment = 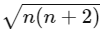
n = number of unpaired e-
Spin only magnetic moment = 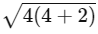
= √24
= 4.9 BM
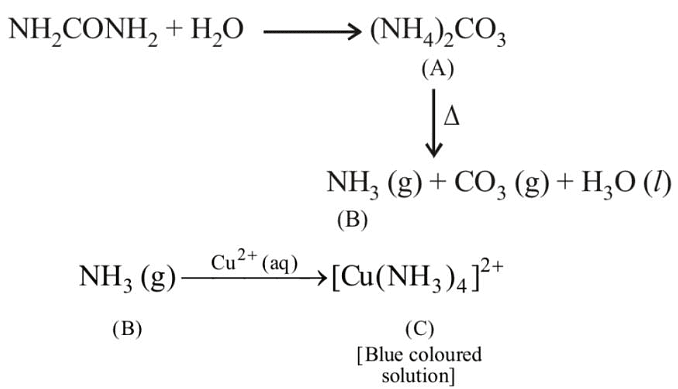
Q2: Urea reacts with water to form A which will decompose to form B. B when passed through Cu2+ (aq), deep blue colour solution C is formed. What is the formula of C from the following?
(a) 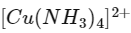
(b) 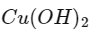
(c) 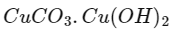
(d) 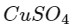
Ans: (a)
Q3: Which of the following is the correct order of increasing field strength of ligands to form coordination compounds? (NEET 2020)
(a) 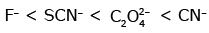
(b) 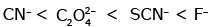
(c)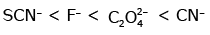
(d)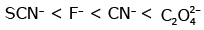
Ans: (c)
Fact from spectrochemical series.
2019
Q8. What is the correct electronic configuration of the central atom in K4[Fe(CN)6] based on crystal field theory? (NEET 2019)
(a)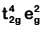
(b)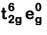
(c)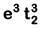
(d)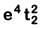
Ans: (b)
K4[Fe(CN)6]
Fe ground state: [Ar]3d64s2
Fe2+: 3d64s0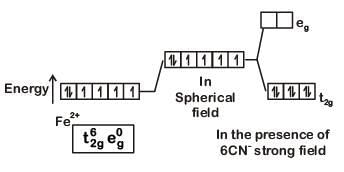
2018
Q1: The geometry and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4] are (NEET 2018)
(a) square planar geometry and diamagnetic
(b) tetrahedral geometry and diamagnetic
(c) square planar geometry and paramagnetic
(d) tetrahedral geometry and paramagnetic
Ans: (b)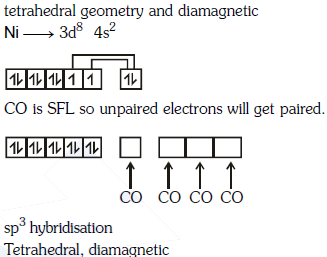
Q2: Iron carbonyl, Fe(CO)5 is (NEET 2018)
(a) Tetranuclear
(b) Mononuclear
(c) Trinuclear
(d) Dinuclear
Ans: (b)
Based on the number of metal atoms present in a complex, they are classified into mononuclear, dinuclear, trinuclear and so on. e.g. :
Fe(CO)5 : mononuclear
Co2(CO)8 : dinuclear
Fe3(CO)12 : trinuclear
Q3: The type of isomerism shown by the complex [CoCl2(en)2] is (NEET 2018)
(a) Geometrical isomerism
(b) Coordination isomerism
(c) Ionization isomerism
(d) Linkage isomerism
Ans: (a)
[CoCl2(en)2] shows geometrical isomerism and exist in cis and trans form. 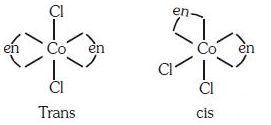
2017
Q1: An example of a sigma bonded organometallic compound is : (NEET 2017)
(a) Grignard's reagent
(b) Ferrocene
(c) Cobaltocene
(d) Ruthenocene
Ans: (a)
Grignard's reagent is an organometallic compound in which carbon atom is bonded to metal ion with sigma bond while in ruthenocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene are the organo metallic compounds in which carbon atom is attached to metal ion through π-bonding.
Q2: The correct order of the stoichiometries of AgCl formed when AgNO3 in excess is treated with the complexes : CoCl3.6NH3, CoCl3.5NH3,CoCl3.4NH3 respectively is :- (NEET 2017)
(a)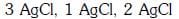
(b)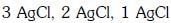
(c)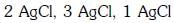
(d)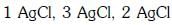
Ans: B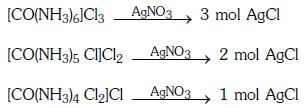
Q3: Correct increasing order for the wavelengths of absorption in the visible region the complexes of Co3+ is :- (NEET 2017)
(a)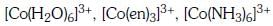
(b)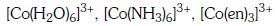
(c)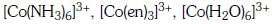
(d)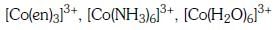
Ans: D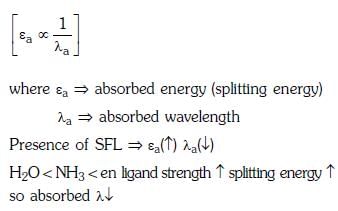
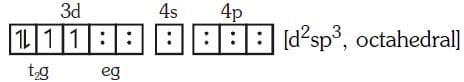
Q4: Pick out the correct statement with respect to[Mn(CN)6]3–:- (NEET 2017)
(a) It is sp3d2 hybridised and tetrahedral
(b) It is d2sp3 hybridised and octahedral
(c) It is dsp2 hybridised and square planar
(d) It is sp3d2 hybridised and octahedral
Ans: B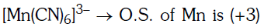
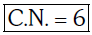
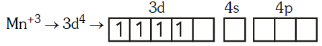
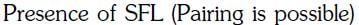
2016
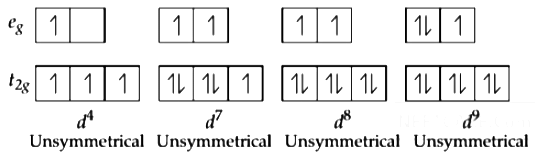
Q1: Jahn-Teller effect is not observed in high spin complexes of (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) d7
(b) d8
(c) d4
(d) d9
Ans: (b)
- Jahn-Teller distortion is generally significant for asymmetrically occupied eg orbitals as they are directed towards the ligands and the energy gain is more.
- On the other hand in unevenly occupied t2g orbitals, the Jahn-Teller distortion is very weak. Since the t2g orbitals does not point directly at the ligand and thus energy gain is less.
Q2: The correct increasing order of trans-effect of the following species is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 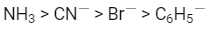
(b) 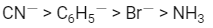
(d) 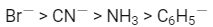
(d) 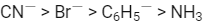
Ans: (b)
The intensity of the trans-effect as measured by the increase in rate of substitution of the trans ligand) follows the sequence :
CN
Q3: Which of the following has longest C-O bond length ? (Free C-O bond length in CO is 1.128Å) (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) [Mn(CO)6]+
(b) Ni(CO)4
(c) [Co(CO)4]-
(d) [Fe(CO)4]2-
Ans: (d)
The greater the negative charge on the carbonyl complex, the more easy it would be for the metal to permit its electrons to participate in the back bonding, the higher would be the M-C bond order and simultaneously there would be larger reduction in the C-O bond order. Thus, [Fe(CO)4]2- has the lowest C-O bond order means the longest bond length.
2015
Q1: Which of these statements about [Co(CN)6]3- is true ? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) [Co(CN)6]3- has no unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configuration
(b) [Co(CN)6]3- has no unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration
(c) [Co(CN)6]3- has four unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration.
(d) [Co(CN)6]3- has four unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configuration
Ans: (b)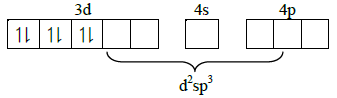
[Co(CN)6]3- has no unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration.
Q2: Cobalt(III) chloride forms several octahedral complexes with ammonia. Which of the following will not give test for chloride ions with silver nitrate at 25°C ? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) CoCl3.6NH3
(b) CoCl3.3NH3
(c) CoCl3.4NH3
(d) CoCl3.5NH3
Ans: (b)
a) [Co(NH3)3Cl3] → [Co(NH3)2Cl3]
b) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl → [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ +Cl-
c) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 → [Co(NH3)5Cl]+ +2Cl-
d) [Co(NH3)6Cl]Cl2 → [Co(NH3)6]+ +3Cl-
The compound (a) does not ionise So it does not give test for chloride ions.
2014
Q1: Among the following complexes the one which shows Zero crystal field stabilization energy (NEET 2014)
(CFSE) is :
(a) [Co(H2O)6]2+
(b) [Co(H2O)6]3+
(c) [Mn(H2O)6]3+
(d) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
Ans: D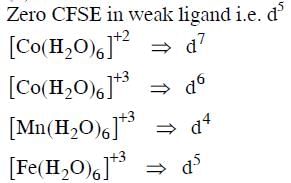
Q2: Which of the following complexes is used to be as an anticancer agent? (NEET 2014)
A: cis − K2 [Pt Cl2 Br2]
(b) Na2CoCl4
(c) mer − [Co (NH3)3Cl3]
(d) cis − [Pt Cl2 (NH3)2]
Ans: D
cis-platin is known as an anticancer agent. The formula for cis-platin is cis-[PtCl2(NH3)2]. Here, the word cis refers to a cis geometrical isomer of [PtCl2(NH3)2].
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Coordination Compounds - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are coordination compounds in chemistry? |  |
| 2. How do ligands coordinate with metal ions in coordination compounds? |  |
| 3. What is the coordination number of a metal ion in a coordination compound? |  |
| 4. How do coordination compounds exhibit different colors? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between coordination isomerism and linkage isomerism in coordination compounds? |  |






















