Maps Summary Class 6 Social Science Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction of the Chapter: |

|
| Direction |

|
| Symbols |

|
| Sketch |

|
| Plan |

|
| Conclusion of the Chapter: |

|
Introduction of the Chapter:
This Class 6 NCERT chapter "Maps" begins by revisiting the advantages of using a globe and highlights its limitations, particularly when focusing on specific regions.
- It introduces maps as crucial tools for detailed exploration and understanding of localized areas, such as countries, states, districts, towns, and villages.
- The chapter emphasizes the representation of the Earth's surface on a flat medium, introducing the concept of scale in map drawing.
Let's have a look at Summary of this NCERT Chapter in the document:
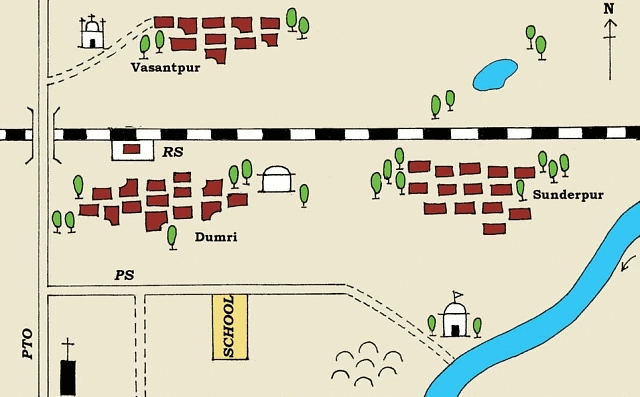 Sunderpur village and its surrounding areas
Sunderpur village and its surrounding areas
Types of Maps
The chapter categorizes maps into three main types based on their focus and content:
Physical Maps
These maps spotlight the natural features of the Earth, including mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, and oceans. Referred to as physical or relief maps, they contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the Earth's topography.
Political Maps
Political maps illustrate cities, towns, villages, countries, and states worldwide, marking their boundaries. These maps are essential for understanding political and administrative divisions.
Thematic Maps
Thematic maps concentrate on specific information, such as road networks, rainfall patterns, and the distribution of forests and industries. Titles are assigned based on the information provided in these maps.
Components of Maps
There are three Components of Maps – distance, direction and symbol.
Distance
- Maps are two-dimensional drawings. It reduces the entire world or a part of the world on a small sheet of paper. While making a map, cartographers pay attention to properly represent the distance between two places. This helps us in finding the actual distance between two places.
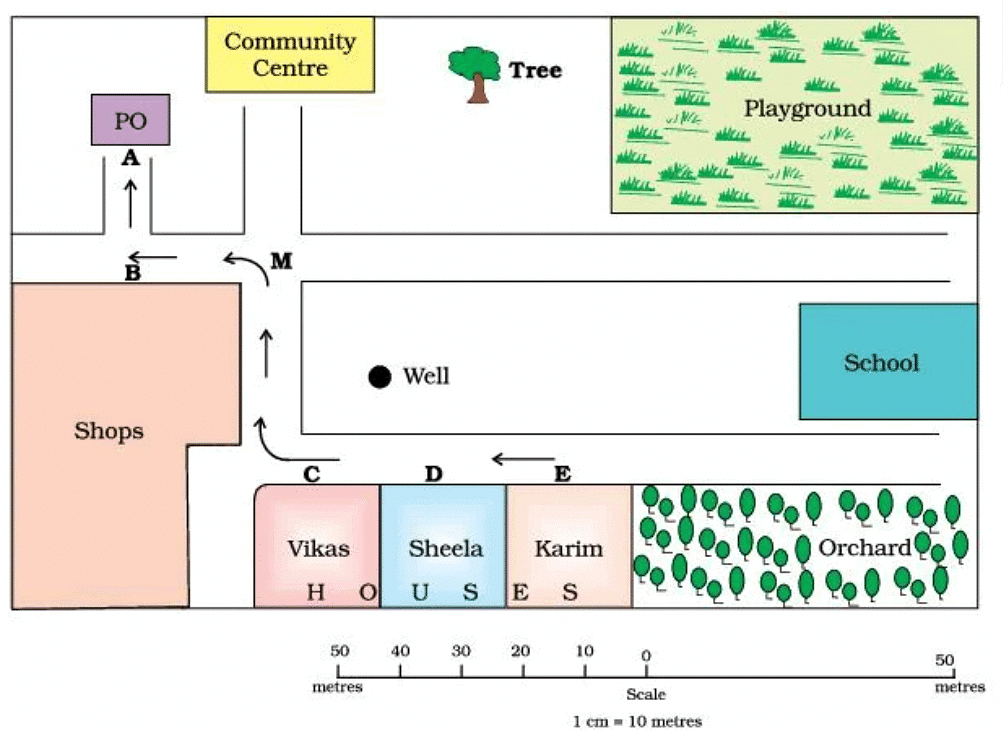 Map of A Village
Map of A Village
- Small Scale Map: When a large area is shown on a small map, such a map is called a small scale map. Example; map of a country or state.
- Large Scale Map: When a small area such as a village is shown on a map, such a map is called a large scale map. A map of a neighbourhood is another example of large scale map. A large scale map gives more details compared to a small scale map.
Direction
- A map also contains information about directions.
- Arrow Direction: On most of the maps, you will usually see an upward arrow and the letter ‘N’. This shows the north direction.
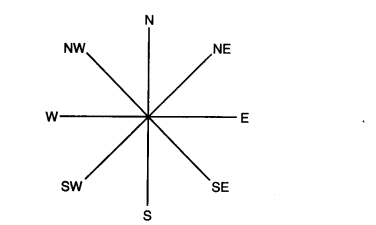
- Cardinal Points: Once we know the north, we can easily find the other directions. North, South, East and West are the four major directions. These are called Cardinal Directions.
 Cardinal Directions
Cardinal Directions
- Intermediate Directions: Some maps also show the intermediate directions, viz. north-east, south-east, south-west and north-west.
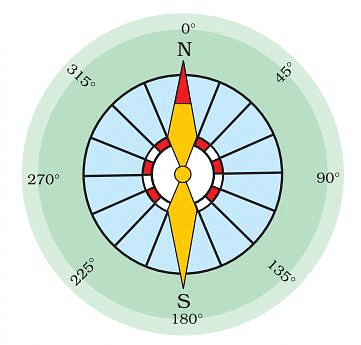
Compass
- Compass is very useful for finding directions at a place.
 A Compass
A Compass - This is a small circular box with a magnetic needle inside.
- The needle of the compass always points in the north-south direction.
- Compass has been used by travellers and sailors since ages.
Symbols
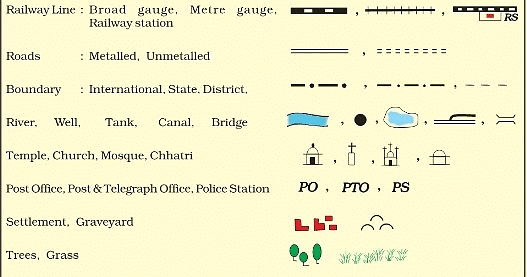
- Importance: Cartographers also need to show various details; like important structures, landmarks, etc. on a map. These things are shown by some standard symbols on the map.
 Conventional Symbols
Conventional Symbols - Conventional Symbols: Conventional Symbols, internationally agreed upon, are employed to depict elements such as mountains, rivers, roads, waterways, etc., ensuring uniformity and consistency across maps.
- Colours in Maps: While using colours to show different themes and items on a map; certain conventions are followed. Mountains are usually shown in brown colour, plains in green, water body in blue and plateau is shown in yellow.
Sketch
- A drawing based on memory is called a sketch. A sketch is not made to scale.
- A sketch map is useful when you need to show directions to your house to your friend.
Plan
- Drawing of a small area on a large scale is called a plan.
- Architects usually make plans to show the layout of a house.
- Helpful when specific details like room dimensions are required.
Conclusion of the Chapter:
The chapter concludes by emphasizing the significance of maps as tools for effective communication and navigation. Understanding the components of maps, including types, distance, direction, and symbols, equips individuals with valuable skills for interpreting geographical information accurately.
|
69 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Maps Summary Class 6 Social Science Chapter 4
| 1. What are the different types of maps? |  |
| 2. How do distance and direction play a role in map reading? |  |
| 3. What are symbols in maps and why are they important? |  |
| 4. How do sketches and plans differ from traditional maps? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of understanding maps in daily life? |  |