Class 11 Economics Short Questions With Answers - Theory Of Consumer Behaviour
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define utility.
Ans: Utility is the measure of satisfaction, value, or benefit that a consumer gains from consuming goods and services. For example, if a person gains a high level of satisfaction from drinking a cup of coffee, this consumption has high utility for them.
Q2. Define Marginal Utility.
Ans: Marginal Utility (MU) is the additional utility derived from consuming one more unit of a commodity. It can be denoted as:
MUn = TUn — TUn-1
Where MU is the marginal utility and TU is the total utility. For example, if eating one slice of pizza gives you 10 units of satisfaction, and a second slice gives you 8 more units of satisfaction, the marginal utility of the second slice is 8.
Q3: What is Total Utility?
Ans: Total Utility is the total psychological satisfaction derived by a consumer from the consumption of total units of a good.
TUn= MU1 + MU2 + MU3 + MUn— ∑MU
For instance, if eating the first slice of pizza gives 10 units of satisfaction and the second slice gives an additional 8 units, then the total utility after consuming two slices would be 18 units (10 + 8).
Q4: How are TU and MU related to each other?
Ans: The relationship between TU and MU is as below
- Total Utility is the summation of Marginal Utility derived from each unit, that is, TU = ∑MU
- TU increases so long as MU is positive.
- When MU is zero, TU is maximum.
- When MU is negative, TU starts decreasing.
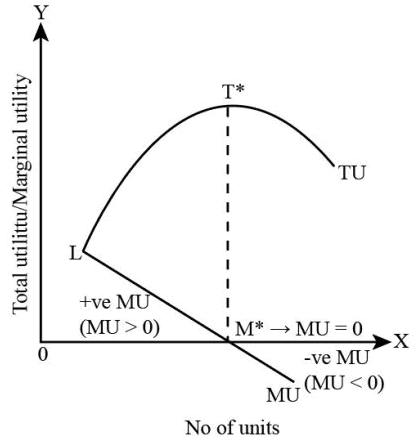
Q5: How is Marginal Utility derived from Total Utility?
Ans: Marginal Utility (MU) is derived from Total Utility (TU) by measuring the change in total utility that results from consuming an additional unit of a good or service.
MUn = TUn - TUn-1
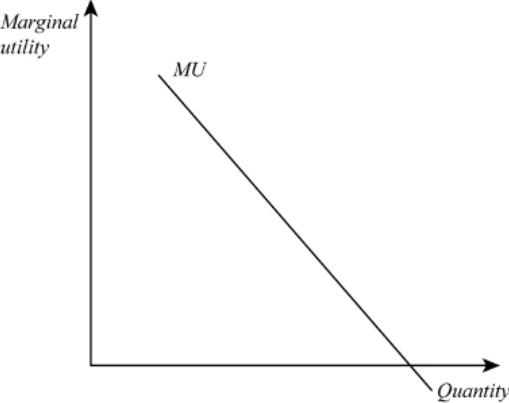
Q6: State the shape of the Marginal Utility curve.
Ans: The marginal utility curve slopes downwards from left to right.
Q7: Is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility applicable in the case of money?
Ans: Yes, the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility applies to money too. This law means that the more of something you get, the less extra satisfaction you feel from each new unit. If someone has very little money, each extra rupee is very valuable because it can help buy essential things like food or shelter. As they get more money, each extra rupee becomes less important since their basic needs are already met, and extra rupees are likely spent on non-essential things.
Q8: Describe the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility.
Ans: The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility states that the amount of good 2 that the consumer is willing to give up for an additional unit of good 1 diminishes as the amount of good 1 increases. When consumers continuously consume units of a good, their Total Utility increases, but it increases at a diminishing rate.
Q9: Explain the difference between cardinal utility and ordinal utility.
Ans: The following are the points of different cardinal utility and ordinal utility: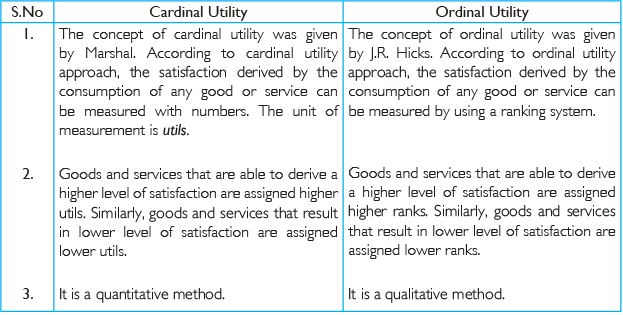
Q10: Describe the Law of Equi-Marginal Utility.
Ans: When a consumer consumes only two commodities (X and Y), his or her equilibrium is determined in accordance with the law of Equi-Marginal Utility. The consumer will allocate his or her money income between two goods in such a way that he or she gets equal Marginal Utility in terms of money from both goods. Thus, the consumer will be in equilibrium when the ratio of the Marginal Utility of good X to the price of X is equal to the ratio of the Marginal Utility of good Y to the price of Y.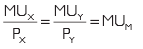
Q11: What is the budget set? Explain what can lead to a change in the budget set.
Ans: The budget set includes all the possible bundles of two goods (commodities) that a consumer- can afford to buy with his or her income at the prevailing market prices. The budget set depends on the income of the consumer and the prices of the goods and services. Accordingly, a budget set will change under the following conditions:
- Change in the money income of the consumer
- Change in the price of any of the goods
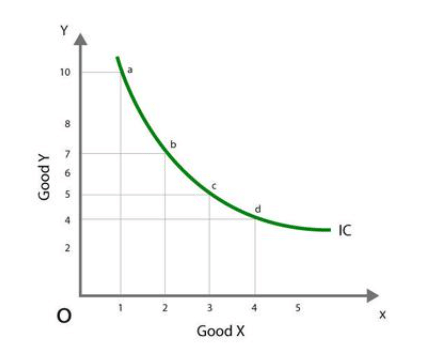
Q12: Define an indifference curve.
Ans: An indifference curve is a locus of all the points representing a combination of two goods among which the consumer is indifferent.
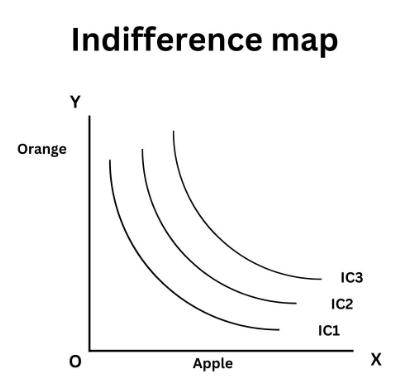
Q13: Define the indifference map.
Ans: The indifference map is a graph that represents a group of indifference curves, each of them representing a given level of satisfaction.
Q14: What is meant by monotonic preference?
Ans: Consumer preferences are said to be monotonic if he or she chooses a bundle, which gives more of either both the goods or at least one good without reducing the quantity of the other.
Q15: What is the Marginal Rate of Substitution?
Ans: The Marginal Rate of Substitution measures the rate at which the consumer is just willing to substitute one good for the other, maintaining the same level of satisfaction.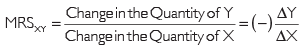
Q16: Describe the properties of the indifference curve.
Ans: The following are the properties of the indifference curve
- The indifference curve slopes downwards from left to right
- The indifference curve is convex to the origin.
- Two indifference curves never intersect each other.
- A higher indifference curve represents a higher level of satisfaction.
- Indifference curves need not be parallel to each other.
Q17: Describe the assumptions of the indifference curve.
Ans: The following are the main assumptions of indifference curve analysis
- The consumer is rational as he wants to maximize his satisfaction with his limited income.
- The consumer consumes only two commodities.
- There is an ordinal measurement of utility, that is, utility is expressed in ranks
- There is a diminishing Marginal Rate of Substitution.
- There is a non-satiety of the consumer.
- The consumer is consistent and transitive in selection.
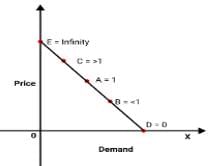
Q18: Explain the five degrees of elasticity of demand.
Ans:
- Perfectly inelastic demand: - Even with a change in price, there is no change in the quantity demanded, the demand is said to be perfectly inelastic Ed =0. The demand curve is parallel to OY axis.
- Perfectly elastic demand:- Even with no change in price there is a great change in quantity demanded, then the demand is said to be perfectly elastic. The demand curve is parallel to OX axis.
- Unitary elastic demand: When proportionate change in quantity demanded is equal to proportionate change in price, Ed is equal to unity. The demand curve resembles a rectangular hyperbola.
- Relatively less elastic: When a proportionate change in quantity demanded is less than the proportionate change in price, Ed is less than unity.
- Relatively more elastic: When a proportionate change in quantity demanded is more than a proportionate change in price, Ed is greater than unity.
Q19: Explain any four factors that affect the elasticity of demand.
Ans: The following are the factors affecting the price elasticity of demand:
- Availability of close substitutes: If close substitutes of products are available, the commodity tends to be more elastic, If they are not available, they tend to be less elastic.
- The proportion of total expenditure spent on the product: If the amount spent on a product constitutes a very small fraction of the total expenditure, then the demand tends to be less elastic if the amount spent is high the elasticity of demand tends to be high.
- Habits: A commodity if it forms an essential part of the individual, the demand tends to be inelastic. It is consumed casually; the demand tends to be elastic.
- Time period: The longer the time period, the more elastic the demand for any product the shorter the time period, the less elastic the demand for any products.
Q20: What is meant by consumer’s equilibrium? State its conditions in the case of the two commodities approach.
Ans:
1. Meaning: A consumer is to be at equilibrium when he is spending his given income on various goods and services to get maximum satisfaction.
2. Conditions:
i. MUx / Px = MUy / Py (MUs are equal to their prices)
ii. PxQx+ PyQy =M (Money spent is equal to income)
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. How is equilibrium achieved with the help of indifference curve analysis?
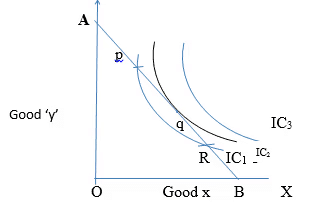
Ans :- a) In the indifference curve approach, consumer’s equilibrium is achieved at the point at which the budget line is tangent to a particular indifference curve. This is the point of maximum satisfaction.
b) Diagram:
 c) Explanation of the diagram:
c) Explanation of the diagram:
i) ‘AB’ is the budget line.
ii) It is sure that consumer’s equilibrium will lie on some point on ‘AB’
iii) Indifference map (set of IC1, IC2 , IC3) shows consumers scale of preferences between different combinations of good ‘x’ and good ‘y’
iv) Consumers’ equilibrium will achieve where budget line (AB) is tangent to the IC2.
d) Essential conditions for consumers equilibrium:
i) Budget line must be tangent to indifference curve i.e., MRS xy = Px / Py
ii) Indifference curve must be convex to the origin or MRS xy should decrease.
e) Consumers cannot achieve the following:
i) P and R points on budget line give satisfaction but they lie on lower indifference curve IC1. Choosing point ‘q’ puts him on a higher IC which gives more satisfaction.
ii) He cannot move on IC3, as it is beyond his money income.
Q.2. Explain the factors affecting the market demand of a commodity.
Ans :- i) Market demand is the aggregates of the quantities demanded by all the consumers in the market at different prices.
ii) Factors affecting market demand :
- Price of the commodity: When the price goes up demand for its falls and vice-versa.
- Income of the consumers: When the income of the consumers goes up the demand for a commodity also goes up.
- Price of related goods :
a. Complementary goods :The demand for a commodity rises with a fall in the price of its complementary good (Car and petrol)
b. Substitute goods: Demand for a commodity falls with a fall in the price of other substitute good (Tea & Coffee). - Tastes and preferences: Any favourable change in consumers’ tastes will lead to increase in market demand and any unfavourable change in consumers tastes will lead to decrease in market demand.
- Consumer’s group: More the consumers more will be market demand and vice-versa.
Q.3. Explain the various degrees of price elasticity of demand with the help of diagrams.
Ans: There are five degrees of price elasticity of demand. They are,
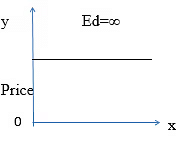
- Perfectly elastic demand (Ed=∞): a slight or no change in the price leads to infinite changes in the quantity demanded.
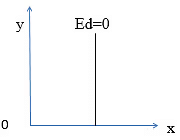
- Perfectly Inelastic demand (Ed=0) : Demand of a commodity does not change at all irrespective of any change in its price.
- Unitary elastic demand (Ed=1): When the percentage change in demand (%) of a commodity is equal to the percentage change in price.
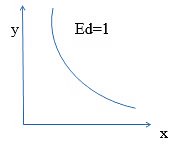
- Greater than unitary elastic demand (Ed>1): When percentage change in demand of a commodity is more than the percentage change in its price.
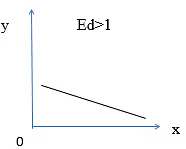
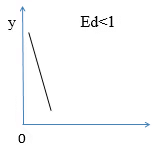
- Less than unitary elastic demand (Ed<1) : When percentage change in demand of a commodity is less than the percentage change in its price.
Q4. How is equilibrium achieved with the help of indifference curve analysis?
Ans: When a consumer gets the maximum satisfaction from their spending, they are considered to be in equilibrium. This is known as "consumer's equilibrium." It means the consumer has reached the highest level of satisfaction they can get based on their income and the prices of goods. The indifference curve technique helps explain this consumer equilibrium.
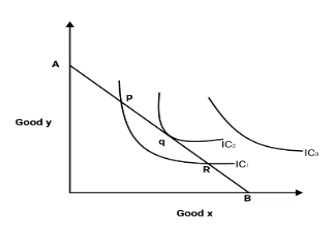
Explanation:
- Budget Line (AB): The budget line is represented by AB.
- Consumer's Equilibrium Position: The consumer's equilibrium will always be at the same position on AB.
- Indifference Map (IC1, IC2, and IC3): The indifference map shows the consumer's preferences for different combinations of goods x and y.
- Equilibrium Achievement: Consumers reach equilibrium when the budget line (AB) is tangent to the indifference curve IC2.
Assumptions for Consumer's Equilibrium:
- Rationality: The consumer is logical and seeks maximum satisfaction given their money and prices.
- Ordinal Utility: The consumer can rank their preferences based on how satisfied different product combinations make them.
- Choice Consistency: The consumer makes consistent choices.
- Perfect Competition: The market where the consumer buys the goods is perfectly competitive.
- Total Utility: The consumer's total utility depends on the quantity of goods consumed.
Q5. What are the methods of measuring price elasticity of demand?
Ans: The methods of measuring price elasticity of demand include the following:
Proportionate or Percentage Method:
- This method calculates elasticity as the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price.
- Formula:
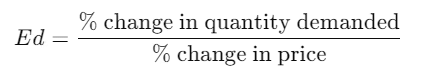
OR
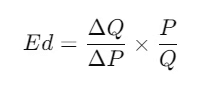
Example: If the price of a product increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 20%, the price elasticity of demand is calculated as follows:
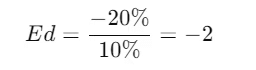
This means the demand is elastic.
Total Outlay Method:
- This method looks at how total spending changes as prices change.
- If total spending increases when prices fall, elasticity is greater than one.
- If total spending remains constant when prices change, elasticity is equal to one.
- If total spending decreases when prices fall, elasticity is less than one.
Example: If the price of a product decreases from $10 to $8 and the total spending increases from $1000 to $1200, then the elasticity of demand is greater than one, indicating elastic demand.
Geometric or Point Method:
- This method measures elasticity at different points along the demand curve.
- Formula:

Example: Suppose a demand curve has a price of $5 at the upper segment and $3 at the lower segment, and the quantity demanded changes from 50 to 70 units. Using the formula:
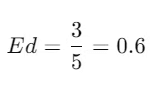
This indicates inelastic demand at this specific point on the demand curve.
These methods help in understanding how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.
Q6. Describe any four factors that affect a commodity’s demand.
Ans: The factors that influence the demand for a commodity include:
Commodity Price (Px):
- The price of a commodity is a major factor affecting its demand. Generally, if the price of a commodity increases, the demand for it decreases, and if the price decreases, the demand increases. This inverse relationship means that consumers tend to buy less of a product when its price goes up and more when its price goes down.
Consumer Income (Y):
- Another important factor affecting demand is consumer income. When consumers have higher income, they tend to buy more goods, increasing the demand for everyday items. Conversely, when income levels drop, the demand for these items decreases. This shows a direct relationship between income and demand.
Price of Related Goods:
- The demand for a commodity is also influenced by the prices of related goods, which include substitute goods and complementary goods.
- Substitute Goods: These are products that can replace each other, like tea and coffee. If the price of tea rises, people might buy more coffee instead, even if the price of coffee remains the same. This positive relationship means that an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for its substitute.
- Complementary Goods: These are products used together, like cars and gasoline. If the price of gasoline increases, the demand for cars might decrease because using the car becomes more expensive. This negative relationship means that an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the demand for its complement.
Tastes and Preferences:
- Changes in consumer tastes and preferences, influenced by factors like fashion, culture, and traditions, significantly affect the demand for commodities. If a product becomes more popular or fashionable, its demand increases. Conversely, if consumer preferences shift away from a product, its demand decreases. Therefore, a commodity’s demand is closely tied to the tastes and preferences of consumers.
Q.7. A consumer buys 50 units of a good at Rs. 4/- per unit. When its price falls by 25 percent its demand rises to 100 units. Find out the price elasticity of demand.
Ans:- Ed=4
Initial Price (P0)=Rs.4
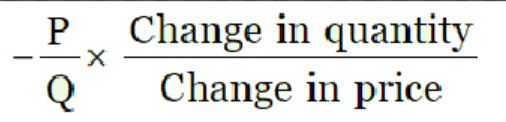
Q.8. Price elasticity of demand for wheat is equal to unity and a household demands 40 Kg of wheat when the price is Rs.1 per kg. At what price will the household demand 36 kg of wheat?
Ans: 
Q.9. The quantity demanded of a commodity at a price of Rs.10 per unit is 40 units. Its price elasticity of demand is -2. Its price falls by Rs.2/- per unit. Calculate its quantity demanded at the new price.
Ans :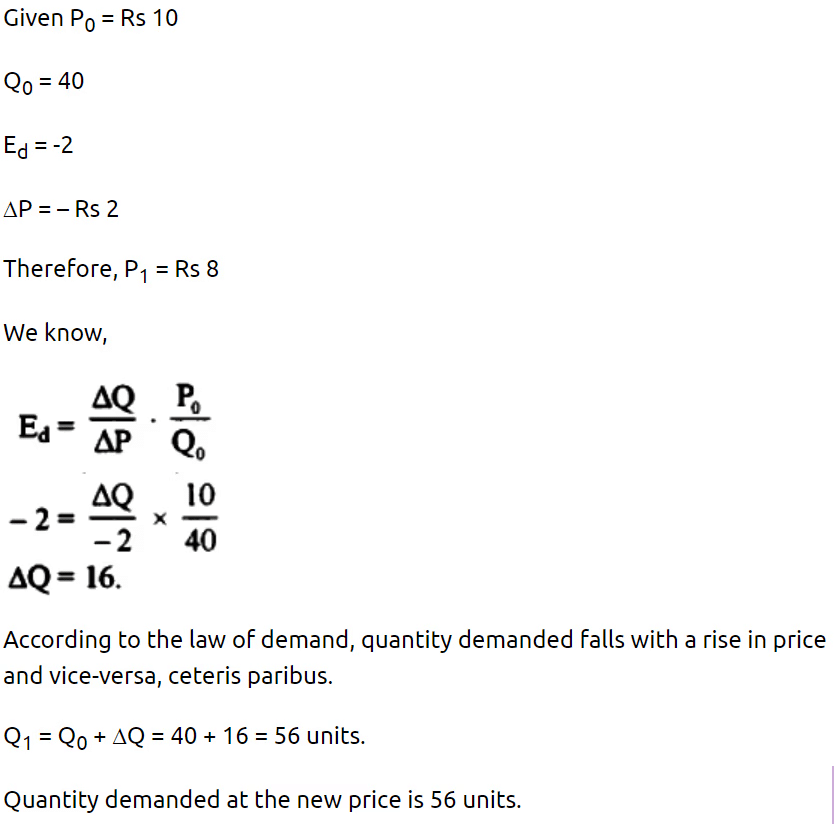
Q10. Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is -0.2. How will the expenditure on the good be affected if there is a 10% increase in its price?
Ans:
According to the question:
- Price elasticity of demand (Ed) = -0.2
- Percentage increase in price = 10%
We can use the elasticity formula:
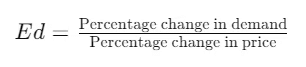
Putting the values:
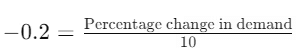
Percentage change in demand=−0.2×10
Percentage change in demand=−2%
From the above calculation, we infer that when the price increases and the elasticity of demand is less than 1 (inelastic), the demand decreases by a smaller percentage compared to the price increase. Therefore, the total expenditure on the good will increase.
|
59 videos|290 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Class 11 Economics Short Questions With Answers - Theory Of Consumer Behaviour
| 1. What is the theory of consumer behaviour? |  |
| 2. What are the key factors influencing consumer behaviour? |  |
| 3. How does the law of diminishing marginal utility relate to consumer behaviour? |  |
| 4. How do budget constraints impact consumer behaviour? |  |
| 5. How does the theory of consumer behaviour help businesses in marketing strategies? |  |

















