Our Soils / Soils of India Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Soil? |

|
| How is Soil Formed? |

|
| What is Soil Fertility? |

|
| What are the Different Types of Soil in India? |

|
| Soil Erosion |

|
| Soil Conservation |

|
What is Soil?
Soil is the uppermost layer of the Earth where plants grow. It is made up of many different substances. Some of these substances include:
- Minerals: These come from rocks and are essential for plant growth.
- Remnants of Plants and Animals: These are tiny pieces of dead plants and animals that help make the soil rich in nutrients.
- Water and Air: Both are necessary for the soil to support plant life.
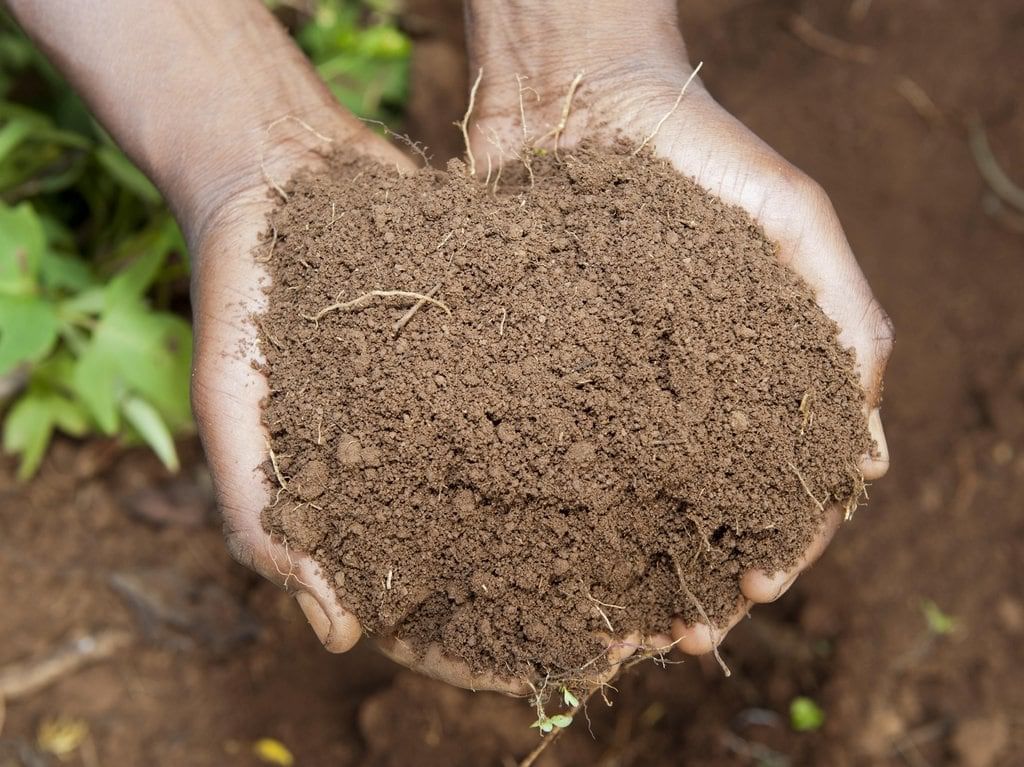 Soil
Soil
Interaction in Soil: The health of soil depends on how well it interacts with air, water, minerals, and the remnants of plants and animals. This interaction helps create a healthy environment for plants to grow.
Importance of Soil
Soil is very important because:
- It provides the foundation and raw materials for plant growth.
- It is a crucial part of our ecosystem, helping support life on Earth.
- In India, soil is a fundamental resource, vital for agriculture and food production.
How is Soil Formed?
Soil formation is a slow and natural process that takes thousands of years.
Here's how it happens:
- Breaking of Rocks: Large rocks break down into smaller pieces due to weathering. This can be caused by natural forces like wind, water, and temperature changes.
- Further Breakdown: These smaller pieces continue to break down into even finer particles like sand and silt.
- Transportation: The sand and silt are carried to different places by running water and wind.
- Soil Formation: Over time, these particles settle and mix with organic matter (like dead plants and animals) to form soil.
What is Soil Fertility?
- Soil fertility is the ability of the soil to help in the growth of plants.
- Manure and fertilizers are added to the soil to increase its fertility.
- Fertile soil produces more crops.
 Fertile Soil
Fertile Soil
What are the Different Types of Soil in India?
India has many types of soil, and the quality of soil decides the produce of the place. Soils found in India are:
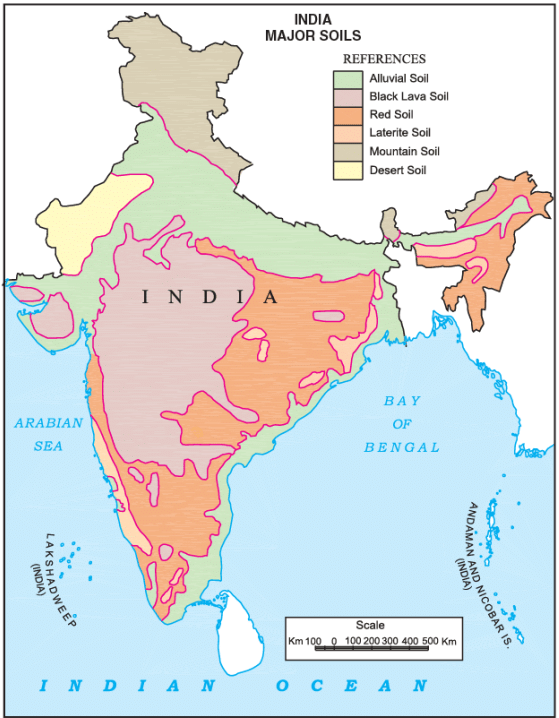 India – Major Soils
India – Major Soils
1. Mountain Soils
- Mountain soil is found in hilly areas. It is very rich in humus.
- Humus is a natural fertilizer found in decomposed dead leaves and plants.
- It is the top layer of the soil.
- Mountain soil is found on the hill slopes in Jammu Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Wheat, barley, maize, fruits, coffee, tea, and spices grow well in mountain soil.
 Mountain Soil
Mountain Soil
2. Alluvial Soils
- Alluvial soil is the most fertile soil.
- It is found in the northern and coastal plains.
- It is made of fine sand and silt.
- These are carried on wash down by the rivers that flow down from the Himalayas and the hills of the Deccan Plateau.
- The fine sand and silt get deposited on the riverbanks during annual flooding.
- It is ideal for growing crops such as rice, wheat, maize, sugar cane, tobacco, oilseeds, pulses, cotton, jute, vegetables, and fruits.
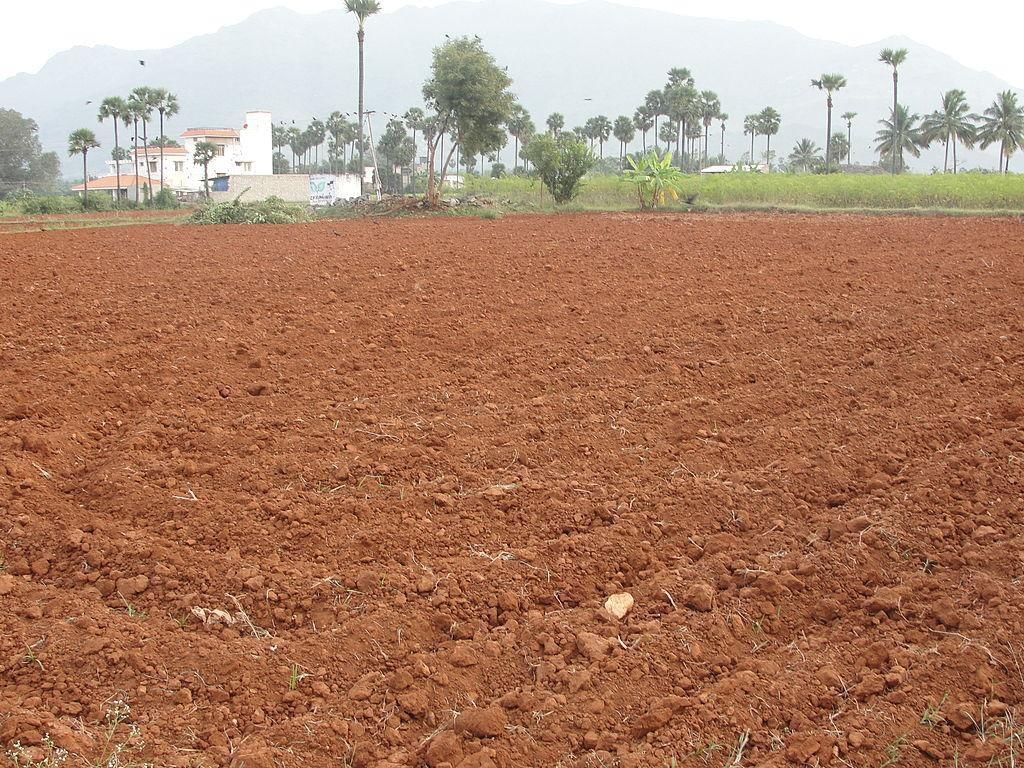 Alluvial Soil
Alluvial Soil
3. Black Soils
- Black soil is also called lava soil. It is formed from the solidification of lava.
- The molten rock flows through cracks and crevices of the earth's surface.
- It is black. Black soil is found in Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
- It holds large amounts of water and moisture.
- Crops like cotton, sugar cane, wheat, millet, tobacco, and oilseeds are grown in this soil type.
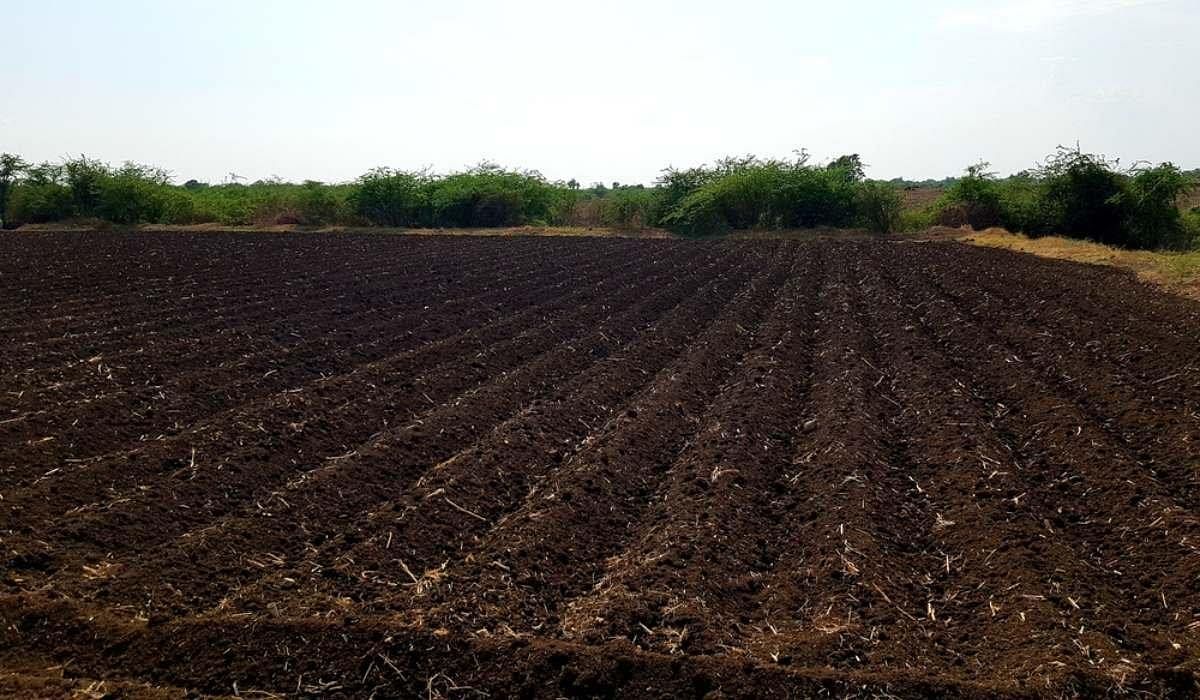 Black Soil
Black Soil
4. Red Soils
- This soil is less fertile, as it cannot retain moisture.
- This soil is generally found in warm and moist climates.
- It is found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, some parts of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Jharkhand.
- The lowermost layer of red soil is dark in color and very fertile.
- To make it fertile, farmers add fertilizers to it.
- Proper use of fertilizers and irrigation high production of cotton, wheat, rice, millet, and pulses.
 Red Soil
Red Soil
5. Laterite Soils
- Laterite soil is found when minerals are washed away from the soil due to heavy rainfall.
- This soil is also not fertile, as all its nutrients are lost due to leaching.
- It has to be replenished with manure to grow crops.
- This soil is rich in iron and aluminum.
- Laterite soil is found in parts of Maharashtra, Karnataka. Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karela, Bihar, Assam, and Meghalaya.
- It is good for growing millets and groundnuts.
- This soil in coastal plains is irrigated by water from canals and rivers.
- It is enriched with manure and made fit to grow rice and sugarcane. Laterite soil is also used for making bricks.
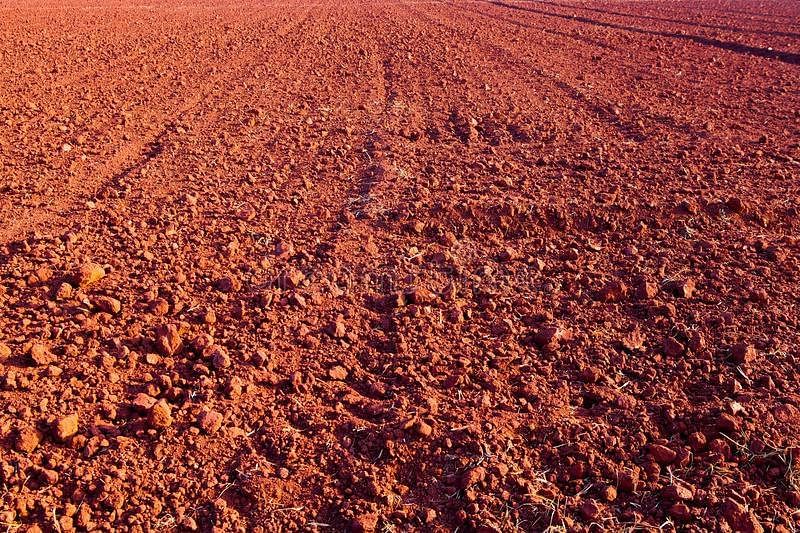 Laterite Soil
Laterite Soil
6. Desert Soils
- Desert soil is sandy and infertile.
- It is found in arid regions.
- As deserts receive little or no rainfall, the sandy soil needs a lot of water for growing crops.
- It is found in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Wheat, millet, barley, maize, and pulses can be grown if water is available for irrigation.
- Otherwise, desert soil only supports cactus, bushes or shrubs.
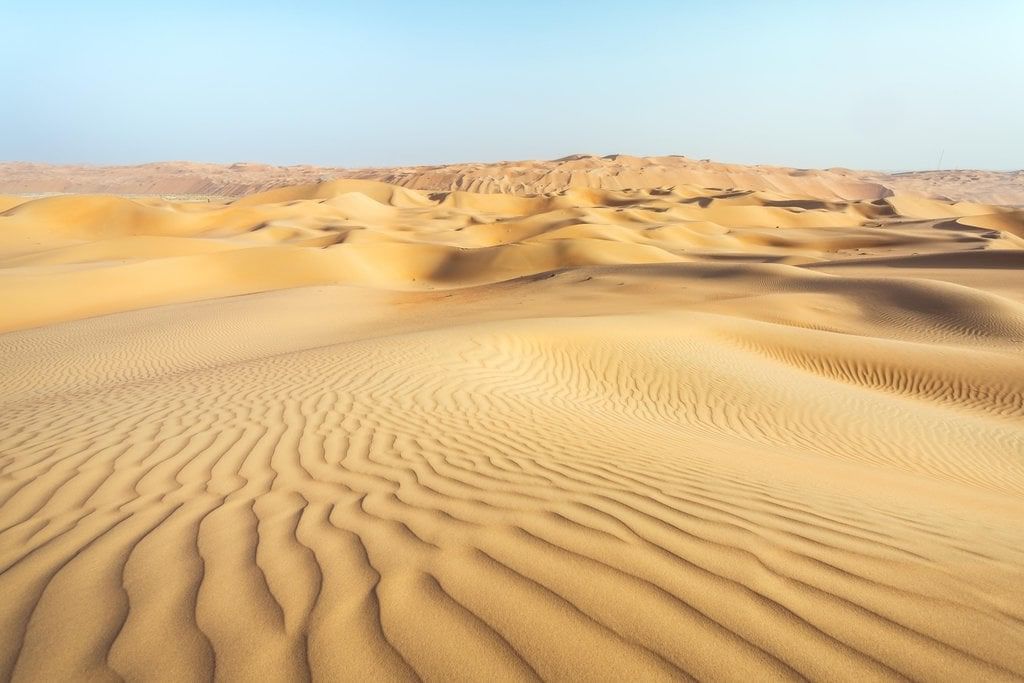 Desert Soil
Desert Soil
Soil Erosion
- Soil erosion is described as the carrying away of soil.
- The Natural elements of soil erosion are wind, rain, landslides, and glaciers.
- Social activities which assist natural forces in soil erosion are overgrazing, deforestation, nature of land use, and cultivation methods.
 Soil Erosion
Soil Erosion
Soil Conservation
To check soil erosion is soil conservation. If the soil is washed away or blown away, it gets lost forever for that particular area or region. In other words, soil conservation is to hold the soil in its place.
To prevent soil erosion and protect soil, the following steps can be taken:
- Plant Trees: Trees hold the soil together with their roots, preventing it from being washed away.
- Avoid Cutting Trees: Preserving existing trees helps maintain soil stability.
- Keep Fields Covered: Plant cover crops to protect the soil when main crops are not being grown.
- Control Grazing: Manage grazing to prevent overgrazing, which can expose soil to erosion.
- Use Natural Fertilizers: Use manure and compost instead of artificial fertilizers to improve soil health naturally.
Things To Remember
- Soil is the fundamental resource of our country.
- Broadly, soils are of six types.
- Soil erosion is described as carrying away of soil.
- To check soil erosion is soil conservation.
- A forestation, tree plantation, planned grazing, small and large dams, contour ploughing, terrace farming are some of the methods of soil conservation.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Our Soils / Soils of India Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What is soil and how is it formed? |  |
| 2. What is soil fertility and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of soil found in India? |  |
| 4. What is soil erosion and how does it impact the environment? |  |
| 5. What are some methods of soil conservation to prevent soil erosion? |  |
















