Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 1 (With Solutions) PDF Download
Social Science
Time : 3 Hours
M.M.: 80
General Instructions:
1. Question paper comprises five Sections - A, B, C, D and E. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section A: Question no. 1 to 16 are Objective Type Questions of 1 mark each.
3. Section B: Question no. 17 to 22 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
4. Section C: Question no. 23 to 26 are Source Based Questions, carrying 4 marks each.
5. Section D: Question no. 27 to 31 are Long Answer Type Questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section E: Question no. 32 is Map Based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 32.1 from History (2 marks) and 32.2 from Geography (3 marks).
7. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
8. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section - A
Q.1. Who wrote Das Kapital?
(a) Karl Marx
(b) Mirabeau
(c) John Locke
(d) Rousseau
Ans. (a)
Q.2. Arrange the following in chronological order:
(a) Napoleon was defeated at Waterloo.
(b) Napoleon becomes emperor of France, annexes large parts of Europe.
(c) Louis XVI becomes King of France, faces empty treasury and growing discontent within the Old Regime society.
(d) A constitution is framed to limit the king’s powers and guarantee fundamental rights to all human beings.
Ans. (d)
Q.3. Which ancient supercontinent is incorporated in present-day South America, Africa, Arabia, Madagascar, India, Australia and Antarctica? (1 Mark)
Ans. Gondwanaland.
OR
What are the pattern of arrival and retreating monsoon?
Ans. Both are irregular
Q.4. Name the highest mountain peak in the world located in Nepal.
(a) Kanchenjunga
(b) Mt. Everest
(c) Rocky Mountains
(d) White Mountain Peak
Ans. (b)
Q.5. Choose the correct option from column A and B. (1 Mark)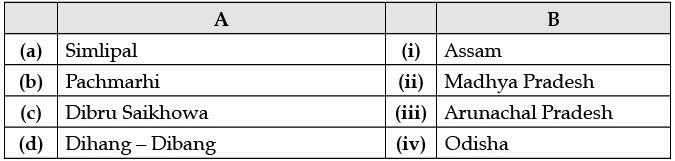
Ans. (b) Pachmarhi - Madhya Pradesh
Q.6. Name the only large river in the Indian desert region. (1 Mark)
Ans. Luni
OR
What is the total area of the Indian landmass?
Ans. The total area of the Indian landmass is 3.28 million square km.
Q.7. Which island is an active volcano found in Andaman and Nicobar islands?
(a) Majuli Island
(b) Barren island
(c) Venadu island
(d) Kutch island
Ans. (b)
Q.8. Read the following information and write a single term for it.
It is an introductory statement in a Constitution that states the reasonsand the guiding values of the Constitution. It contains the philosophy on which the entire Constitution has been built.
(a) The Charter
(b) The Preamble
(c) The Directive Principles
(d) The Fundamental Rights
Ans. (b)
Q.9. What has been the reason for the decline in poverty in West Bengal? (1 Mark)
Ans. Land reforms.
OR
What are the prescribed minimum wages for a farm labourer?
Ans. Rs. 115 per day.
Q.10. Picture Based Question
Study the given picture carefully:

This picture is related to which of the following :
(a) General meeting
(b) Assembly meeting
(c) Cabinet meeting
(d) None of these
Ans. (c)
Q.11. Correct and rewrite the sentences : (1 Mark)
The Rajya Sabha is the Upper House of India’s Parliament. It consists of 255 members, of which the President of India nominates 15.
Ans. The Rajya Sabha is the Upper House of India’s Parliament. It consists of 250 members, of which the President of India nominates 12.
OR
A judge can be removed only when an impeachment motion is passed separately by one-third majority of members of each of the two houses of the Parliament.
Ans. A judge can be removed only when an impeachment motion is passed separately by a two-thirds majority of members of each of the two houses of the Parliament.
Q.12. Fill in the blank : (1 Mark)
Orchids is example of _________________ plants.
Ans. Exotic
OR
Weather describes the day to day _________________ conditions.
Ans. Meteorological
Q.13. Assertion and Reason Type Question:In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): A large population’s positive aspect is the vast human resource.
Reason (R): The negpartaspect of a large population is limited food and resources.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is right, but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is correct.
Ans. (b)
Q.14. Consider the following statements regarding Election Photo Identity Card (EPIC).
(1) The Indian government has introduced the Election Photo Identity Card (EPIC) System.
(2) Every eligible voter on the list is issued a Photo Identity Card.
(3) Carrying this EPIC is not mandatory.
Choose the correct opinion from the following :
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) only 1
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
Q.15. In which state is Dachigam National Park located?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Assam
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
Ans. (d)
Q.16. Fill in the blank:
__________ has been implemented to encourage attendance and retention of children and improve their nutritional status.
(a) Free Books Scheme
(b) Free Uniform Scheme
(c) Mid-day-meal Scheme
(d) Free Gifts Scheme
Ans. (c)
Section - B
Q.17. How was the taxation policy responsible for the French Revolution? Explain. (3 Mark)
Ans.
(i) About 60 per cent of the land was owned by nobles, Church, and other more affluent Third Estate members. Peasants made up about 90% of the population, and very few of them held the land they cultivated.
(ii) The clergy and the nobility (first two estates) were exempted from paying taxes to the State.
(iii) Church, too extracted its share of taxes called tithes from the peasants.
(iv) All Third Estate members had to pay taxes to the State, including a direct tax called taille and several indirect taxes.
(v) These indirect taxes were levied on everyday consumption articles like salt or tobacco. The State’s financing activities’ burden through taxes was borne by the third estate alone.
OR
Explain the three changes brought about by industrialisation in Europe.
Ans.
Three changes are:
- Industrialization brought men, women and children to factories.
- Working conditions were poor.
- Unemployment was common, especially during times of low demand.
- With the growth of cities rapidly, there were housing and sanitation problems.
Q.18. Describe the status of the nobles in France before the Revolution. (3 Mark)
Ans.
- The clergy and the nobles led a life of luxury and enjoyed numerous privileges.
- The middle class comprising of lawyers, doctors, teachers, etc., also suffered humiliation at the clergy and the nobles’ hands.
- The nobles further enjoyed feudal privileges.
- Nobles were exempted from paying taxes.
OR
Describe the ideas of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels about the capitalists.
Ans.
- Marx argued that industrialist society was ‘Capitalist’.
- The workers’ condition could not improve as long as private capitalists accumulated the profit.
- Marx believed that to free themselves from capitalist exploitation, the workers had to construct a radical society.
- He thought that communist society was the natural society of the future.
Q.19. Where is Mawsynram located? Why does Mawsynram receive the highest amount of rainfall? (3 Mark)
Ans.
- Mawsynram is situated in the Khasi Hills’ Khasi Hills’ southern ranges at the height of 1,500 m above sea level. It receives the highest rainfall in the world. Annual rainfall is about 1,140 cm.
- This place gets the highest amount of rainfall because hills enclose it on three sides. The relief features give this place a tunnel-shaped location. The Bay of Bengal monsoon is trapped in these hills.
- The winds try to get out of it but are forced to pour down there.
Q.20. What is meant by the independence of the judiciary? Explain. (3 Mark)
Ans.
Independence of judiciary:
- Judiciary is not under the legislature or the control executives’ control.
- The judges do not act on the direction of the government or according to the wishes of the party in power.
- The Constitution of India provides security to the service of the judges. Once appointed by the President, their service cannot be terminated by will or any authority.
- There is a security of pay and allowances of the judges. Their salaries cannot be reduced.
- The Supreme Court and the High Courts are free to decide their work and establishment procedure.
- Judge is not allowed to practice after retirement to influence the court’s judgements.
OR
What are the main functions of the Election Commission of India?
Ans.
- The Election Commission (EC) has the right to make decisions on every aspect of conducting and controlling elections.
- It implements the Code of Conduct and punishes violators.
- It prevents misuse of government machinery at the time of elections.
- All government officers on election duty are under the Election Commission’s control.
Q.21. ‘Employment structure is characterised by self-employment in the primary sector.’ Explain the statement. (3 Mark)
Ans.
Employment structure is characterised by self-employment in the primary sector:
- The whole family contributes to a field even though not everybody is needed. So, there is disguised unemployment in the agricultural industry.
- But, the entire family shares what has been produced. However, this does not reduce the poverty of the family. When the surplus-labour does not get sufficient employment in agriculture, they migrate to cities searching for jobs.
Q.22. "The inequality that existed in the French Society in the Old Regime became the cause of French Revolution." Justify the statement by giving three suitable examples. (3 Mark)
Ans.
The examples are:
- French Society was divided into three Estates. The First Estate comprised of clergy, the Second Estate comprised of nobility and the Third Estate comprised of businessmen, traders, merchants, artisans, peasants and servants.
- The members of Church and nobility enjoyed certain privileges by birth, the most important was being exempted from paying taxes to the State.
- Feudal dues were extracted by nobles from peasants and one-tenth of the agricultural produce of peasants, in the form of ‘Tithes’ came to the share of the clergy. All the members of the Third Estate, including peasants, paid taxes, thus, the burden of financing activities of the State through taxes was borne by the Third Estate alone, creating heavy discontentment.
Section - C
Q.23. Read the source given below and answer the following questions : (4 Mark)
French Society during the late Eighteenth Century
The Church, too, extracted its share of taxes called tithes from the peasants, and finally, all members of the third estate had to pay taxes to the state. These included a direct tax, called taille, and several indirect taxes levied on everyday consumption articles like salt or tobacco. The burden of the state’s financing activities through taxes was borne by the third estate alone.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) A group of persons invested with a special function in the church are called _______.
(a) Priest
(b) Clergy
(c) Noble
(d) Feudal Lords
Ans. (b)
(ii) Who enjoyed feudal privileges by firth?
(a) The First Estate
(b) The Second Estate
(c) The Third Estate
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b)
(iii) A tax levied by the church was paid by Third Estate in whichcurrency?
(a) Francs
(b) Dollars
(c) Pounds
(d) Livre
Ans. (d)
(iv) The _____ that existed in the French Society in the Old Regime became the cause of the French Revolution.
(a) inequality
(b) equality
(c) partiality
(d) discrimination
Ans. (a)
Q.24. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow : (4 Mark)
The Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayas, geologically young and structurally fold mountains stretch over India’s northern borders. These mountain ranges run in a west-east direction from the Indus to the Brahmaputra. The Himalayas represent the loftiest and one of the world’s most rugged mountain barriers. They form an arc, which covers a distance of about 2,400 Km. Their width varies from 400 Km in Kashmir to 150 Km in Arunachal Pradesh. The altitudinal variations are more significant in the eastern half than those in the western half. The Himalaya consists of three parallel ranges in its longitudinal extent. Several valleys lie between these ranges. The northern-most range is known as the Great or Inner Himalayas or the Himadri. It is the most continuous range of the loftiest peaks with an average height of 6,000 metres. It contains all prominent Himalayan peaks.
The folds of the Great Himalayas are asymmetrical. The core of this part of the Himalayas is composed of granite. It is perennially snowing bound, and several glaciers descend from this range.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Geologically, how old are the Himalayan Mountains?
(a) Young and fold
(b) Ancient and fold
(c) Old and fold
(d) Modern and fold
Ans. (a)
(ii) The Northernmost range of Himalayan is called :
(a) Greater Himalayan
(b) Inner Himalayan
(c) Himadri
(d) All the abov
Ans. (d)
(iii) The range is lying to the ________ of the Himadri forms the most rugged mountain system called Himachal.
(a) East
(b) North
(c) South
(d) Wes
Ans. (c)
(iv) The Himalayas consists of ________ parallel ranges.
(a) two
(b) four
(c) three
(d) six
Ans. (c)
Q.25. Read the source given below and answer the following questions: (4 Mark)
Like South Africa, India's Constitution was also drawn up under challenging circumstances. Making the constitution for a vast and diverse country like India was not an easy affair. At that time, India’s people were emerging from the status of subjects to citizens. The country was born through a partition based on religious differences. This was a traumatic experience for the people of India and Pakistan. At least ten lakh people were killed on both sides of the border in partition related violence. There was another problem. The British had left it to the princely states’ rulers to decide whether they wanted to merge with India or Pakistan or remain independent. The merger of these princely states was a difficult and uncertain task. When the constitution was written, the country’s future did not look as secure as it does today. The constitution’s makers had anxieties about the present and the country’s future.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Besides India, which other country's constitution was drawn under challenging circumstances?
(a) Africa
(b) South Africa
(c) Belgium
(d) Pakistan
Ans. (b)
(ii) At that time, the country was going through a partition based on _________ differences.
(a) racial
(b) political
(c) economic
(d) religious
Ans. (d)
(iii) The partition was between which two countries?
(a) India and Pakistan
(b) India and Bangladesh
(c) India and China
(d) India and Nepal
Ans. (a)
(iv) Why did the makers of the constitution had anxieties when the constitution was being written?
(a) They were worried about the past of the country.
(b) They were concerned about the presence of the country.
(c) They were worried about the future of the country.
(d) They were concerned about the country’s present and future.
Ans. (d)
Q.26. Read the source given below and answer the following questions: (4 Mark)
Infrastructure of Palampur This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper-caste families own the majority of land in the village. Some of them are pretty large and made of brick with cement plastering. The SCs (Dalits) comprise one-third of the population and live in one corner of the village and much smaller houses, including mud and straw. Most of the homes have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tubewells in the fields and is used in various small business types. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school. There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick are treated. The description above shows that Palampur has a relatively well-developed system of roads, transport, electricity, irrigation, schools and health centre. Compare these facilities with those in your nearby village. The story of Palampur, an imaginary town, will take us through the different types of production activities in the village. In villages across India, farming is the main production activity. The other production activities, referred to as non-farm activities, include small manufacturing, transport, shop-keeping, etc. We shall look at both these activities after learning a few general things about the production.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) This story related to which imaginary village?
(a) Balrampur
(b) Palampur
(c) Rampur
(d) Raipur
Ans. (c)
(ii) Give an example of Small Scale manufacturing in Palampur.
(a) Cane furniture
(b) Handicrafts industry
(c) Jaggery manufacturing
(d) Sugar manufacturing
Ans. (b)
(iii) Palampur has _______ Primary School and _______ High Schools.
(a) Four, three
(b) Three, two
(c) Three, one
(d) Two, one
Ans. (d)
(iv) Source of irrigation in Palampur is:
(a) Wells
(b) Tubewells
(c) Rivers
(d) Ponds
Ans. (b)
 |
Download the notes
Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 1 (With Solutions)
|
Download as PDF |
Section - D
Q.27. Explain any five economic conditions of France that led to the Revolution. (5 Mark)
Ans. Economic situation of France:
(i) Constant wars.
(ii) Cost of maintaining extravagant court at the immense Palace of Versailles.
(iii) Extension of help to American countries. Under Louis XVI, France helped the thirteen common enemies of Britain.
(iv) Increase in debt by war. The war added more than a billion lives to debt that had already risen to more than 2 billion lives. Lenders, who gave the State credit, now began to charge 10 per cent interest on loans.
(v) Rise in the rate of interest by 10%.
Detailed Answer:
France’s economic condition:
(i) Extravagant and luxurious lives of France’s rulers was one of the causes. Louis XVI emptied the royal treasury.
(ii) Unfair distribution of taxes was another economic factor that burdened a section of society while exempting the other team.
(iii) Extension of financial support to thirteen American colonies.
(iv) Lenders who gave the State credit now began to charge 10 per cent on loans.
(v) To meet the expenses, such as maintaining an army, the court, running government offices or universities, the State was forced to increase the tax.
OR
'The First World War left a deep imprint on European society and polity. Elaborate on the given statement.
Ans.
The First World War’s impact on European society and polity was immense:
- Soldiers were to be placed above civilians.
- Politicians and publicists laid great stress on men’s need to be aggressive, muscular and masculine.
- Media glorified trench life.
- Aggressive war propaganda and national honour occupied centre stage.
- Popular support grew for conservative dictatorships.
Q.28. Explain which two forces are responsible for shaping India’s present geographic features. Which continents were parts of Gondwanaland? (5 Mark)
Ans.
- Divergent and convergent movements are the two forces responsible for two continental plates to fracture and fold.
- The continents’ position and size have changed due to these crustal plates’ movements over millions of years. The present landform features and reliefs of India are part of this process.
- The Gondwana land included Asia (Deccan Plateau of India), Australia, South America, South Africa and Antarctica.
OR
Differentiate between the cold weather season and India’s hot weather season while explaining each’s distinctive features.
Ans.
Cold Weather Season:
- It begins from mid-November in northern India and stays till February.
- The temperature decreases from South to North.
- Days are warm, and nights are cold.
Hot Weather Season:
- It begins in March and stays till May.
- Experiences rise in temperature and fall in air pressure in North India.
- The hot and dry wind called ‘loo’ blow during the day.
Q.29. Differentiate between the political executive and the permanent executive. Which executive is more powerful? (5 Mark)
Ans.
Political Executive:
- The people elect it for a specified period.
- The political executive is more potent than the permanent executive.
- The people elect the ministers of political executives, so they are answerable for their work. That’s why the ministers take all the final decisions.
Permanent Executive:
- In the second category, people are appointed on a long-term basis, called permanent executives.
- Officials working in civil services are called civil servants. They are also called bureaucrats.
- They remain in office even when the ruling party changes. These officers work under the political executive and assist them in carrying out day to day administration. Thus, the permanent executive is more powerful.
Q.30. The formation of the Indian Constitution was no less complex than that of South Africa. Do you agree? Explain with five arguments. (5 Mark)
Ans.
Points to argue:
(i) Size of the country.
(ii) Diversity is comparatively more prominent in India.
(iii) The communal attitude among various groups.
(iv) The merger of princely states.
(v) Partition and violence at the time of independence.
Detailed Answer
Circumstances
(i) Making a constitution for a vast and diverse country like India was not easy.
(ii) At that time, the people of India are emerging from the status of subjects to citizens.
(iii) The country was born through a partition based on religious differences.
(iv) The British had left the princely states to decide their future independently.
(v) At that time, the country’s future did not look very secure.
(vi) Makers of the constitution had anxieties about the present and the future.
(vii) The country’s vast size and diversity was a matter of concern.
Q.31. “Unemployment leads to a depressed economy.” Justify the statement with five arguments. (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) Because of the unemployment, people who are an asset turn into a liability.
(ii) There is a feeling of hopelessness and despair among youth.
(iii) People don’t have money to support their family.
(iv) The quality of life of an individual and society is adversely affected.
(v) When the family has to live at a bare subsistence level, there is a decline in health.
(vi) Wastage of natural resources is another factor that emerges due to unemployment.
OR
How has electricity become the base of all economic and non-economic activities in rural areas?
Ans.
Electricity has become the base of all financial and non-economic activities in rural areas, especially for agriculture, in the following manner:
(i) With electricity, tube wells can be run to meet the water demand.
(ii) Mechanical inputs like a threshing machine, etc., can easily be managed.
(iii) Farmers could use the internet to find the best crop prices for non-farm activities.
(iv) This could attract many entrepreneurs to set up industries over here.
(v) With such combination facilities, life could become more accessible.
Section - E
Q.32. (A) 1. On the given political map of the world, locate and label: Austria- Hungary
2. Identify the Nation that was a Member of the Allied Powers during World War II. (2 Mark)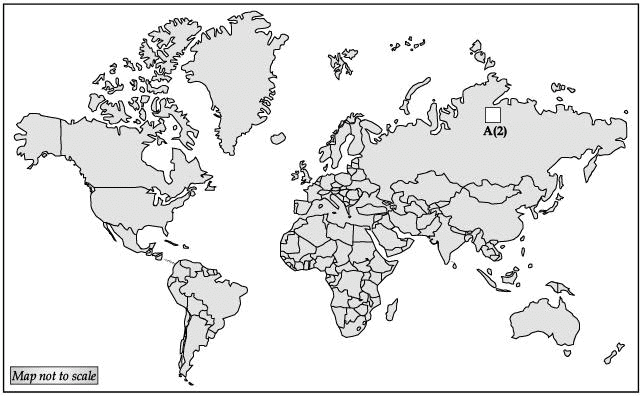
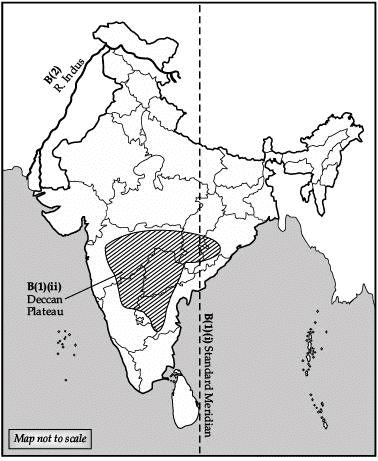
(B) 1. On the given political map of India, locate and label the following :
(i) Standard Meridian
(ii) Deccan Plateau
2. Identify the river in the map (3 Mark) Ans. (A) 1. Ref. to map work
Ans. (A) 1. Ref. to map work
2. Russia
(B) 1. Ref. to map work
2. River Indus
FAQs on Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 1 (With Solutions)
| 1. What is Social Science? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of studying Social Science? |  |
| 3. What are the different subjects covered in Social Science? |  |
| 4. How can studying Social Science benefit us in our daily lives? |  |
| 5. Can you provide examples of real-world applications of Social Science? |  |



























