Dipole in Uniform & Non-Uniform Electric Field | Physics for JAMB PDF Download
INTRODUCTION TO DIPOLE IN UNIFORM EXTERNAL FIELD
If a dipole is kept in an external electric field, it experiences a rotating effect. By external electric field, we mean electric field that is not induced by dipole itself. The rotating effect is also called torque on the dipole. How we can calculate the torque on a dipole and what are its applications? This can be done by calculating the net torque on opposite charges of the dipole.
Dipole in Uniform External Field
To find torque on a dipole from an external field, consider there is electric dipole placed in an uniform external field. The uniform external electric field is produced externally and is not induced by dipole.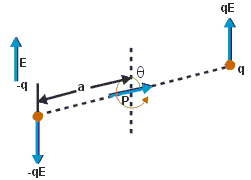
The external electric field 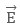 will produce electric force
will produce electric force 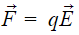 on positive charge in upward direction (same direction as
on positive charge in upward direction (same direction as 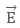 ) and on negative charge in downward direction (opposite direction to
) and on negative charge in downward direction (opposite direction to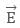 ).
).
We can see that the dipole is in transitional equilibrium as net force on the dipole is zero.
What about the rotational equilibrium? Is it also zero? If that was the case, then the dipole would have been stationary in position, but experimentally it is found that the dipole rotates with some angular velocity.
This is because, both the electrostatic force that is,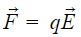 acts a torque in a clockwise direction, thereby making the dipole to rotate in a uniform external electric field.
acts a torque in a clockwise direction, thereby making the dipole to rotate in a uniform external electric field.
Torque always acts in a couple, and its magnitude equals to the product of force and its arm. Arm is the distance between the point where the force acts and the point which rotates the dipole. In the dipole placed in the uniform external electric field, we take origin as the point. Torque is denoted by the symbol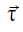 and as it has a direction, it is a vector quantity.
and as it has a direction, it is a vector quantity.
Mathematically,
Magnitude of torque = q E × 2a sin θ
τ = 2 q a E sin θ
Since, the dipole moment (p = 2qa)
τ = p E sin θ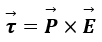
The vector form of torque is the cross product of dipole moment and electric field.
To understand what cross product is, let’s take an example.
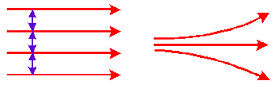
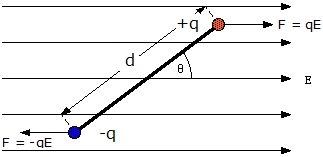 Fig: Torque rotates the dipole in uniform electric field
Fig: Torque rotates the dipole in uniform electric field
The net external force acting on the dipole will be zero, hence it will not translate in space. But the same cannot be said about the net torque on the dipole.
In short, 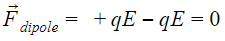
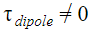
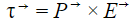
Where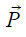 represents the dipole moment of the electric dipole and
represents the dipole moment of the electric dipole and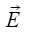 represents the external electric field in which the dipole is kept.
represents the external electric field in which the dipole is kept.
Observations in net force and torque
Taking the nature of electric field and position of the dipole, following remarks will come out:
- If the dipole
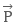 and external electric field
and external electric field 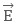 are parallel, that is, angle between them is zero, then the dipole will feel zero torque. That is, no rotational effect.
are parallel, that is, angle between them is zero, then the dipole will feel zero torque. That is, no rotational effect. - If the external electric field
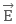 is non-uniform, then net force on the dipole ≠ 0, and torque will create rotation. Hence, it would be a combined rotational and translational motion.
is non-uniform, then net force on the dipole ≠ 0, and torque will create rotation. Hence, it would be a combined rotational and translational motion. - If the dipole external electric field
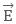 are antiparallel, that is, angle between them is non-zero, then the dipole will feel zero torque.
are antiparallel, that is, angle between them is non-zero, then the dipole will feel zero torque. - When the electric dipole
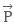 and electric field
and electric field 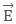 are parallel, the direction of net force will be in direction of increasing electric field.
are parallel, the direction of net force will be in direction of increasing electric field.
- When the electric dipole
 and electric field
and electric field  are anti-parallel, then the direction of net force will be in direction of decreasing electric field.
are anti-parallel, then the direction of net force will be in direction of decreasing electric field. - Force and Torque on a dipole placed in a uniform external field
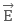 varies with the orientation of dipole in free space
varies with the orientation of dipole in free space
PHYSICAL SIGNIFICANCE
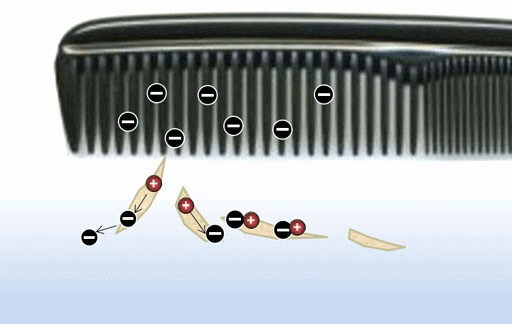
Fig: Comb attract dry paper piece
When we comb our dry hair and bring it near to some paper pieces, we find that the comb attracts the paper pieces. The comb gains charge, from our hair by the process of rubbing and induce a charge in the uncharged paper. In another way, the comb polarizes the pieces of paper that is, generate a net dipole moment in the direction of electric field. Also, since the electric field is non-uniform, the paper pieces move in the direction of the comb.
|
263 videos|252 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Dipole in Uniform & Non-Uniform Electric Field - Physics for JAMB
| 1. What is a dipole in an electric field? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between a uniform and non-uniform electric field? |  |
| 3. How does a dipole behave in a uniform electric field? |  |
| 4. What happens to a dipole in a non-uniform electric field? |  |
| 5. Can a dipole experience a net force in a uniform electric field? |  |





















