Very Short Answers - Some Natural Phenomena, Science, Class 8 | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Q. 1. What is lightning?
Ans. Lightning is a big spark of electricity in the sky that happens during storms.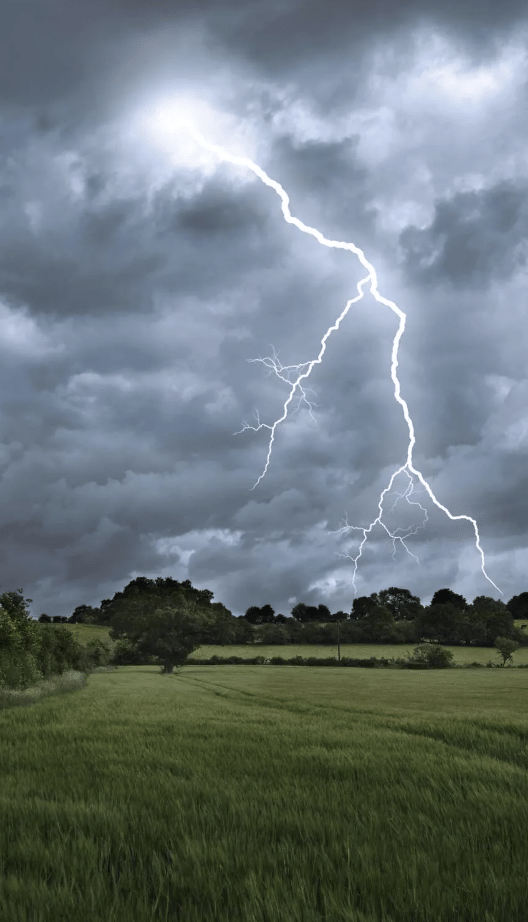
Q. 2. What is the cause of lightning?
Ans. Lightning happens when electric charges build up in clouds and then quickly release as a spark.
Q. 3. What is static electricity?
Ans. The electricity generated by rubbing is called static electricity because the charges do not move.
Q. 4. Who discovered the static electricity or lightning in clouds?
Ans. Benjamin Franklin found out about static electricity and lightning in clouds in 1752. 
Q. 5. What are the two types of charges?
Ans. There are two types of charges:
(i) Positive charges
(ii) Negative charges.
Q. 6. How the two types of charges interact with each other?
Ans. The interaction between two types of charges is characterized by like charges repelling each other, while unlike charges exhibit an attractive force towards one another.
Q. 7. What do you mean by earthing?
Ans. The process of transferring of charge from a charged body to the earth is called earthing.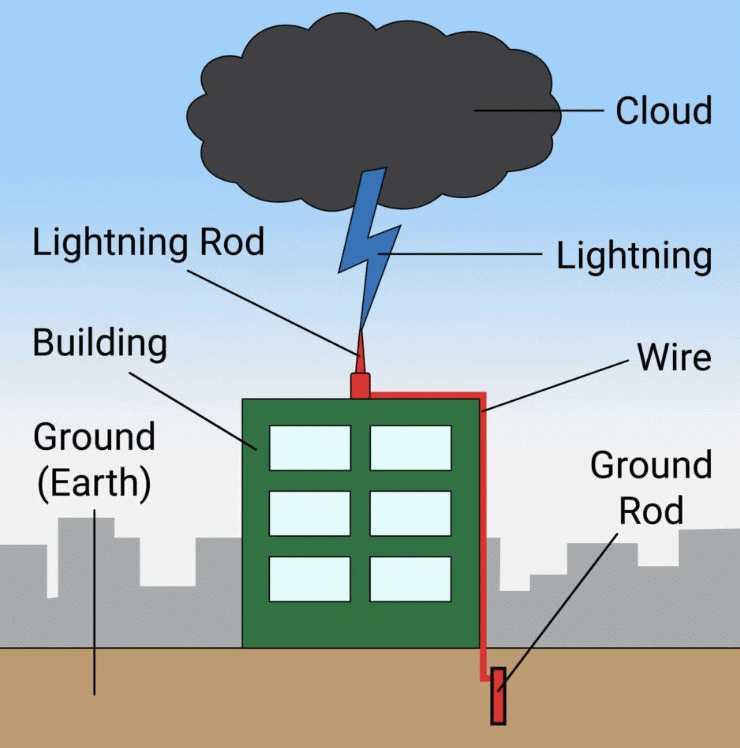
Q. 8. Write the importance of earthing.
Ans. Earthing is provided in building to protect us from electrical shocks due to any leakage of electrical current.
Q. 9. What is an electric discharge?
Ans. The process of meeting of negative and positive charges to release huge amount of energy is called electric discharge.
Q. 10. Name the device used to save multistoryed building from lightning.
Ans. A lightning rod conductor safeguards tall buildings from lightning.
Q. 11. What are seismic or fault zones?
Ans. The weak zones where earthquakes are more likely to occur are called seismic or fault zones.
Q. 12. Which regions in India are most threatened by earthquakes?
Ans. Kashmir, Western and Central Himalayas, the entire North-East region, Rann of Kutch, Rajasthan, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and some parts of South India.
Q. 13. What is Amber?
Ans. Amber is a type of resin. Amber Resin
Amber Resin
Q. 14. What is an earthquake?
Ans. An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth which lasts for a very short time.
Q. 15. Write the cause of earthquake.
Ans. Earthquake is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
Q. 16. What are other natural phenomenon caused by earthquake?
Ans. Earthquake can cause floods, landslides and tsunamis.
Q. 17. What is tsunami?
Ans. The earthquake under the oceans is called tsunami.
Q. 18. When and where a major tsunami took place in India?
Ans. A major tsunami occurred in the Indian Ocean on 26 December 2004.
Q. 19. Is it true that earth is balanced on the horn of a bull, when bull shifts its horn an earthquake takes place?
Ans. No. It is not true.
Q. 20. Name the instrument used to measure earthquake.
Ans. A seismograph is used to measure earthquakes..
Q. 21. Write the other causes of tremors on earth.
Ans. Tremors on earth can also be caused when a volcano erupts, underground nuclear explosion and meteor hits the earth.
Q. 22. What are the safe places during thunderstorm?
Ans. The covered vehicles and buildings are safe during thunderstorm.
Q. 23. During lightening if you are in open where should you take shelter?
Ans. We should take shelter under small trees.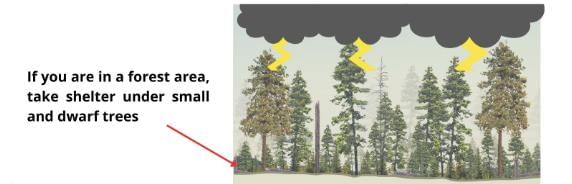
Q. 24. Is sitting on motor cycle safe or not during lightning?
Ans. No, it is not safe.
Q. 25. What are the harmful effects of lightning on a lightning victim?
Ans. Lightning can lead to memory loss, sight or hearing problems, and even broken bones..
Q. 26. Name some natural phenomenon which can be predicted to some extent.
Ans. Thunderstorms, lightning, and cyclones can be predicted to some extent.
Q. 27. Name a natural phenomenon which cannot be predicted yet now.
Ans. Earthquakes cannot be predicted accurately yet..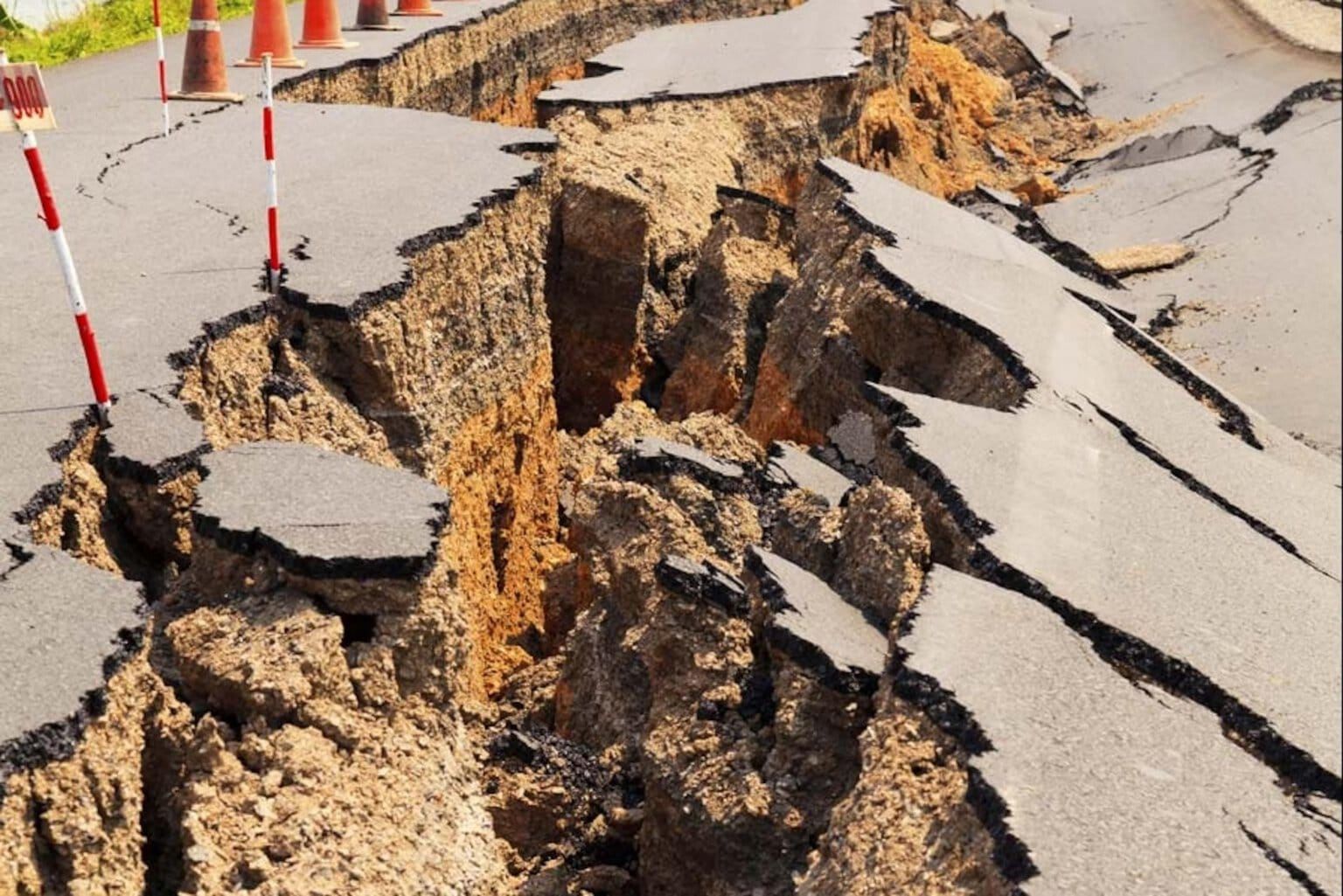
Q. 28. What are the three destructive natural phenomenon?
Ans. Winds, storms and cyclones are the three natural phenomenon which are destructive.
Q. 29. What is an electric current?
Ans. The flow of charges is called electric current.
Q. 30. Name the device which is used to test whether an object is charged or not.
Ans. An electroscope is used to test if an object has electric charge..
Q. 31. Name the material used to transfer charges from one body to other.
Ans. Metal conductors help move charges from one material to another.
Q. 32. What are charged objects?
Ans. The objects which acquire a small charge on rubbing are called charged objects.
Q. 33. Write the nature of charges on a glass rod and silk cloth when they are rubbed with each other.
Ans. When rubbed, a glass rod gets a positive charge and a silk cloth gets a negative charge.
Q. 35. What happens when amber is rubbed with fur?
Ans. When amber is rubbed with fur, it attracts light object.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Answers - Some Natural Phenomena, Science, Class 8 - Science Class 8
| 1. What are some examples of natural phenomena? |  |
| 2. How do natural phenomena affect humans? |  |
| 3. What causes earthquakes? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of clouds and their significance? |  |
| 5. What is the water cycle and why is it important? |  |

















