NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fractions & Decimals | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
Exercise Page: 57
In questions 1 to 20, out of the four options, only one answer is correct. Choose the correct answer.
Q1: The fraction which is not equal to 4/5 is
(a) 40/50
(b) 12/15
(c) 16/20
(d) 9/15
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
(D) 9/15
All the options given in the question are further simplified as,
(A) 40/50 = 4/5
(B) 12/15
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 4/5
(C) 16/20
Divide both numerator and denominator by 4.
= 4/5
(D) 9/15
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 3/5
Therefore, 3/5 ≠ 4/5
Q2: The two consecutive integers between which the fraction 5/7 lies are
(a) 5 and 6
(b) 0 and 1
(c) 5 and 7
(d) 6 and 7
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
A fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
So, 5/7 = 0.715
Therefore, 5/7 lies between 0 and 1.
Q3: When ¼ is written with denominator as 12, its numerator is
(a) 3
(b) 8
(c) 24
(d) 12
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(1 × 3)/(4 × 3) = 3/12
Consider, 3/12
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3.
= 1/4
Q4: Which of the following is not in the lowest form?
(a) 7/5
(b) 15/20
(c) 13/33
(d) 27/28
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Divide both numerator and denominator by 5.
= 3/4
Q5: If (5/8) = (20/p), then value of p is
(a) 23
(b) 2
(c) 32
(d) 16
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Consider the given fraction, (5/8) = (20/P)
P = 20 × (8/5)
P= 4 × 8
P = 32
Q6: Which of the following is not equal to the others?
(a) 6/8
(b) 12/16
(c) 15/25
(d) 18/24
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
(C) 15/25
All the options given in the question are further simplified as,
(A) 6/8
Divide both numerator and denominator by 2.
= 3/4
(B) 12/16
Divide both numerator and denominator by 4.
= 3/4
(C) 15/25
Divide both numerator and denominator by 5.
= 3/5
(D) 18/24
Divide both numerator and denominator by 6.
= ¾
Comparing all results, (¾ = ¾ = ¾) ≠ 3/5
Therefore, (6/8 = 12/16 = 18/24) ≠ 15/25
Q7: Which of the following fractions is the greatest?
(a) 5/7
(b) 5/6
(c) 5/9
(d) 5/8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
We know that, among all fractions with same numerator, the one having smaller denominator will be the highest fraction.
5/9 < 5/8 < 5/7 < 5/6
Therefore, among four options, (b) 5/6 has small denominator. So, it is the greatest fraction.
Q8: Which of the following fractions is the smallest?
(a) 7/8
(b) 9/8
(c) 3/8
(d) 5/8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
We know that, among all fractions with same denominator, the one having smaller numerator will be the smallest fraction.
3/8 < 5/8 < 7/8 < 9/8
Therefore, among four options, (c) 3/8 has small numerator. So, it is the smallest fraction.
Q9: Sum of 4/17 and 15/17 is
(a) 19/17
(b) 11/17
(c) 19/34
(d) 2/17
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
If denominators of the given fractions are same, we can add both fractions.
So, (4/17) + (15/17)
= (4 + 15)/17
= 19/17
Q10: On subtracting 5/9 from 19/9, the result is
(a) 24/9
(b) 14/9
(c) 14/18
(d) 14/0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
If denominators of the given fractions are same, we can subtract both fractions.
So, (19/9) – (5/9)
= (19 – 5)/9
= 14/9
Q11: 0.7499 lies between
(a) 0.7 and 0.74
(b) 0.75 and 0.79
(c) 0.749 and 0.75
(d) 0.74992 and 0.75
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
0.7499 lies between 0.749 and 0.75
Q12: 0. 023 lies between
(a) 0.2 and 0.3
(b) 0.02 and 0.03
(c) 0.03 and 0.029
(d) 0.026 and 0.024
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
0. 023 lies between 0.02 and 0.03
Q13: 11/7 can be expressed in the form
(a) 7(1/4)
(b) 4(1/7)
(c) 1(4/7)
(d) 11(1/7)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
To convert an improper fraction 11/7 into a mixed fraction:
Divide the numerator (11) by the denominator (7): 11 ÷ 7 = 1 remainder 4
Write the quotient as the whole number, and the remainder as the numerator over the original denominator: 1(4/7)
So, 11/7 = 1(4/7), making option (c) the correct answer.
Q14: The mixed fraction 5(4/7) can be expressed as
(a) 33/7
(b) 39/7
(c) 33/4
(d) 39/4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
5(4/7) can be expressed as = 5 + (4/7)
= (35 + 4)/7
= 39/7
Q15: 0.07 + 0.008 is equal to
(a) 0.15
(b) 0.015
(c) 0.078
(d) 0.78
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.070 + 0.008
So, sum of 0.070 and 0.008 = 0.070 + 0.008
= 0.078
Q16: Which of the following decimals is the greatest?
(a) 0.182
(b) 0.0925
(c) 0.29
(d) 0.038
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.1820, 0.0925, 0.2900, 0.0380
Now, by comparing 4 decimal numbers, 0.2900 is the greatest.
Q17: Which of the following decimals is the smallest?
(a) 0.27
(b) 1.5
(c) 0.082
(d) 0.103
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 0.270, 1.500, 0.082, 0.103
Now, by comparing 4 decimal numbers, 0.082 is the smallest.
Q18: 13.572 correct to the tenths place is
(a) 10
(b) 13.57
(c) 14.5
(d) 13.6
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Place value of the place immediately after the decimal point (i.e. tenth place) is 1/10, that of next place (i.e. hundredths place) is 1/100 and so on.
13.572 correct to the tenths place is 13.6
Q19: 15.8 – 6.73 is equal to
(a) 8.07
(b) 9.07
(c) 9.13
(d) 9.25
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
First we have to convert given decimals into like decimals = 15.80
Now, 15.80 – 6.73 = 9.07
Q20: The decimal 0.238 is equal to the fraction
(a) 119/500
(b) 238/25
(c) 119/25
(d) 119/50
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Decimals can be converted into fractions by removing their decimal points and writing 10,100, etc in the denominators, depending upon the number of decimal places in the decimals.
So, 0.238 = 238/1000
Divide both numerator and denominator by 2
= 119/500
In questions 21 to 44, fill in the blanks to make the statements true:
Q21: A number representing a part of a _________ is called a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A number representing a part of a whole is called a fraction.
Example: ¼, ¾, 1/5, 3/6 etc.
Q22: A fraction with denominator greater than the numerator is called a _________ fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
A fraction with denominator greater than the numerator is called a proper fraction.
Example: 2/5, 3/8, 10/11 etc. are proper fractions.
Q23: Fractions with the same denominator are called _________ fractions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Fractions with the same denominator are called like fractions.
Example: ½, 3/2, 5/2, 7/2 etc.
Q24: 135/18 is a _________ fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Mixed fraction.
Q25: 18/5 is an fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
18/5 is an improper fraction.
A fraction whose numerator is greater than the denominator is called an improper fraction.
Q26: 7/19 is a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
7/19 is a proper fraction.
A fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
Q27: 5/8 and 3/8 are proper fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
5/8 and 3/8 are like proper fraction.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Q28: 6/11 and 6/13 are proper fractions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
6/11 and 6/13 are unlike proper fractions.
If the denominators are different, then they are called unlike fractions.
Q29: The fraction 6/15 in simplest form is.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The fraction 6/15 in simplest form is 2/5.
The given fraction 6/15, is further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 3.
Q30: The fraction 17/34 in simplest form is .
 View Answer
View Answer 
The fraction 17/34 in simplest form is ½.
The given fraction 17/34, is further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 17.
Q31: 18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and fractions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and equivalent fractions.
Consider the two given fractions, 18/135 and 90/675
So, (18/135) = (90/675)
By cross multiplication, we get
(18 × 675) = (90 × 135)
12,150 = 12,150
Therefore, 18/135 and 90/675 are proper, unlike and equivalent fractions.
Q32: 8(2/7) is equal to the improper fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
8(2/7) is equal to the improper fraction 58/7.
Given mixed fraction is converted into improper fraction as = ((7 × 8) + 2)/7
= (56 + 2)/7
= 58/7
Q33: 87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction
12(3/7)
We know that, mixed fraction = Quotient Remainder/Divisor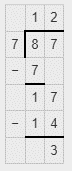
Therefore, 87/7 is equal to the mixed fraction
12(3/7)
Q34: 9 + (2/10) + (6/100) is equal to the decimal number ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
9 + (2/10) + (6/100) is equal to the decimal number 9.26.
Fractions with denominators 10,100, etc. can be written in a form, using a decimal point, called decimal numbers or decimals.
9 + (2/10) + (6/100) = 9 + 0.2 + 0.06
= 9.26
Q35: Decimal 16.25 is equal to the fraction ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Decimal 16.25 is equal to the fraction 16¼ or 65/4.
Decimals can be converted into fractions by removing their decimal points and writing 10,100, etc in the denominators, depending upon the number of decimal places in the decimals.
16.25 = 1625/100
Divide both numerator and denominator by 25.
= 65/4
= 16¼
Q36: Fraction 7/25 is equal to the decimal number ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Fraction 7/25 is equal to the decimal number 0.28.
Multiply numerator and denominator by 4 to get denominator 100.
(7/25) = (7 × 4)/(25 × 4)
= 28/100
We know that, fractions with denominators 10,100, etc. can be written in a form, using a decimal point, called decimal numbers or decimals.
= 0.28
Q37: (17/9) + (41/9) = .
 View Answer
View Answer 
(17/9) + (41/9) = 58/9.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Sum of two like fractions = (17 + 41)/9
= 58/9
Q38: (67/14) – (24/14) = .
 View Answer
View Answer 
(67/14) – (24/14) = 43/14.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Difference of two fractions = (67 – 24)/14
= 43/14
Q39: 17/2 + 3½ = .
 View Answer
View Answer 
17/2 + 3½ = 12.
First we have to convert mixed fraction into improper fraction = 3½ = 7/2
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Sum of two like fractions = (17/2) + (7/2)
= (17 + 7)/2
= 24/2
= 12
Q40: 9 ¼ – 5/4 = _________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
9 ¼ – 5/4 = 37/4 – 5/4 = (37 – 5)/4 = 32/4 = 8.
Q41: 4.55 + 9.73 = ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
4.55 + 9.73 = 14.28.
Q42: 8.76 – 2.68 = ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
8.76 – 2.68 = 6.08.
Q43: The value of 50 coins of 50 paisa = ₹______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The value of 50 coins of 50 paisa = ₹25.
We know that, ₹ 1 = 100 paisa
So, 50 coins of 50 paisa = 50 × 50
= 2500 paisa.
Then,
= 2500/100
= ₹ 25
Q44: 3 Hundredths + 3 tenths = ______.
 View Answer
View Answer 
3 Hundredths + 3 tenths = 0.33.
Place value of the place immediately after the decimal point (i.e. tenth place) is 1/10, that of next place (i.e. hundredths place) is 1/100 and so on.
3 Hundredths is written as = 3 × (1/100)
= 0.03
3 tenths is written as = 3 × (1/10)
= 0.3
Then sum of 3 Hundredths, 3 tenths = 0.03 + 0.3
= 0.33
In each of the questions 45 to 65, state whether the statement is true or false:
Q45: Fractions with same numerator are called like fractions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions.
Q46: Fraction 18/39 is in its lowest form.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Lowest form of given fraction 18/39
Divide both numerator and denominator by 3,
= 6/13
Q47: Fractions 15/39 and 45/117 are equivalent fractions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider the two given fractions, 15/39 and 45/117
So, (15/39) = (45/117)
By cross multiplication, we get
(15 × 117) = (45 × 39)
1,755 = 1,755
Q48: The sum of two fractions is always a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
For example: consider two fractions 10/5 and 15/5.
Sum of two fractions = (10 + 15)/5
= 25/5
= 5
= 5/1
A fraction in which there is no common factor, except 1, in its numerator and denominator is called a fraction in the simplest or lowest form.
When 2 fractions are added, the result in most cases will be a fraction p/q form, but in some case if it does happen to be just an integer, it can always be written with denominator 1 (hence p/q form).
Q49: The result obtained by subtracting a fraction from another fraction is necessarily a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Not necessarily a fraction. But can be written in fraction.
Q50: If a whole or an object is divided into a number of equal parts, then each part represents a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. This whole may be a single object or a group of objects.
For example: consider a circle is divided into 4 equal parts. Out of four equal parts 3 of them are shaded.
So, it can be represented in the form of fraction = 3/4
Q51: The place value of a digit at the tenths place is 10 times the same digit at the ones place.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Let us assume a digit be ‘y’.
The place value of a digit at the tenths place = y × (1/10)
= y/10
Then,
The tenths place is 10 times the same digit at the ones place.
y/10 = 10y is not possible.
Q52: The place value of a digit at the hundredths place is 1/10 times the same digit at the tenths place.
 View Answer
View Answer 
True
Let ‘a’ be the same digit at tens and hundreds place in a number.
Place value of digit at tens place = 10 × a = 10a
Place value of digit at hundreds place = 100 × a = 100a
Hence, the place value of a digit at the hundreds place is 10 times the same digit at the tens place.
Q53: The decimal 3.725 is equal to 3.72 correct to two decimal places.
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Consider the given decimal number, 3.725
The thousandths place has number 5.
Then, hundredths has number 2 it will be increased by 1 number to correct two decimal places.
Therefore, the decimal 3.725 is equal to 3.73 correct to two decimal places.
Q54: In the decimal form, fraction 25/8 = 3.125
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
25/8 can be further simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 8.
= 3.125
Q55: The decimal 23.2 = 23(2/5)
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
The decimal 23.2 = 232/10
Dividing both denominator and numerator by 2, we get.
= 116/5 =
23(1/5)
Q56: The fraction represented by the shaded portion in the adjoining figure is 3/8.
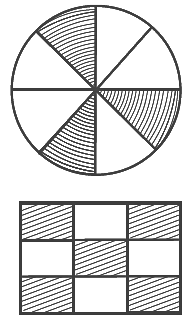
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Circle is divided into 8 equal parts. Out of 8 equal parts 3 of them are shaded.
Q57: The fraction represented by the unshaded portion in the adjoining figure is 5/9.
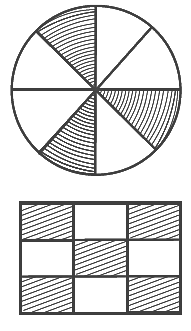
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Rectangle is divided into 9 equal parts. Out of 9 equal parts 4 of them are unshaded. So, fraction represented by the unshaded portion in the adjoining figure = 4/9.
Q58: (25/19) + (6/19) = 31/38
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
So, (25/19) + (6/19)
= (25 + 6)/19
= 31/19
Hence, 31/19 ≠ 31/38
Q59: (8/18) – (8/15) = 8/3
 View Answer
View Answer 
False.
Consider Left Hand Side (LHS),
LCM of 18 and 15 = 90
Then,
(8/18) = (8 × 5)/(18 × 5) = 40/90
(8/15) = (8 × 6)/(15 × 6) = 48/90
Difference of two fractions (40/90) – (48/90)
= -8/90
Right Hand Side (RHS) = 8/3
By comparing LHS and RHS,
LHS ≠ RHS
-8/90 ≠ 8/3
Q60: (7/12) + (11/12) = 3/2
 View Answer
View Answer 
True.
Consider Left Hand Side (LHS),
Sum of like fractions = (7/12) + (11/12)
= (7 + 11)/12
= 18/12
Divide both numerator and denominator by 6, we get,
= 3/2
Right Hand Side (RHS) = 3/2
By comparing LHS and RHS,
LHS = RHS
3/2 = 3/2
Q61: 3.03 + 0.016 = 3.019
 View Answer
View Answer 
False
Firstly convert 3.03 and 0.016 into like fractions, writing the decimals in column form and finally by adding we get,
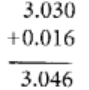
Q62: 42.28 – 3.19 = 39.09
 View Answer
View Answer 
True
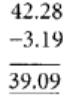
Q63: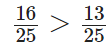
 View Answer
View Answer 
True
The given fractions are like fractions. On comparing the numerators, we get
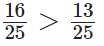
Q64: 19.25 < 19.053
 View Answer
View Answer 
False
Since, the digit at tenth place of 19.25 is 2 and the digit at tenth place of 19.053 is 0, where 2 > 0.
∴ 19.25 >19.053
Q65: 13.730 = 13.73
 View Answer
View Answer 
True
Since, after converting the given decimals in like decimals we get, 13.730 = 13.73.
Directions: In each of the questions 66 to 71, fill in the blanks using ’<’, ‘>’ or ‘=’
Q66:
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M. of 16 and 15 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 = 240
Thus,
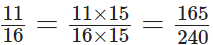
and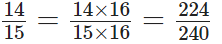
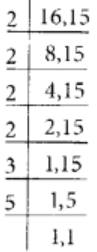
On comparing, we observe that
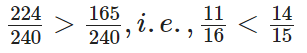
Q67:
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M of 15 and 14 is
2 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 120
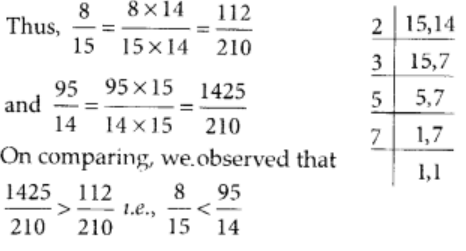
Q68:
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M of 75 and 200 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 5 = 600
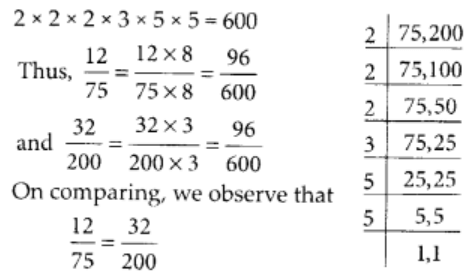
Q69: 3.25 … 3.4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Converting the given decimals into like decimals, they become 3.25 and 3.40. The whole number part of these is same. On comparing, we get their tenths digits 2 < 4
∴ 3.25 < 3.4
Q70: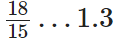
 View Answer
View Answer 
1.3 = (13/10)
∵ The L.C.M. of 15 and 10 is 2 × 3 × 5 = 30
Now, 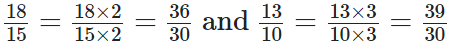

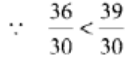
Thus, 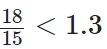
Q71: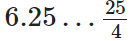
 View Answer
View Answer 
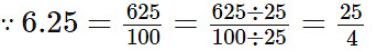
∴ 6.25 = 25/4
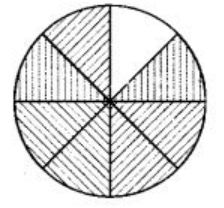
Q72: Write the fraction represented by the shaded portion of the adjoining figure:
 View Answer
View Answer 
In the given figure, total parts in which figure has been divided is 8 and out of which 7 parts are shaded.
∴ The required fraction is 7/8
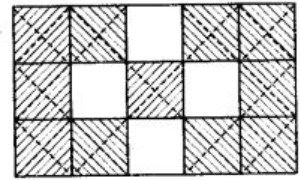
Q73: Write the fraction represented by the unshaded portion of the adjoining figure:
 View Answer
View Answer 
In the given figure, total parts in which figure has been divided is 15 and out of which 4 parts are unshaded.
∴ The required fraction is 4/15.
Q74: Ali divided one fruit cake equally among six persons. What part of the cake he gave to each person?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Since, Ali has to divide one fruit cake equally among 6 persons
∴ Each person will get 1/6 part.
Q75: Arrange 12.142, 12.124, 12.104, 12.401 and 12.214 in ascending order.
 View Answer
View Answer 
∵ The digits are already given in the form of like decimals.
Clearly,
12.104 < 12.124 < 12.142 < 12.214 < 12.401
Q76: Write the largest four digit decimal number less than 1 using the digits 1,5,3 and 8 once.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The required number is 0.8531, which is the largest four digit decimal number less than 1.
Q77: Using the digits 2, 4, 5 and 3 once, write the smallest four digit decimal number.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The required number is 0.2345, which is the smallest four digit decimal number.
Q78: Express 11/20 as a decimal.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have, 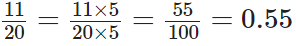
Q79: Express 6(2/3)as an improper fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have, 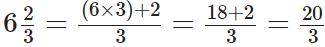
Q80: Express 3(2/5)as a decimal.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have, 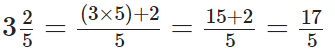
Now, 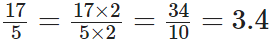
Q81: Express 0.041 as a fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
0.041 = 41/1000
Q82: Express 6.03 as a mixed fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
6.03 = 603/100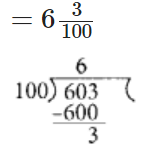
Q83: Convert 5201 g to kg.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
5201g = (5201/1000) kg
[∵ 1 kg = 1000 g]
= 5.201 kg
Q84: Convert 2009 paise to rupees and express the result as a mixed fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
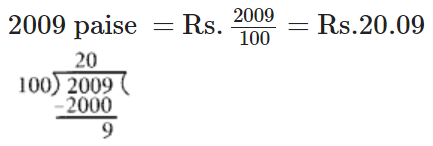
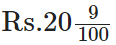
Q85: Convert 1537 cm to m and express the result as an improper fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
1537 cm = (1537/100) m
[∵ 1 m = 100 cm]
= 15.37 m
Q86: Convert 2435 m to km and express the result as mixed fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have,
2435m = (2435/1000) km
[ ∵ 1 km = 1000 m]
= 2.435 km
Firstly, convert the fraction (2435/1000) into the simplest form, for this dividing the numerator and denominator by 5, we get
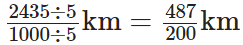
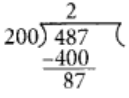
i.e.,
2(87/200) km
Q87: Arrange the fractions 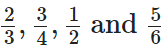 in ascending order.
in ascending order.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have given, 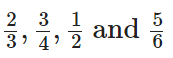
Firstly find the L.C.M. of 3, 4, 2 and 6.
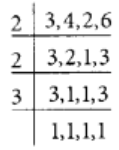
The L.C.M. of 3, 4, 2 and 6 is 2 × 2 × 3 = 12
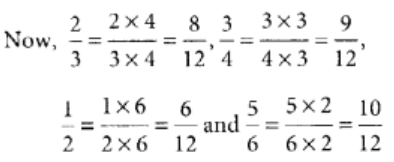
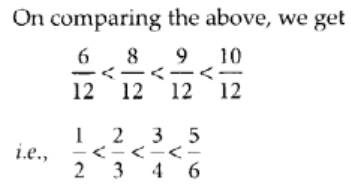
Q88: Arrange the fractions 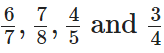 in descending order.
in descending order.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have given, 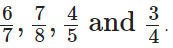

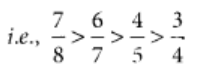
Q89: Write 3/4 as a fraction with denominator 44.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Let 3/4 = ?/44
Then, we have to find the missing numeral.
To get 44 in the denominator, we multiply 4 by 11.
So, we multiply the numerator and denominator by 11.
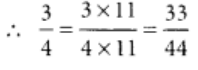
Hence, 3/4 and 33/44are equivalent fractions.
Q90: Write 5/6 as a fraction with numerator 60.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Let 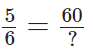
Then, we have to find the missing numeral. To get 60 in the numerator, we multiply 5 by 12.
So, we multiply the numerator and denominator by 12.
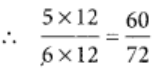
Hence, 5/6 and 60/72 are equivalent fractions.
Q91: Write 129/8 as a mixed fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have, 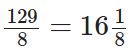
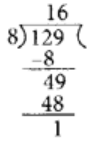
Q92: Round off 20.83 to nearest tenths.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The estimated value of 20.83 to the nearest tenths is 20.8
Q93: Round off 75.195 to nearest hundredths.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The estimated value of 75.195 to the nearest hundredths is 75.20
Q94: Round off 27.981 to nearest tenths.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The estimated value of 27.981 to the nearest tenths is 28.0
Q95: Add the fractions 3/8 and 2/3.
 View Answer
View Answer 
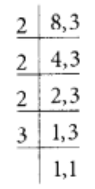
L.C.M. of 8 and 3 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 24
Now, 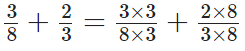
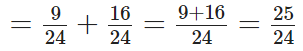
Q96: Add the fractions 3/8 and 6(3/4).
 View Answer
View Answer 
L.C.M of 8 and 4 is 2 × 2 × 2 = 8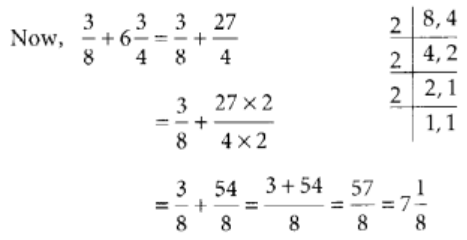
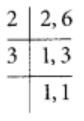
Q97: Subtract 1/6 from 1/2.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M of 6 and 2 = 6
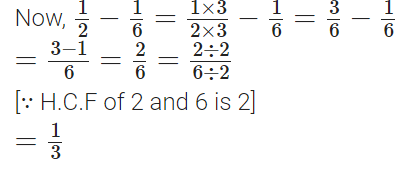
Q98: Subtract 8(1/3) from (100/9).
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M of 3 and 9 = 9
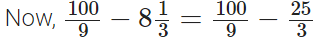
Q99: Subtract 1(1/4) from 6(1/2).
 View Answer
View Answer 
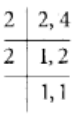
The L.C.M of 4 and 2 = 4
Now, 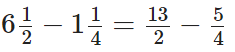
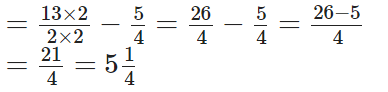
Q100: Add 1(1/4) and 6(1/2).
 View Answer
View Answer 
The L.C.M. of 4 and 2 = 4
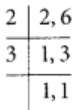
Now,
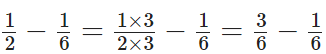
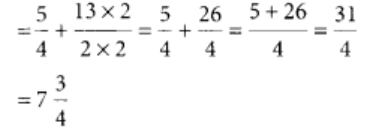
Q101: Katrina rode her bicycle 6(1/2) km in the morning and 8(3/4) km in the evening. Find the distance travelled by her altogether on that day.
 View Answer
View Answer 
The distance travelled by Katrina in the morning 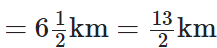
The distance travelled by Katrina in the evening 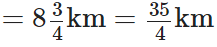
∴ Total distance travelled by her

Q102: A rectangle is divided into certain number of equal parts. If 16 of the parts so formed represent the fraction 1/4. find the number of parts in which the rectangle has been divided.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Let the number of parts in which the rectangle has been divided be x.
According to question, 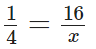
By cross-multiplication, x = 16 × 4 = 64
∴ The required number of parts is 64.
Q103: Grip size of a tennis racquet is 11(9/80) cm.
Express the size as an improper fraction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have given, a grip size of a tennis racquet 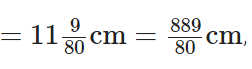 which is the required improper fraction.
which is the required improper fraction.
Q104: On an average 1/10 of the food eaten is turned into organism’s own body and is available for the next level of consumer in a food chain. What fraction of the food eaten is not available for the next level?
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have given, 1/10 of the food eaten is turned into organism’s own body.
∴ The required fraction of the food eaten not available for the next level is 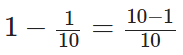
[∵ L.C.M. of 1 and 10 is 10]
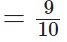
Q105: Mr. Rajan got a job at the age of 24 years and he got retired from the job at the age of 60 years. What fraction of his age till retirement was he in the job?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Mr. Rajan got a job at the age of 24 years.
He got retired at the age of 60 years.
He worked for (60 – 24) years = 36 years
∴ The required fraction 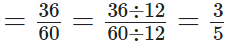
[ ∵ H.C.F. of 36 and 60 is 12]
Q106: The food we eat remains in the stomach for a maximum of 4 hours. For what fraction of a day, does it remain there?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The food we eat remains in the stomach for a maximum of 4 hours.
Total number of hours in a day = 24 hours
∴ The required fraction 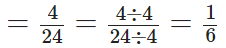
[∵ H.C.F of 4 and 24 is 4]
Q107: What should be added to 25.5 to get 50?
Q108: Alok purchased 1 kg 200 g potatoes, 250 g dhania, 5 kg 300 g onion, 500 g palak and 2 kg 600 g tomatoes. Find the total weight of his purchases in kilograms.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Alok purchased,
Potatoes = 1 kg 200 g = 1.200 kg
Dhania = 250 g = 0.250 kg
Onion = 5 kg 300 g = 5.300 kg
Palak = 500 g = 0.500 kg
Tomatoes = 2 kg 600 g = 2.600 kg
∴ The total weight of the above purchases

Q109: Arrange in ascending order:
0.011, 1.001, 0.101, 0.110
 View Answer
View Answer 
Since, all the decimals are already given in like fractions, i.e., 0.011, 1.001, 0.101, 0.110
∴ Arranging them in ascending order, we get
0.011, 0.101, 0.110, 1.001
Q110: Add the following:
20.02 and 2.002
 View Answer
View Answer 
We have, 20.02 and 2.002
To add the above decimals, we must convert them into like decimals first.
Writing 20.020 and 2.002 in a column
So,
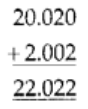
which is the required sum.
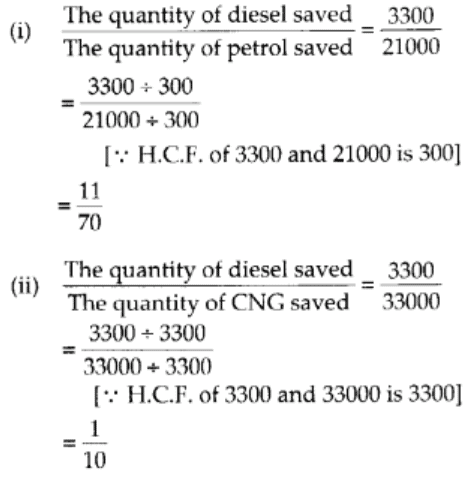
Q111: It was estimated that because of people switching to Metro trains, about 33000 tonnes of CNG, 3300 tonnes of diesel and 21000 tonnes of petrol was saved by the end of year 2007. Find the fraction of:
(i) the quantity of diesel saved to the quantity of petrol saved.
(ii) the quantity of diesel saved to the quantity of CNG saved.
 View Answer
View Answer 
By the end of year 2007,
The quantity of CNG saved 33000 tonnes,
The quantity of diesel saved 3300 tonnes and The quantity of petrol saved 21000 tonnes
Q112: Energy content of different foods are as follows: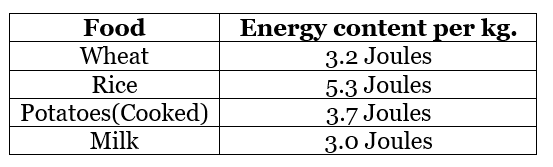 Which food provides the least energy and which provides the maximum?
Which food provides the least energy and which provides the maximum?
Express the least energy as a fraction of the maximum energy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Milk provides the least energy and rice provides the maximum energy.
∴ The required fraction 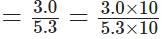
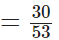
Q113: A cup is 1/3 full of milk. What part of the cup is still to be filled by milk to make it full?
 View Answer
View Answer 
A cup is 1/3 full of milk.
∴ The remaining part of the cup which is still to be filled by milk = 1 - (1/3)
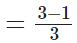
[∵ L.C.M of 1 and 3 is 3]
= 2/3
Q114: Mary bought 3(1/2)m of lace. She used 1(3/4)m of lace for her new dress. How much lace is left with her ?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Mary bought the lace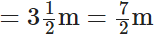
Lace used by Mary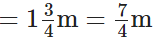
∴ She is left with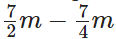
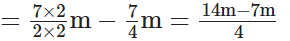
[ ∵ L.C.M. of 2 and 4 is 4]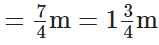
of lace
Q115: When Sunita weighed herself on Monday, she found that she had gained 1(1/4) kg.Earlier her weight was 46(3/8)kg. What was her weight on Monday?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Sunita had gained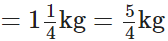 Earlier her weight was
Earlier her weight was 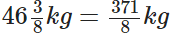
∴ Her total weight on Monday

Q.116. Sunil purchased 12(1/2) litres of juice on Monday and 14(3/4) litres of juice on Tuesday. How many litres of juice did he purchase together in two days?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Sunil purchased juice on Monday
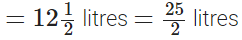
∴ Total quantity of juice Sunil purchased in two days 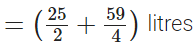
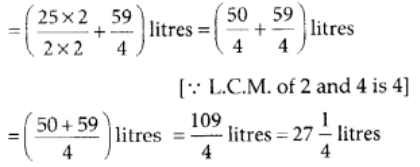
Q117: Nazima gave 2(3/4) litres out of the 5(1/2) litres of juice she purchased to her friends. How many litres of juice is left with her?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total quantity of juice 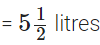
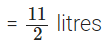
Nazima gave to her friends =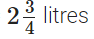
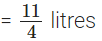
∴ The required quantity of juice she is left
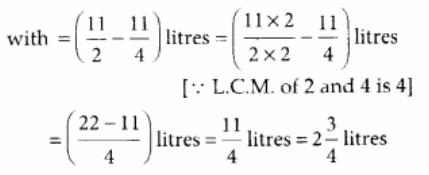
Q118: Roma gave a wooden board of length 150(1/4) cm to a carpenter for making a shelf. The Carpenter sawed off a piece of 40(1/5) cm from it. What is the length of the remaining piece?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Total length of a wooden board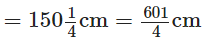 The carpenter sawed off a piece of length
The carpenter sawed off a piece of length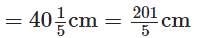 The carpenter sawed off a piece of length
The carpenter sawed off a piece of length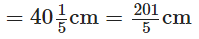 ∴ The length of the remaining piece
∴ The length of the remaining piece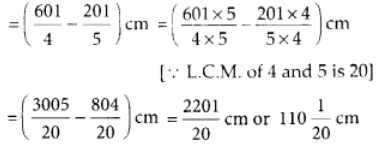
Q119: Nasir travelled 3(1/2) km in a bus and then walked 1(1/8)km to reach a town. How much did he travel to reach the town?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Nasir travelled by a bus 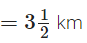
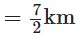 Nasir walked =
Nasir walked = 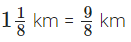 ∴ Total distance travelled by him
∴ Total distance travelled by him
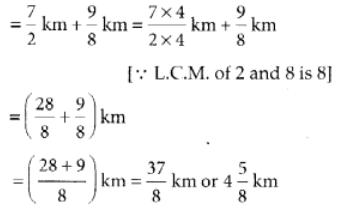
Q120: The fish caught by Neetu was of weight 3(3/4) kg and the fish caught by Narendra was of weight 2(1/2)kg. How much more did Neetu’s fish weigh than that of Narendra?
 View Answer
View Answer 
The weight of fish caught by Neetu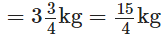 The weight of fish caught by Narendra
The weight of fish caught by Narendra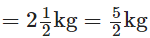 ∴ Neetu’s fish weigh more than that of Narendra by
∴ Neetu’s fish weigh more than that of Narendra by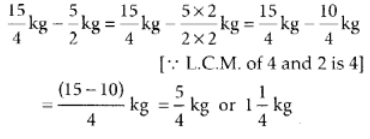
Q121: Neelam’s father needs 1(3/4)m of cloth for the skirt of Neelam’s new dress and 1/2 m for the scarf. How much cloth must he buy in all?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Neelam’s father purchased the length of cloth for the skirt 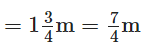 and for the scarf
and for the scarf 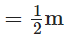 ∴ Total length he buys in all
∴ Total length he buys in all 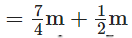
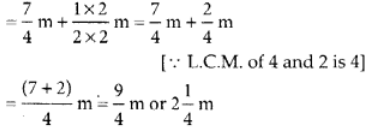
Q122: What is wrong in the following additions?
 View Answer
View Answer 
(a) Equal denominators are added.
(b) Numerators and denominators are added.
Q123: Which one is greater?
1 metre 40 centimetres + 60 centimetres or 2.6 metres.
 View Answer
View Answer 
1 metre 40 centimetres + 60 centimetres = 1.40 metres + 0.60 metres
[ 100 centimetres = 1 metre]
= 2.00 metres
Since, 2.6 > 2.00
∴ 2.6 metres is greater.
Q124: Match the fractions of Column I with the shaded or marked portion of figures of Column II: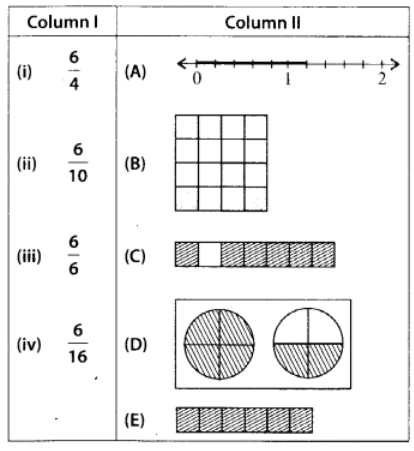
 View Answer
View Answer 
(i) ➝ (D) ; (ii) ➝ (A) ; (iii) ➝ (E) ; (iv) ➝ (B)
Marked point in (A) = 6/10
Shaded fraction in (B)= 6/16
Shaded fraction in (C) = 6/7
Shaded fraction in (D) 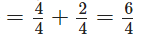
Shaded fraction in (E)= 6/6
Q125: Find the fraction that represents the number of natural numbers to total numbers in the collection 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. What fraction will it be for whole numbers?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Out of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ➝ 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 are the natural numbers.
∴ The fraction that represents the number of natural numbers to the total numbers = 5/6 and the whole numbers are 0,1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
∴ The fraction that represents the number of whole numbers to the total numbers = 6/6.
Q126: Write the fraction representing the total number of natural numbers in the collection of numbers -3, -2, -1,0,1,2, 3. What fraction will it be for whole numbers? What fraction will it be for integers?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Out of -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 -> 1, 2 and 3 are the natural numbers, 0,1, 2 and 3 are the whole numbers and -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 are integers.
∴ The fraction representing the natural numbers to the total numbers = 3/7=37
The fraction representing the whole numbers to the total numbers = 4/7=47
And the required fraction representing the integers to the total numbers = 7/7
Q127: Write a pair of fractions whose sum is 7/11 and difference is 2/11.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Let one fraction be x.
Another fraction be (7/11) - x711−x
Now, according to question,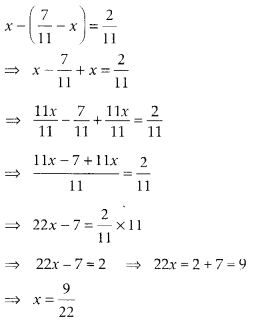 Thus, one fraction is 9/22 and another fraction is
Thus, one fraction is 9/22 and another fraction is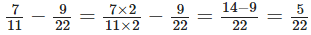
Q128: What fraction of a straight angle is a right angle?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Since, we know that the measurement of a straight angle is 180° and a right angle is 90°.
∴ The required fraction is 90°/180° = 1/2.
Q129:Put the right card in the right bag.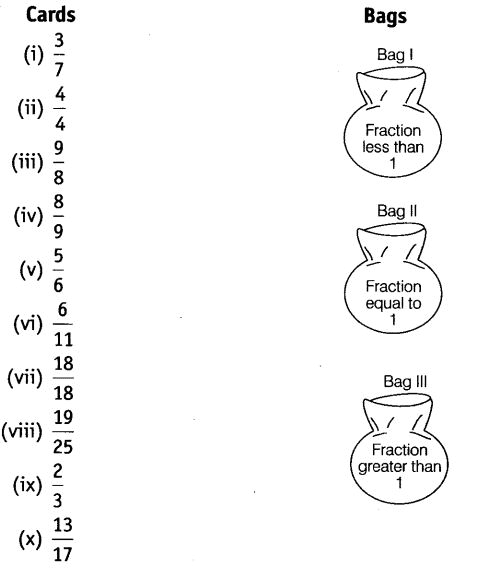
 View Answer
View Answer 
We know that if numerator is less than the denominator, then the fraction is less than 1.
If numerator is equal to the denominator, then the fraction is equal to 1 and if numerator is greater than the denominator, then the fraction is greater than 1.
Cards in Bag I are
(i) 3/7,
(iv) 8/9
(v) 5/6
(vi) 6/11
(viii) 19/25
(ix) 2/3 and
(x) 13/17
Cards in Bag II are (ii) 4/4 , (vii) 18/18
And cards in Bag III are (iii) 9/8.
|
30 videos|115 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fractions & Decimals - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in the Fractions & Decimals chapter of NCERT Exemplar? |  |
| 2. How can I convert a fraction into a decimal? |  |
| 3. What are the steps to add two fractions with different denominators? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to simplify fractions? |  |
| 5. How do I multiply two decimals? |  |























