Air Around Us Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 11
What is Air?
- The invisible gas we call air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and other gases. It may also contain some dust particles.
- Oxygen is essential for combustion and is vital for living organisms.
- Air is colourless and can be seen through; it is transparent.
- Air takes up space and exists in both water and soil.
- The layer of air surrounding the Earth is referred to as the atmosphere.
- The atmosphere is essential for life on our planet.
- Aquatic animals breathe by using dissolved air in water.
- Plants and animals depend on one another to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide from the air.
- The largest component of air, which does not support combustion, is nitrogen. The remaining 1% consists of carbon dioxide, a few other gases, and water vapour.
 Air
Air
Is Air Present Everywhere Around Us?
- Air is made up of a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and a few other gases, along with some dust particles.
- Oxygen is essential for burning and is crucial for living things.
- Air takes up space and can be found in both water and soil.
- Aquatic animals rely on dissolved air in water for breathing.
- Plants and animals rely on each other to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide from the air.
- The Earth is surrounded by a thin layer of air called the atmosphere, which stretches for several kilometres above the ground.
- The atmosphere is critical for supporting life on our planet.
- As we go higher in the atmosphere, the air becomes less dense.
Atmosphere: The thin blanket of air surrounding the surface of the Earth is called the atmosphere
What is Air Made Up Of?
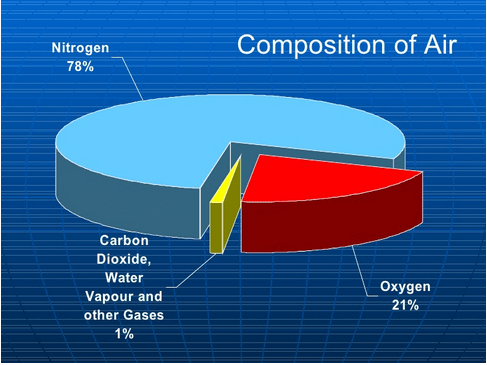 Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and a few other gases. The layer of air around the Earth is called the atmosphere, which is essential for life. Air is colourless and transparent, meaning we can see through it. It occupies space and can also be present in water and soil.
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and a few other gases. The layer of air around the Earth is called the atmosphere, which is essential for life. Air is colourless and transparent, meaning we can see through it. It occupies space and can also be present in water and soil.
Water Vapour
- Air contains water vapour which helps maintain the water cycle.
- When air comes in contact with cold surfaces, it is these vapours that turn into or condense into droplets of water.
- The amount of water vapor in the air vary from place to place and time to time.
Oxygen
- It is the oxygen in the air that helps humans and animals carry out the respiration process.
- Oxygen is also required for fire to keep burning. If we were to keep an inverted tumbler covering a burning candle, the candle will go off in a few seconds because of the lack of oxygen-containing air due to the tumbler.
- Dry air is said contain about 21% of oxygen.
Nitrogen
- Dry air contains approximately 78% nitrogen.
- The main gases in the air are nitrogen, oxygen, small amounts of carbon dioxide, and various other gases.
Carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide is created by plants and animals during respiration, and it also comes from burning organic materials.
- Although carbon dioxide is a smaller part of air, it is important for environmental processes and must be controlled to prevent pollution.
- In a closed room, burning materials can lead to a build-up of carbon dioxide, which can reduce oxygen levels, causing suffocation.
Dust and Smoke
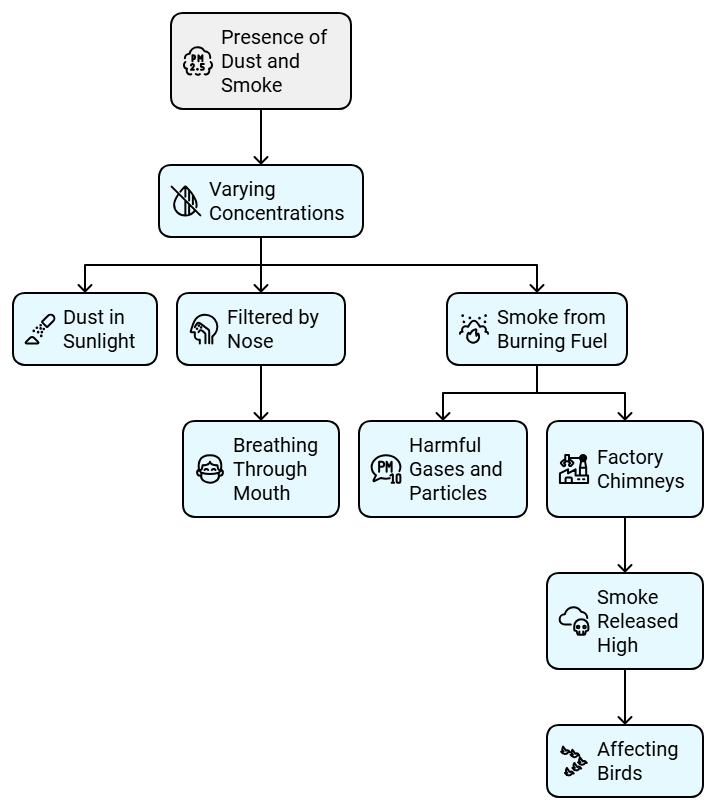
- Dust particles are always present in the air, though their concentration varies depending on time and place.
- Dust particles can be observed in a beam of sunlight, especially in a dark room or during winter when sunlight filters through trees.
- When we breathe through our nostrils, fine hair and mucus in the nose help prevent dust particles from entering the respiratory system.
- Breathing through the mouth can allow harmful dust particles to enter the body, which is why it is advisable to breathe through the nose.
- Smoke is a byproduct of burning fuel and contains a mixture of gases and fine dust particles.
- Smoke is often harmful due to the presence of these fine particles and gases, which can affect health when inhaled.
- Long chimneys in factories are used to release smoke high into the air, keeping it away from people on the ground, but it can still affect birds flying in the sky.
How Does Oxygen become available to Animals and Plants Living in Water and Soil?
Characteristics of Air in Water
 Air bubbles can be seen when water is heated
Air bubbles can be seen when water is heated
- Air occupies space.
- Water contains dissolved air. When heated, this air escapes.
- As heating continues, the water turns into vapour and eventually begins to boil.
- The dissolved oxygen in water is essential for the breathing of aquatic animals.
- Organisms living in the soil need oxygen to breathe. Many burrows and holes are created in deep soil by animals, allowing these organisms to access air.
- Plants and animals depend on each other to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide from the air.
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and several other gases. The layer of air surrounding the Earth is called the atmosphere. The atmosphere is crucial for life on Earth.
 |
Download the notes
Study Notes: Air Around Us
|
Download as PDF |
Characteristics of Air in Soil
Air particles present in soil
- Soil contains air, which is essential for the respiration of living organisms.
- Air takes up space.
- When water is added to soil, it pushes out the air.
- Animals that live in soil create many burrows and holes, allowing air to move in and out, providing oxygen for respiration.
- However, when there is heavy rain, water fills all the spaces where air was, forcing soil-dwelling animals to come out for oxygen.
- Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and some other gases. It may also contain dust particles.
- Oxygen is crucial for burning and is necessary for living beings.
- Aquatic animals use dissolved air in water for their respiration.
- The balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is maintained through respiration in plants and animals, as well as by photosynthesis in plants.
- The layer of air that surrounds the Earth is called the atmosphere.
Role of Oxygen in the Atmosphere
Have you ever thought about why the atmosphere's oxygen isn't completely used up, even though many living things are using it? What is responsible for putting oxygen back into the atmosphere?
What keeps the oxygen levels full? Despite numerous organisms constantly consuming oxygen, the levels stay balanced, showing there is a natural way to replace it.
How is Oxygen in the Atmosphere Replaced?
- Photosynthesis Process: Oxygen is replenished through photosynthesis, where plants create their own food and release oxygen as a byproduct.
- Oxygen Production vs. Consumption: While plants use oxygen for respiration, they produce more oxygen during photosynthesis than they consume. This demonstrates how plants and animals rely on each other to keep the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Interdependence of Plants and Animals: The balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is maintained through the respiration of both plants and animals, as well as photosynthesis in plants.
- Vital Role of Plants: Plants are crucial for life on Earth as they generate the oxygen needed for animals to survive, highlighting the important connection between plants and animals.
Other Uses of Air: Windmills: Wind causes the windmill to turn. Windmills are used to pump water from tubewells and to operate flour mills. They are also used for generating electricity.

|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Air Around Us Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 11
| 1. What is air and why is it important for life on Earth? |  |
| 2. Is air present everywhere around us? |  |
| 3. What is air made up of? |  |
| 4. How does oxygen become available to animals and plants living in water and soil? |  |
| 5. How is oxygen in the atmosphere replaced? |  |






















