Key Concepts - Physical Features of India | Chapter Notes For Class 9 PDF Download
Location
- India has all major physical features of the Earth, i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands.
- In India the soil color varies from place to place as it is formed from different types of rocks.
- The physical features of India can be grouped under the following physiographic divisions:
(i) The Himalayan Mountains.
(ii) The Northern Plains
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau
(iv) The Indian Desert
(v) The Coastal Plains
(vi) The Islands
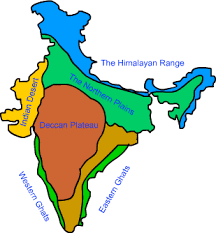 Physiographic divisions of India
Physiographic divisions of India
The Himalayan Mountains
- Young and Rugged: The Himalayas are relatively young in geological terms and are known for their rugged terrain. They are among the highest mountains in the world.
- Length and Width: The Himalayas stretch approximately 2400 kilometers across northern India, with a width varying from 400 kilometers to 150 kilometers, ranging from Kashmir in the west to Arunachal Pradesh in the east.
- Parallel Ranges:The Himalayas consist of three main parallel ranges:
- Great or Inner Himalayas (Himadri): This is the highest and most remote range, home to some of the tallest peaks, including Mount Everest and Kanchenjunga.
- Middle Himalayas (Himachal): This range is located south of the Great Himalayas and is known for its picturesque valleys, hill stations, and moderate elevations.
- Outer Himalayas (Shivalik): The southernmost range, the Shivaliks, is characterized by lower elevations and hilly terrain.
- Sections of the Himalayas:The Himalayas can be divided into four main sections, each with its unique features:
- Punjab Himalayas: Located between the Indus and Satluj Rivers, this region is known for its scenic beauty and cultural significance.
- Kumaon Himalayas: Situated between the Satluj and Kali Rivers, this area is famous for its trekking routes, lakes, and wildlife.
- Nepal Himalayas: This section lies between the Kali and Teesta Rivers and includes a significant portion of Nepal, known for its stunning landscapes and trekking opportunities.
- Assam Himalayas (Eastern Himalayas): Located between the Teesta and Dibang Rivers, this region is known for its biodiversity, tea plantations, and unique cultures.
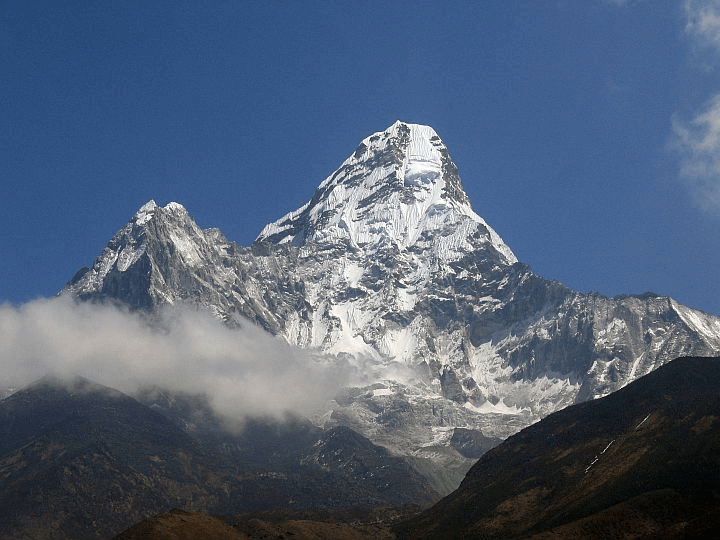 Himalayas
Himalayas
The Northern Plains
The Northern Plains of India are a vast and fertile region that extends across approximately 700,000 square kilometers. This region is roughly 2400 kilometers long and varies in width from 240 kilometers to 320 kilometers. The Northern Plains are primarily formed by the alluvial deposits brought down by the rivers flowing from the Himalayas. These rivers play a crucial role in soil formation, making the region highly fertile and suitable for agriculture.
The Northern Plains can be further divided into four distinct regions based on their terrain and soil characteristics:
- Bhabar: This region is located at the foothills of the Shivalik range and is characterized by a narrow belt of pebbles and gravel. The Bhabar region is known for its porous soil, which allows water to percolate quickly.
- Terai: Adjacent to the Bhabar region, the Terai is a wet and marshy area covered with dense forests. This region is known for its high water table and rich biodiversity. The Terai region is also suitable for agriculture due to its fertile soil.
- Bangar: The Bangar region is an older alluvial plain located above the floodplains. This area is characterized by its elevated land and is known for its clayey soil. The Bangar region is less fertile compared to the Khadar region but is still suitable for agriculture.
- Khadar: The Khadar region is situated in the floodplains and is characterized by younger alluvial soil. This soil is brought down by the rivers during floods, making it highly fertile and suitable for agriculture. The Khadar region is known for its high agricultural productivity.
The Peninsular Plateau
The Peninsular Plateau is a vast tableland that was formed due to the breaking and drifting of the ancient landmass Gondwanaland. This plateau is characterized by its hard and crystalline rocks, with the northern part being covered by a thin layer of soil. The Peninsular Plateau is home to a variety of minerals, making it an important region for mining and industrial activities.
The Peninsular Plateau can be broadly divided into two main regions: (i) Central Highlands and (ii) Deccan Plateau.
(i) Central Highlands: This region is located to the north of the Narmada River and includes several smaller plateaus and highlands. Some of the prominent features of the Central Highlands are:
- Bundelkhand:. region known for its historical significance and rich cultural heritage.
- Baghelkhand:. region characterized by its dense forests and diverse wildlife.
- Chhota Nagpur Plateau: Located further east, this plateau is drained by the Damodar River and is known for its rich mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, and mica.
(ii) Deccan Plateau: This triangular region is located south of the Narmada River and is bordered by the Western Ghats to the west and the Eastern Ghats to the east. The Deccan Plateau is known for its:
- Rich volcanic soil: The black soil, also known as Regur soil, is a key feature of the Deccan Plateau. This soil is highly fertile and is suitable for growing cash crops such as cotton, sugarcane, and tobacco.
- Unique geographical features: The Deccan Plateau is home to several hill stations, lakes, and rivers, making it a popular destination for tourism and agriculture.
The Indian Desert
The Indian Desert, also known as the Thar Desert, is characterized by its sandy plains and dunes. It is located at the western edge of the Aravalli Hills, which act as a natural barrier to the moisture-laden winds from the Arabian Sea. The desert is known for its extreme temperature variations, with scorching heat during the day and cooler temperatures at night.
The Indian Desert is home to several unique features:
- Crescent-shaped dunes: These dunes, known as barchans, are a prominent feature of the desert landscape. They are formed by the wind and can cover large areas of the desert.
- Luni River: The Luni River is the only major river in this region. However, it is an ephemeral river, meaning it is not always flowing. The river originates in the Aravalli Range and flows towards the Rann of Kutch, where it eventually disappears into the desert.
- Flora and fauna: Despite the harsh conditions, the Indian Desert is home to a variety of flora and fauna adapted to the arid environment. Some of the common plants include cacti, shrubs, and grasses, while animals such as camels, foxes, and various species of birds are also found in the region.
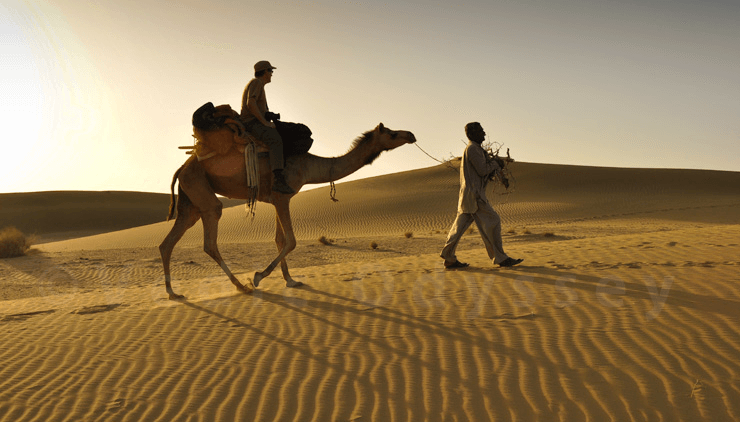 Indian Desert
Indian Desert
The Coastal Plains
The coastal plains of India are diverse and rich in geography.
Western Coastal Plain
- Konkan Coast: This region stretches from Mumbai to Goa along the western coastline.
- Kannad Plain: Located south of the Konkan coast, this plain is known for its agricultural richness.
- Malabar Coast: This coastal stretch runs from the northern part of Kerala to the southern tip of India, known for its lush greenery and backwaters.
Eastern Coastal Plain
- Northern Circars: This region extends along the northeastern part of the east coast, known for its beaches and agricultural land.
- Coromandel Coast: Stretching from northern Tamil Nadu to southern Andhra Pradesh, this coast is famous for its temples and cultural heritage.
The Islands
 Islands
Islands
- The Lakshadweep Islands group in the Arabian Sea is near Kerala.
- The Lakshadweep Islands were previously called Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindive.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a long chain of islands located in the Bay of Bengal.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are an elevated part of underwater mountains.
FAQs on Key Concepts - Physical Features of India - Chapter Notes For Class 9
| 1. What are the major physical features of India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Himalayas for India? |  |
| 3. How do the rivers of India contribute to the country's agriculture? |  |
| 4. What are the unique features of the Indian coastline? |  |
| 5. What are the major islands of India and what is their significance? |  |

















