NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Collection of Data
Q1: Frame at least four appropriate multiple-choice options for the following questions:
(i) Which of the following is the most important when you buy a new dress?
Ans:
a. Colour
b. Brand
c. Price
d. Size
(ii) How often do you use computers?
Ans:
a. Less than 1 hour a day
b. 1 to 3 hours a day
c. 3 to 5 hours a day
d. More than 5 hours
(iii) Which of the following newspaper/s do you read regularly?
Ans:
a. The Times of India
b. The Hindustan Times
c. Indian Express
d. The Tribune
(iv) Rise in the price of petrol is justified.
Ans:
a. Because of the rise in demand for petrol
b. Because of the rise in the supply of petrol
c. Because of the rise in petrol duty
d. Because of no close substitute for petrol
(v) What is the monthly income of your family?
Ans:
a. Less than Rs 10,000
b. Rs 10,000 to Rs 20,000
c. Rs 20,000 to Rs 30,000
d. More than Rs 30,000
Q2: Frame five two-way questions (with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’).
Ans:
a. Do you smoke?
b. Do you use cosmetics daily?
c. Have you ever been to any foreign country?
d. Are you satisfied with your present income?
e. Do you have a two-wheeler?
Q3: State whether the following statments are True or False:
(i) There are many sources of data.
Ans: False
There are only two sources of data- primary and secondary data sources. The collection of data from its original source is termed as primary source of data. On the other hand, the collection of data that has already been collected by somebody else in the past is termed as secondary source of data.
(ii) Telephone survey is the most suitable method of collecting data, when the population is literate and spread over a large area.
Ans: False
In a Telephone Survey, the investigator asks questions over the phone or mobile. So, there is no need for the person to read the survey form. Hence, this method of collecting information is the most suitable for the illiterate population spread over a large area. Moreover, this method is less time-consuming as the investigator does not need to visit each person individually from door to door.
(iii) Data collected by investigator is called the secondary data.
Ans: False
The data collected by an investigator is called the primary data, whereas, the data that is already in existence being collected by any other investigator is known as secondary data.
(iv) There is a certain bias involved in the non-random selection of samples.
Ans: True
Non-random selection of items obstructs the equal chance of every item of the Universe getting selected. Hence, there may be a high probability of involvement of personal biases of the investigator in the non-random sample selected.
(v) Non-sampling errors can be minimised by taking large samples.
Ans: False
The errors that are related to the collection of data are termed Non-sampling Errors. If the field of investigation or the population size is large, then the possibility of Non-sampling Errors also increases. So, Non-sampling Errors are maximised by taking large samples.
Q4: What do you think about the following questions? Do you find any problem with these questions? If yes, how?
(i) How far do you live from the closest market?
Ans: This question is ambiguous. The respondents will not be able to answer the question correctly. The correct question should be:
How many kilometres is your home away from the closest market?
a) Less than 1 km
b) Between 1 km to 2 km
c) More than 2 km
(ii) If plastic bags are only 5 percent of our garbage, should it be banned?
Ans: The particular question, ‘If plastic bags are only 5 per cent of our garbage, should it be banned?’ is too long which discourages people from completing the questionnaire. The correct question should be:
Do you think the use of plastic bags should be banned?
a) Yes b) No
(iii) Wouldn’t you be opposed to increase in price of petrol?
Ans: This question comprises two negatives which create confusion for the respondents and may lead to biased responses. A better question would be Would: you oppose the increase in the price of petrol?
(iv)
(a) Do you agree with the use of chemical fertilizers?
(b) Do you use fertilizers in your fields?
(c) What is the yield per hectare in your field?
Ans: The order or sequence of questions is incorrect. The series of questions should move from general to specific. The correct order would be
(a) What is the yield per hectare in your field?
(b) Do you use fertilizers in your fields?
(c) Do you agree with the use of chemical fertilizers?
Q5: You want to research on the popularity of Vegetable Atta Noodles among children. Design a suitable questionnaire for collecting this information.
Ans:

Q6: In a village of 200 farms, a study was conducted to find the cropping pattern. Out of the 50 farms surveyed, 50% grew only wheat. Identify the population and the sample here.
Ans: Population refers to the aggregate or the total items to be studied for an investigation. So, the population here is 200 farms. A sample is the subset of the population. In other words, a small set selected from the population for statistical study is referred to as a sample population. Out of 200 farms, only 50 farms were selected for the survey; therefore, the sample population is 50 farms.
Q7: Give two examples each of sample, population and variable.
Ans: The sample is the subset of the population. In other words, a small set selected from the population for statistical study is referred as a sample population. For example, to study the growth pattern of students, the heights of 50 students (sample) are recorded from a school of 500 students (population). Similarly, to record the level of sugar in the blood, a blood sample of 2000 people (sample) was taken from 20,000 people (population). Population refers to the aggregate or the total items to be studied for an investigation. In the above examples, 500 students and 20,000 people constitute the population. Variables are the characteristics of a sample or population that can be expressed in numbers such as height, income, age, etc.
Q8: Which of the following methods give better results and why?
(a) Census
(b) Sample
Ans: The sample Method gives better results than the Census Method due to the following reasons.
- Accuracy- Although the census method provides more accurate and reliable results as compared to the sampling method, however, in the sample method the errors can be easily located and rectified in the sampling methods due to the smaller number of items. Therefore, despite the sample method providing lesser reliable results (as not all units are studied) the sample method is efficient in the sense that errors committed can be easily located.
- Less Time and Energy Consuming- The Sample Method involves the study of fewer items of the universe. So, this method not only saves time but also the energy of the investigator.
- Cost Efficient- The cost of approaching each individual unit for interrogation and collection of data is comparatively lower due to the small size of the sample.
- Lesser Non-sampling Errors- The probability of Non-sampling Errors is also low as the sample size is smaller as compared to that of the Census Method.
- More Efficient- As the sample size is smaller, so small teams of enumerators can be formed. These small teams can easily be well-trained and supervised. Consequently, the team can work more efficiently than the team engaged in the Census Method.
Q9: Which of the following errors is more serious and why?
(a) Sampling error
(b) Non-sampling error
Ans: Non-sampling Errors are more serious than Sampling Errors because the latter can be minimised by taking a larger sample. Non-sampling Errors emerge due to the use of faulty means of collection of data, whereas, the Sampling Errors emerge due to the divergence between the estimated and the actual value of a parameter of a small-sized sample population. For example, errors due to personal biases, misinterpretation of results, miscalculations, etc. The Sampling Errors can be minimised by increasing the size of a small sample so that the difference between the actual and the estimated value is reduced. However, the Non-sampling Errors are difficult to rectify as it would require the selection of a new sample and conducting a fresh survey. Thus, Non-sampling Errors are more serious than Sampling Errors.
Q10: Suppose there are 10 students in your class. You want to select three out of them. How many samples are possible?
Ans: Population = 10
Number of possible samples=
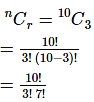
= 120
Thus, 120 samples are possible in the above scenario.
Q11: Discuss how you would use the lottery method to select 3 students out of 10 in your class?
Ans: The following method can be used while selecting 3 students out of 10 of the class. (i) Make ten paper slips of equal size.
- Write the name of each student on each slip.
- Make sure that no two slips contain the same names.
- Now, put all the slips in a box and mix them well.
- Draw three slips at random without replacement (i.e. one by one).
- The names of the three students that are written on the three slips drawn are considered as selected.
Q12: Does the lottery method always give you a random sample? Explain.
Ans: Yes, the lottery method always gives a random sample’s outcome. In a random sample, each individual unit has an equal chance of getting selected. Similarly, in a lottery method, each individual unit is selected at random from the population and thereby has an equal opportunity of getting selected. For example, in order to select a student as a monitor, the slips containing the names of all the students are mixed well, and then a slip is drawn out at random. In this case, all students in the class have an equal chance of getting selected. The probability of a student getting selected through the lottery method is the same as the probability of any one student being randomly selected.
Q13: Explain the procedure of selecting a random sample of 3 students out of 10 in your class, by using random number tables.
Ans: The procedure of selecting a random sample of 3 students out of 10 in a class is as follows:
- Assign a particular number between 1 to 10 to all the 10 students like, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10.
- Select a number randomly. Let us assume that the number selected is 05.
- Consult the Two-Digit Random Number Table, two numbers successive to the selected random number (i.e. 05) either horizontally or vertically are the remaining two students (i.e. 06 and 07)
Q14: Do samples provide better results than surveys? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: Samples provide better results than surveys. The advantages of samples over survey are as follows:
- Provides Reliable and Accurate Results-The Sample Method provides reliable and accurate results. This is because errors can be easily located and rectified in the sampling methods due to the smaller number of items.
- Less Time and Energy Consuming- The Sample Method involves the study of fewer items of the universe. So, this method not only saves time but also the energy of the investigator.
- Cost Efficient- The cost of approaching each individual unit for interrogation and collection of data is comparatively lower due to the small size of the sample.
- Lesser Non-sampling Errors- The probability of Non-sampling Errors is also low as the sample size is smaller.
- More Efficient- As the sample size is smaller, so small teams of enumerators can be formed. These small teams can easily be well-trained and supervised. Consequently, the team is more efficient than that of the team engaged in the surveys.
- Large Investigations- When the size of the population is very large and inapproachable, the method of sampling is the most feasible.
|
58 videos|215 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Collection of Data
| 1. What is the importance of collecting data in research? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods of data collection? |  |
| 3. How do you ensure the reliability and validity of collected data? |  |
| 4. What are primary and secondary data? |  |
| 5. What role does technology play in data collection? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|


















