Joints & Its Types | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
Joints
Joints aka articular surface can be defined as a point where two or more bones are connected in a human skeletal system. Cartilage is a type of tissue which keeps two adjacent bones to come in contact (or articulate) with each other. 3 Types of joints are Synovial Joints, Fibrous Joints, and Cartilaginous Joints. Joints help in bringing about movements in different parts of the body. Let us see the classification of joints and anatomy of different types of joints.
Classification of Joints
Joints can be classified in different ways depending on:
- The amount of mobility permitted by the joints
- Type of tissue connecting the bones
Each of these types can be further subdivided. Let’s look at each classification individually.
1. The amount of mobility permitted by the joint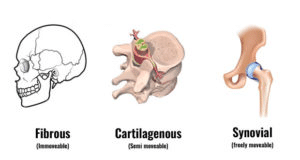 Depending on the degree of mobility permitted by the joint, we can classify them as:
Depending on the degree of mobility permitted by the joint, we can classify them as:
- Fixed Joint or Synarthroses: The word ‘syn-‘ tells us that the bones are fused and therefore permit minimal or no movement. These joints are fibrous joints which means that the binding tissue between two bones is ‘fibrous’ in nature. Example of a fixed joint is the sutures between skull bones.
- Slightly Movable Joint or Amphiarthroses: This joint permits slight mobility that is more than what is seen in a fixed joint. The binding tissue in this type of joint is cartilaginous in nature. Example of a slightly moveable joint is those found between intervertebral discs.
- Freely Moveable Joint or Synovial Joints: These joints permit maximum movement between the bones involved. They are also called as ‘diarthroses’ and are further classified into 6 types depending on the kind of movements possible.
Types of Synovial Joints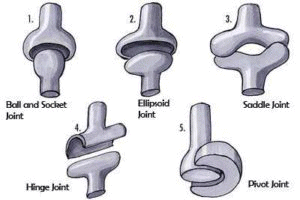
- Ball and socket joint: This kind of joint involves two bones. One of the bone has a large rounded end which fits into a cup-like socket of the other bone. This kind of joint is generally found in large bones such as the shoulder joint and hip joint. A ball and socket joint provides the greatest degree of movement among different kinds of joints including rotation, flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
- Hinge joint: This joint is said to be a very simple joint that allows movement only in one axis. It allows only two kinds of movements- flexion and extension. Example of this joint is the joints found between in the elbow and knee.
- Pivot joint: This type of joint allows rotation along one axis only. A common example of this type of joint is the atlantooccipital joint in the neck.
- Ellipsoid/gliding joint: This joint is very similar to the ball and socket joint but without rotation. It allows movements only in two axes. Example of this is the wrist joint.
- Saddle joint: It is similar to an ellipsoid joint which involves two bones- one of the bones has a convex surface while the other has a concave surface. The convex surface of one bone articulates with the concave of the other to allow limited rotational movement. A very classic example of this kind of a joint is the carpo-metacarpal joint in the thumb.
2. Type of Tissue Connecting the Bones
Based on the type of tissue connecting the bones, we can classify joints as:
- Fibrous: The tissue connecting the two bones is fibrous in nature.
- Cartilaginous: Cartilage forms the connecting tissue between two or more bones.
- Synovial: The two bones form a synovial cavity with synovial fluid which forms the connecting tissue.
Apart from movement and locomotion, joints also help stabilize the different parts of the body.
|
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|
FAQs on Joints & Its Types - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What are joints and why are they important in the human body? |  |
| 2. How many types of joints are there in the human body? |  |
| 3. What are the functions of synovial joints? |  |
| 4. How do arthritis and joint injuries affect the joints? |  |
| 5. How can one maintain healthy joints? |  |
















