Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Notes > Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) > Mind Map: Neural Control & Coordination
Mind Map: Neural Control & Coordination | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) PDF Download
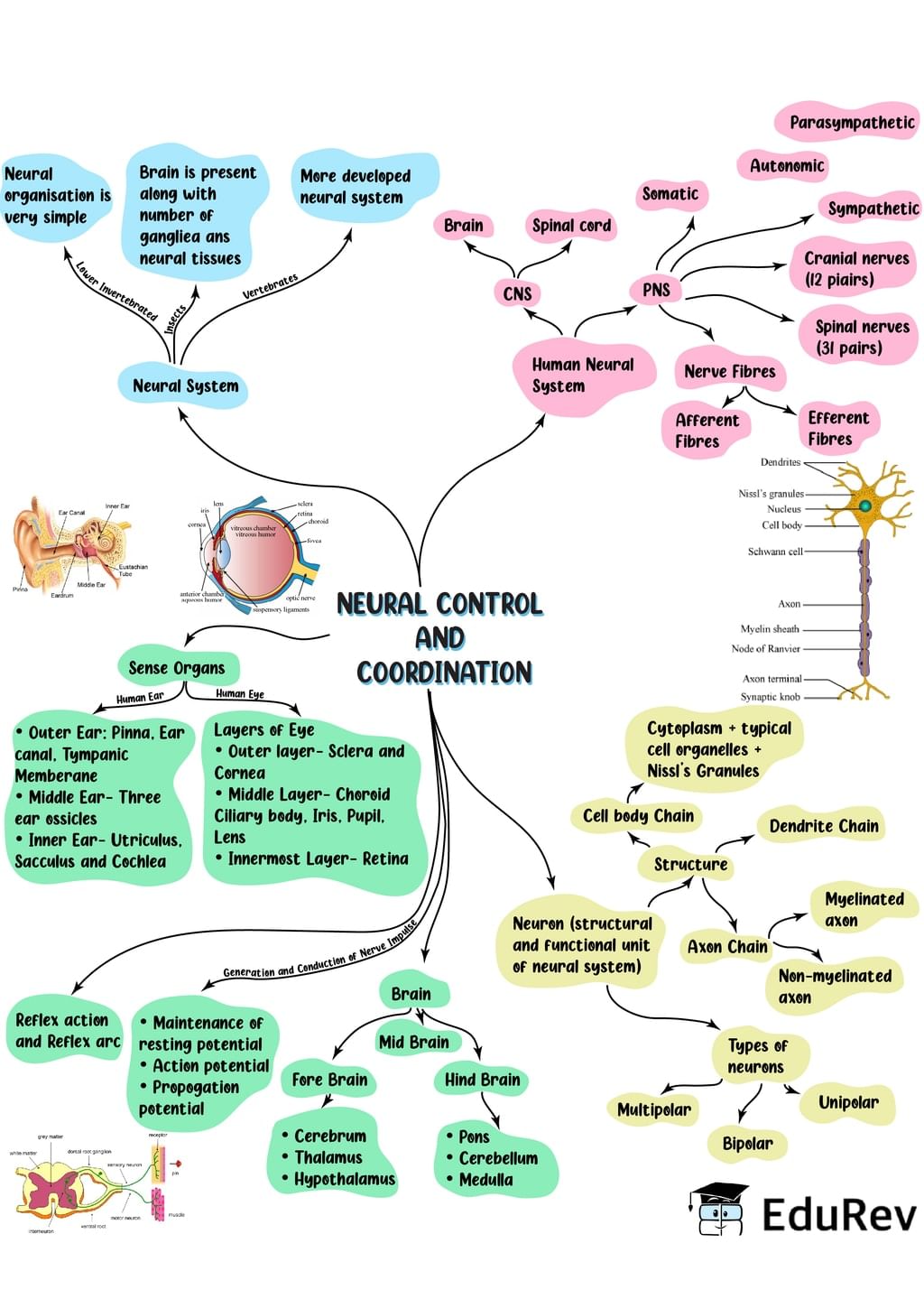
The document Mind Map: Neural Control & Coordination | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science) is a part of the Class 11 Course Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science).
All you need of Class 11 at this link: Class 11
FAQs on Mind Map: Neural Control & Coordination - Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 11 (Science)
| 1. What is neural control and coordination? |  |
Ans. Neural control and coordination refers to the process by which the nervous system receives and interprets information from the environment, integrates it with internal stimuli, and coordinates the response of the body. It involves the transmission of electrical signals through neurons and the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters to communicate between different parts of the body.
| 2. How does the nervous system transmit signals? |  |
Ans. The nervous system transmits signals through specialized cells called neurons. Neurons have a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. When a stimulus is received, it triggers an electrical impulse that travels along the axon. At the end of the axon, the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal in the form of neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, the tiny gap between neurons, and bind to receptors on the next neuron, thus transmitting the signal.
| 3. What is the role of the central nervous system in neural control and coordination? |  |
Ans. The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in neural control and coordination. It consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is responsible for processing sensory information, initiating responses, and coordinating complex behaviors. The spinal cord acts as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body. It also controls reflex actions, which are rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli.
| 4. How does the endocrine system interact with neural control and coordination? |  |
Ans. The endocrine system and neural control and coordination are closely interconnected. While the nervous system uses electrical impulses to transmit signals quickly, the endocrine system uses hormones to regulate bodily functions over longer periods. The hypothalamus, a part of the brain, acts as a bridge between the nervous and endocrine systems. It produces hormones that control the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, which in turn regulates various other endocrine glands throughout the body.
| 5. How does the autonomic nervous system regulate involuntary functions? |  |
Ans. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for regulating involuntary functions of the body, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It has two main divisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic division prepares the body for "fight or flight" responses, increasing heart rate, dilating blood vessels, and releasing stress hormones. The parasympathetic division, on the other hand, promotes "rest and digest" responses, slowing heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and enhancing digestion. These two divisions work in balance to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Related Searches

















