Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Maths Olympiad Class 6 > NCERT Summary: Basic Geometrical Ideas
Basic Geometrical Ideas Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
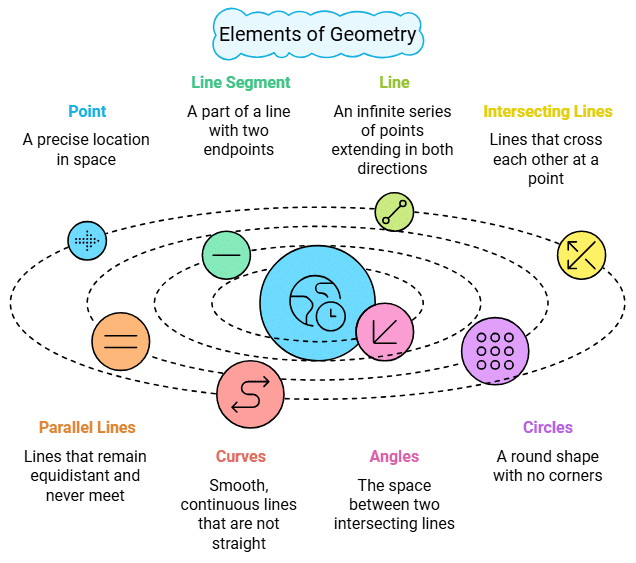
Introduction
- The term ‘Geometry’ is the English equivalent of the Greek word ‘Geometron’. ‘Geo’ means Earth and ‘metron’ means Measurement.
Point
- A point determines a location and has no length, breadth and height. Usually denoted by a single capital letter like A, B, C.
Line Segment
- A part of a line is called a line segment. It is the shortest distance between two points.
A Line
- A line is a straight one- dimensional figure that has no thickness and extends endlessly in both directions.
Intersecting Lines
- If two lines have one common point, they are called intersecting lines.
Parallel Lines
- Two parallel lines in a plane do not meet each other.
- The perpendicular distance between two parallel lines is the same throughout.
Curves
- Any drawing (straight or non straight) done without lifting the pencil. This means, in mathematics, a line is also a curve.
- A simple curve is one that does not cross itself.
- A curve is said to be closed if its ends are joined.
- A curve is said to be open if its ends are open.
- Polygon is a simple closed curve made up of line segments. Sides: The line segment forming a polygon.
- Vertex: The meeting point of a pair of sides.
- Adjacent sides: Any two sides with a common end point.
- Adjacent vertices: The end points of the same side of a polygon.
- Diagonal: The line joining any two non-adjacent vertices.
Angles
- An angle is made up of two rays starting from a common initial point.
- The two rays forming the angle are called the arms or sides of the angle.
- The common initial point is the vertex of the angle.
- A triangle is a three-sided polygon.
- A four sided polygon is a quadrilateral. It has 4 sides and 4 angles.
Circles
- A circle is a simple closed curve which is not a polygon.
- The path of a point moving at the same distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is the centre.
- Radius: A line segment that connects the centre to a point on the circle.
- Diameter: A line segment passing through the centre and having its end points on the circle.
- Chord: A line segment connecting any two points on a circle.
- A diameter is a chord passing through the centre of a circle. It is a longest chord of a circle.
- Arc: A portion of a circle.
- Sector: A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc on one side and a pair of radii on the other two sides.
- Segment: A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc and chord.
- Circumference: The distance around a circle.
- Semi-circle: A diameter of a circle divides it into two equal parts, each part is a semi-circle.
The document Basic Geometrical Ideas Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 4 is a part of the Class 6 Course Maths Olympiad Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Geometrical Ideas Summary Class 6 Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What are the basic geometrical ideas covered in the NCERT chapter? |  |
Ans. The NCERT chapter on Basic Geometrical Ideas covers fundamental concepts such as points, lines, line segments, rays, angles, and various types of shapes including polygons and circles. It also discusses properties of these shapes and the relationships between different geometrical figures.
| 2. How can we differentiate between a line segment and a ray? |  |
Ans. A line segment is a part of a line that has two endpoints, while a ray has one endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction. This distinction is important in understanding basic geometrical constructions and properties.
| 3. What are the different types of angles mentioned in the chapter? |  |
Ans. The chapter discusses various types of angles including acute angles (less than 90 degrees), right angles (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees), and straight angles (exactly 180 degrees). Each type has specific characteristics and applications in geometry.
| 4. Why are polygons classified into different types? |  |
Ans. Polygons are classified into different types based on the number of sides they have, such as triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), and so on. This classification helps in understanding their properties, such as angles and side lengths, which are crucial for solving geometrical problems.
| 5. How do we construct basic geometrical figures using a compass and ruler? |  |
Ans. To construct basic geometrical figures like circles and triangles, a compass is used to draw arcs and circles, while a ruler helps in drawing straight lines and measuring lengths. The chapter provides step-by-step instructions for accurate constructions, emphasizing the importance of precision in geometry.
Related Searches





















