Chapter 20 - Mensuration - I (Part - 3), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 20.28:
Question 1:
Find the area of the pentagon shown in fig. 20.48, if AD = 10 cm, AG = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AF = 5 cm, BF = 5 cm, CG = 7 cm and EH = 3 cm.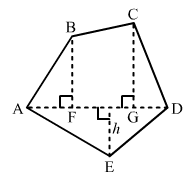
ANSWER:
The given figure is: 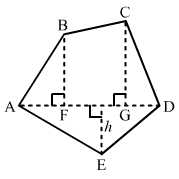
Given:AD = 10 cm, AG = 8 cm, AH = 6 cm, AF = 5 cmBF = 5 cm, CG = 7 cm, EH = 3 cm
∴ FG = AG - AF = 8 - 5 = 3 cm
And, GD = AD - AG = 10 - 8 = 2 cm
From given figure:Area of Pantagon = (Area of triangle AFB) + (Area of trapezium FBCG) + (Area of triangle CGD) + (Area of triangle ADE)
= (1/2 × AF × BF) + [1/2 × (BF + CG) × (FG)] + (1/2 × GD × CG) + (1/2 × AD × EH)
= (1/2 × 5 × 5) + [1/2 × (5 + 7) × (3)] + (1/2 × 2 × 7) + (1/2 × 10 × 3)
= (25/2) + [36/2] + (14/2) + (30/2)
= 12.5 + 18 + 7 + 15
= 52.5 cm²
Question 2:
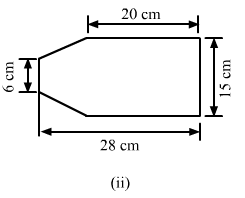
Find the area enclosed by each of the following figures [Fig. 20.49 (i)-(iii)] as the sum of the areas of a rectangle and a trapezium: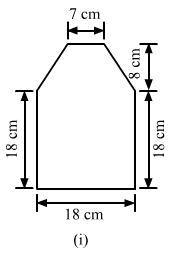
ANSWER:



(i)The given figure can be divided into a rectangle and a trapezium as shown below:
From the above firgure:
Area of the complete figure = (Area of square ABCF) + (Area of trapezium CDEF)
= (AB × BC) + [1/2 × (FC + ED) × (Distance between FC and ED)]
= (18 × 18) + [1/2 × (18 + 7) × (8)]
= 324 + 100
= 424 cm²
(ii)The given figure can be divided in the following manner:
From the above figure:
AB = AC-BC = 28-20 = 8 cm
So that area of the complete figure = (area of rectangle BCDE) + (area of trapezium ABEF)
= (BC × CD) + [1/2 × (BE + AF) × (AB)]
= (20 × 15) + [1/2 × (15 + 6) × (8)]
= 300 + 84
= 384 cm²
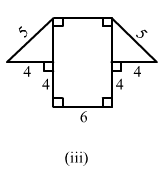
(iii)The given figure can be divided in the following manner:
From the above figure:
EF = AB = 6 cm
Now, using the Pythagoras theorem in the right angle triangle CDE:
52 = 42 + CE2
CE2 = 25-16 = 9
CE = √9 = 3 cm
And, GD = GH + HC + CD
= 4 + 6 + 4 = 14 cm
∴ Area of the complete figure = (Area of rectangle ABCH) + (Area of trapezium GDEF)
= (AB × BC) + [1/2 × (GD + EF) × (CE)]
= (6 × 4) + [1/2 × (14 + 6) × (3)]
= 24 + 30 = 54 cm²
Question 3:
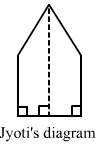
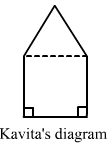
There is a pentagonal shaped park as shown in Fig. 20.50. Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways.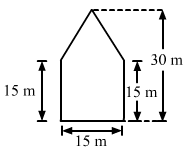
Find the area of this park using both ways. Can you suggest some another way of finding its areas?
ANSWER:
A pentagonal park is given below: 


Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways.
(i) Jyoti divided is into two trapeziums as shown below:
Jyoti and Kavita divided it in two different ways.
It is clear that the park is divided in two equal trapeziums whose parallel sides are 30 m and 15 m.
And, the distance between the two parallel lines: 15/2 = 7.5 m
∴ Area of the park = 2 × (Area of a trapazium)
= 2 × [1/2 × (30 + 15) × (7.5)] = 337.5 m²
(ii)Kavita divided the park into a rectangle and a triangle, as shown in the figure.
Here, the height of the triangle = 30-15 = 15 m
∴ Area of the park = (Area of square with sides 15 cm) + (Area of triangle with base 15 m and altitude 15 m)
= (15 × 15) + (1/2 × 15 × 15)
= 225 + 112.5
= 337.5 m²
PAGE NO 20.29:
Question 4:
Find the area of the following polygon, if AL = 10 cm, AM = 20 cm, AN = 50 cm, AO = 60 cm and AD = 90 cm.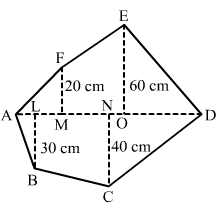
ANSWER:
The given polygon is: The given polygon is: 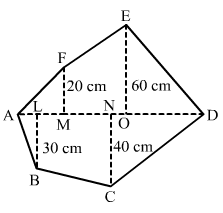
Given: AL = 10 cm, AM = 20 cm, AN = 50 cm
AO = 60 cm, AD = 90 cm
Hence, we have the following: MO = AO-AM = 60-20 = 40 cm
OD = AD-AO = 90-60 = 30 cm
ND = AD-AN = 90-50 = 40 cm
LN = AN-AL = 50-10
= 40 cm
From given figure:
Area of Polygon = (Area of triangle AMF) + (Area of trapezium MOEF) + (Area of triangle EOD) + (Area of triangle DNC) + (Area of trapezium NLBC) + (Area of triangle ALB)
=(1/2 × AM × MF) + [1/2 × (MF + OE) × (OM)] + (1/2 × OD × OE) + (1/2 × DN × NC) + [1/2 × (LB + NC) × (NL)] + (1/2 × AL × LB)
= (1/2 × 20 × 20) + [1/2 × (20 + 60) × (40)] + (1/2 × 30 × 60) + (1/2 × 40 × 40) + [1/2 × (30 + 40) × (40)] + (1/2 × 10 × 30)
= 200 + 1600 + 900 + 800 + 1400 + 150
= 5050 cm2
Question 5:
Find the area of the following regular hexagon.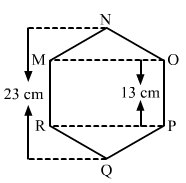
ANSWER:
The given figure is: The given figure is:
Join QN.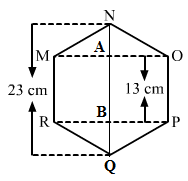
It is given that the hexagon is regular.
So, all its sides must be equal to 13 cm.
Also, AN = BQ
QB + BA + AN = QN
AN + 13 + AN = 23
2AN = 23-13
= 10AN = 10/2 = 5 cm
Hence, AN = BQ = 5 cm
Now, in the right angle triangle MAN:
MN² = AN² + AM²
132 = 52 + AM²
Am² = 169-25 = 144
AM =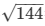 = 12cm
= 12cm
∴ OM = RP = 2 × AM = 2 × 12 = 24 cm
Hence, area of the regular hexagon = (area of triangle MON) + (area of rectangle MOPR) + (area of triangle RPQ)
= (1/2 × OM × AN) + (RP × PO) + (1/2 × RP × BQ)
= (1/2 × 24 × 5) + (24 × 13) + (1/2 × 24 × 5)
= 60 + 312 + 60
= 432 cm²
FAQs on Chapter 20 - Mensuration - I (Part - 3), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is Mensuration? |  |
| 2. How is mensuration useful in real life? |  |
| 3. What are the different formulas used in mensuration? |  |
| 4. How can I calculate the volume of irregular shapes? |  |
| 5. Can you give an example of how mensuration is used in construction? |  |
















