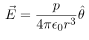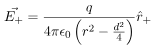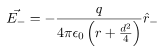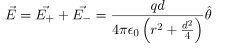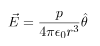Additional Information about Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole for JAMB Preparation
Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole Free PDF Download
The Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the JAMB exam.
These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
With the help of these notes, you can grasp complex subjects quickly, revise important points easily,
and reinforce your understanding of key concepts. The study notes are presented in a concise and easy-to-understand manner,
allowing you to optimize your learning process. Whether you're looking for best-recommended books, sample papers, study material,
or toppers' notes, this PDF has got you covered. Download the Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole now and kickstart your journey towards success in the JAMB exam.
Importance of Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole
The importance of Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole cannot be overstated, especially for JAMB aspirants.
This document holds the key to success in the JAMB exam.
It offers a detailed understanding of the concept, providing invaluable insights into the topic.
By knowing the concepts well in advance, students can plan their preparation effectively.
Utilize this indispensable guide for a well-rounded preparation and achieve your desired results.
Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole Notes
Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole Notes offer in-depth insights into the specific topic to help you master it with ease.
This comprehensive document covers all aspects related to Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole.
It includes detailed information about the exam syllabus, recommended books, and study materials for a well-rounded preparation.
Practice papers and question papers enable you to assess your progress effectively.
Additionally, the paper analysis provides valuable tips for tackling the exam strategically.
Access to Toppers' notes gives you an edge in understanding complex concepts.
Whether you're a beginner or aiming for advanced proficiency, Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole Notes on EduRev are your ultimate resource for success.
Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole JAMB Questions
The "Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole JAMB Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the
JAMB exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge
their understanding of the exam topics. These questions cover the entire syllabus, ensuring comprehensive preparation.
The guide includes previous years' question papers for students to familiarize themselves with the exam's format and difficulty level.
Additionally, it offers subject-specific question banks, allowing students to focus on weak areas and improve their performance.
Study Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole on the App
Students of JAMB can study Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole alongwith tests & analysis from the EduRev app,
which will help them while preparing for their exam. Apart from the Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole,
students can also utilize the EduRev App for other study materials such as previous year question papers, syllabus, important questions, etc.
The EduRev App will make your learning easier as you can access it from anywhere you want.
The content of Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole is prepared as per the latest JAMB syllabus.
If
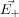 and
and  be the electric field at point P due to the positive and the negative charges separately then the total electric field
be the electric field at point P due to the positive and the negative charges separately then the total electric field  at Point P can be calculated by using the superposition principle.
at Point P can be calculated by using the superposition principle.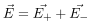
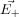 and
and  are along
are along  and
and  respectively. This is the most general form of the electric field due to a dipole. However, we will express this vector in terms of radial and inclination vectors as shown in the diagram below.
respectively. This is the most general form of the electric field due to a dipole. However, we will express this vector in terms of radial and inclination vectors as shown in the diagram below.In order to calculate the electric field in the polar coordinate, we will use the expression of the electric potential due to an electric dipole which we have calculated earlier.
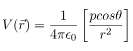
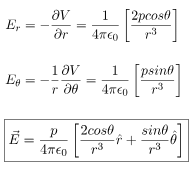
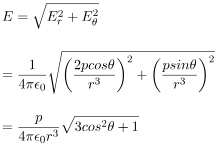
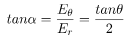
In this case, the test point P is on the axis of the dipole. Consequently θ= 0 or π. The electric field at point P is
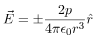
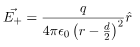
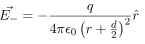
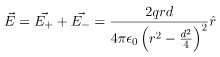
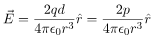
In this case, the test point P is on the perpendicular bisector of the dipole. Consequently θ= π/2. The electric field at point P is