Subphylum - Vertebrata | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
Introduction
- One of the ways life is classified is through the presence or absence of the vertebrate.
- Vertebrates and invertebrates evolved from a common ancestor that was speculated to have lived around 600 million years ago.
- Evidence of true vertebrates began to appear 525 million years ago and ever since then, vertebrates have branched off into a long lineage that includes armoured fish and giant sauropods to woolly mammoths and modern man.
 Subphylum: Vertebrata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Characteristics of Vertebrata
– In these animals, notochord is completely or partially replaced by vertebral column.
Vertebral column is made up of many vertebrae.
– Brain is covered by a protective covering made up of bones or cartilage, calledcranium.
– There is a prominant head and well developed and complicated brain.
– Nerve cord remain enclosed within the vertebral column.
– Single or paired nostrils.
– 2 - 3 semicircular canals in each internal ear.
– Animals are unisexual.
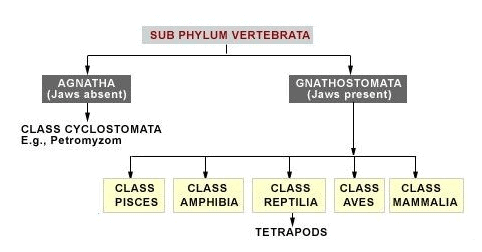
Classification of Vertebrata
Sub-phylum Vertebrata is further divided into two division.
1) Agnatha (2) Gnathostomata
1. Agnatha (Jawless) :
– Jaws are absent in these animals .
– Notochord persistant.
– Mouth at the anterior end of body, round, funnel shaped and suctorial.
– Paired appendages (fins) are absent.
– Single nostril. (Monorhynous)
– cold blooded.
– Genital ducts are absent.
– Two semi - circular canals are found in internal ear.
– One median pineal eye is found along with lateral eyes on head.
Group Agnatha is divided into two classes. (Only one is living)
Class-Cyclostomata :
– Mostly marine, except some fresh water species.
– These are parasite as well as scavanger.
– Also called as Jawless fishes (false - fishes).
– Body long, thin, tubular, tail is flat.
– Skin soft, smooth and scaleless.
– Mouth is rounded, sucker like and biting - eating type.
– Three eyes are found on the head, one medain pineal eye and two lateral eyes.
– Only one Nostril (Monorhynous).
– Internal ear contains one or two semicircular canals. Internal ear works as statoreceptor only. ie. Organ of balance.
– Gill clefts are 6 to 15 pairs.
– Digestive system is without stomach. Intestine has spiral typhlosole.
– Notochord and vertebral column both are present. Cranium and Vertebral column is made up of cartilage.
– Bones are absent.
– Heart is two - chambered. It is called Venous - heart.
– Kidneys are protonephric or mesonephric type.
– Paired fins absent. Dorsal median and tail fin is present.
– Tail is protocercal type. In this type of tail, notochord is extended at the last end of tail and tail fin is divided into two equal dorsal and ventral lobes.
– Animals unisexual, fertilization external, larval stage absent,
– In Petromyzon - Ammocoete larva is present.
Petromyzon or Lamprey :
– It is a living fossil.
– Shows Anadromous migration.
Larva Ammocoete is considered as connecting link between Cephalochordata and Cyclostomata.
– It has wrinkled lips just like an old woman.
– It usually remain attached with the gills of host.
– It has Archaenephric kidney in young ones i.e. which can filter blood and coelomic fluid.
2. Gnathostomata
– Mouth is surrounded by true jaws.
– Vertebral column well developed.
– Movement by paired fins or legs.
– Gonads are paired, genital ducts are present.
– 3 Semi circular canals are found in internal ear.
– Pineal eye is absent.
– Animals are unisexual.
– Gills or lungs are meant for respiration.
– Gnathostomata is classified into two super classes on the basis of locomotory organs, respiratory organs, heart and blood vascular system.
Super Class : - [1] Pisces [2] Reptilia [3] Amhibia [4] Aves [5] Mammalia
Myxine or Hag fish : -
Ectoparasite (Sanguivorous) on true fishes. Many teeth are found in mouth.
No exoskeleton.
|
225 videos|175 docs|156 tests
|
FAQs on Subphylum - Vertebrata - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What are the main characteristics of Vertebrata? |  |
| 2. How are Vertebrata classified? |  |
| 3. What are the sub-phyla of Vertebrata? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the vertebral column in Vertebrata? |  |
| 5. How do vertebrates differ from invertebrates? |  |





















