NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths - (Ex: 14.1 to 14.3): Practical Geometry
Exercise 14.1
Question 1: Draw a circle of radius 3.2 cm.
Answer 1:
Steps of construction:
(a) Open the compass for the required radius of 3.2 cm.
(b) Make a point with a sharp pencil where we want the centre of circle to be.
(c) Name it O.
(d) Place the pointer of compasses on O.
(e) Turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle.
Hence, it is the required circle.
Question 2: With the same centre O, draw two circles of radii 4 cm and 2.5 cm.
Answer 2:
Steps of construction:
(a) Marks a point ‘O’ with a sharp pencil where we want the centre of the circle.
(b) Open the compasses 4 cm.
(c) Place the pointer of the compasses on O.
(d) Turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle.
(e) Again open the compasses 2.5 cm and place the pointer of the compasses on D.
(f) Turn the compasses slowly to draw the second circle.
Hence, it is the required figure.
Question 3: Draw a circle and any two of its diameters. If you join the ends of these diameters, what is the figure obtained? What figure is obtained if the diameters are perpendicular to each other? How do you check your answer?
Answer 3:
(i) By joining the ends of two diameters, we get a rectangle. By measuring, we find AB = CD = 3 cm, BC = AD = 2 cm i.e., pairs of opposite sides are equal and also ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90o i.e., each angle is of 90o.
Hence, it is a rectangle.
(ii) If the diameters are perpendicular to each other, then by joining the ends of two diameters, we get a square. By measuring, we find that AB = BC = CD = DA = 2.5 cm, i.e., all four sides are equal. Also ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90o, i.e., each angle is of 90o.
Hence, it is a square.
Question 4: Draw any circle and mark points A, B and C such that:
(a) A is on the circle.
(b) B is in the interior of the circle.
(c) C is in the exterior of the circle.
Answer 4:
(i) Mark a point ‘O’ with sharp pencil where we want centre of the circle.
(ii) Place the pointer of the compasses at ‘O’. Then move the compasses slowly to draw a circle.
(a) Point A is on the circle.
(b) Point B is in interior of the circle.
(c) Point C is in the exterior of the circle.
Question 5: Let A, B be the centres of two circles of equal radii; draw them so that each one of them passes through the centre of the other. Let them intersect at C and D.
Examine whether 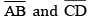 are at right angles.
are at right angles.
Answer 5:
Draw two circles of equal radii taking A and B as their centre such that one of them passes through the centre of the other. They intersect at C and D. Join AB and CD.
Yes, AB and CD intersect at right angle as ∠COB is 90o .
Exercise 14.2
Question 1: Draw a line segment of length 7.3 cm, using a ruler.
Answer 1:
Steps of construction:
(i) Place the zero mark of the ruler at a point A.
(ii) Mark a point B at a distance of 7.3 cm from A.
(iii) Join AB.
Hence, is the required line segment of length 7.3 cm.
Question 2: Construct a line segment of length 5.6 cm using ruler and compasses.
Answer 2: Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line 'l'. l Mark a point A on this line.
(ii) Place the compasses pointer on zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point up to 5.6 cm mark.
(iii) Without changing the opening of the compasses. Place the pointer on A and cut an arc 'l' at B. is the required line segment of length 5.6 cm.
Question 3:
Construct of length 7.8 cm. From this, cut off
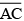 of length 4.7 cm. Measure
of length 4.7 cm. Measure 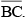
Answer:
Steps of construction:
(i) Place the zero mark of the ruler at A.
(ii) Mark a point B at a distance 7.8 cm from A.
(iii) Again, mark a point C at a distance 4.7 from A.
Hence, by measuring 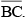 , we find that BC = 3.1 cm.
, we find that BC = 3.1 cm.
Question 4: Given of length 3.9 cm, construct
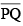 such that the length of
such that the length of 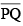 is twice that of
is twice that of . Verify by measurement.
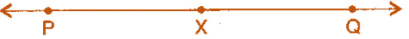 (Hint: construct
(Hint: construct 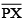 such that length of
such that length of 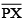 = length of
= length of ; then cut off
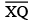 such that
such that 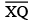 also has the length of
also has the length of .)
Answer 4:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line 'l'.
(ii) Construct 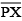 such that length of
such that length of 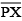 = length of
= length of 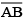
(iii) Then cut of 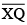 such that
such that 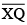 also has the length of
also has the length of 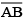 .
.
(iv) Thus the length of 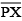 and the length of
and the length of 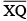 added together make twice the length of
added together make twice the length of 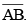
Verification: Hence, by measurement we find that PQ = 7.8 cm
= 3.9 cm + 3.9 cm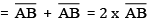
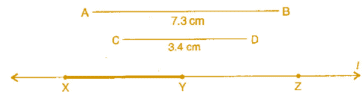
Question 5: Given 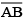 of length 7.3 cm and
of length 7.3 cm and 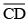 of length 3.4 cm, construct a line segment
of length 3.4 cm, construct a line segment 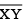 such that the length of
such that the length of 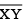 is equal to the difference between the lengths of
is equal to the difference between the lengths of  Verify by measurement.
Verify by measurement.
Answer 5:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line 'l' and take a point X on it.
(ii) Construct 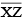 such that length
such that length 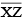 = length of
= length of 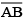 = 7.3 cm
= 7.3 cm
(iii) Then cut off 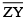 = length of
= length of 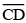 = 3.4 cm
= 3.4 cm
(iv) Thus the length of 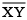 = length of
= length of 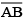 – length of
– length of 
Verification:
Hence, by measurement we find that length of 
= 3.9 cm
= 73. cm – 3.4 cm
=  -
- 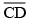
Exercise 14.3
Question 1:
Draw any line segment 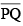 . Without measuring
. Without measuring 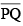 , construct a copy of
, construct a copy of 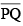 .
.
Answer 1:
Steps of construction:
(i) Given 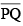 whose length is not known.
whose length is not known.
(ii) Fix the compasses pointer on P and the pencil end on Q. The opening of the instrument now gives the length of 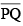 .
.
(iii) Draw any line 'l'. Choose a point A on 'l'. Without changing the compasses setting, place the pointer on A.
(iv) Draw an arc that cuts 'l' at a point, say B.
Hence, 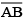 is the copy of
is the copy of 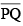 .
.
Question 2:
Given some line segment 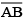 , whose length you do not know, construct
, whose length you do not know, construct 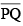 such that the length of
such that the length of 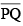 is twice that of
is twice that of 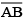 .
.
Answer 2:
Steps of construction:
(i) Given 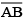 whose length is not known.
whose length is not known.
(ii) Fix the compasses pointer on A and the pencil end on B. The opening of the instrument now gives the length of 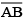 .
.
(iii) Draw any line 'l'. Choose a point P on 'l'. Without changing the compasses setting, place the pointer on Q.
(iv) Draw an arc that cuts 'l' at a point R.
(v) Now place the pointer on R and without changing the compasses setting, draw another arc that cuts 'l' at a point Q.
Hence, 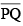 is the required line segment whose length is twice that of AB.
is the required line segment whose length is twice that of AB.
|
82 videos|273 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths - (Ex: 14.1 to 14.3): Practical Geometry
| 1. What is practical geometry? |  |
| 2. What are some essential tools required for practical geometry? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a ruler and a compass? |  |
| 4. What are some common constructions in practical geometry? |  |
| 5. How is practical geometry useful in real-life situations? |  |

















