Permanent Magnets & Electromagnets | Physics for JAMB PDF Download
Permanent Magnets
Commonly steel is used to make a permanent magnet because steel has high residual magnetism and high coercivity.
Electromagnets
Electromagnets are made of soft iron because area of hysteresis loop for soft iron is small. Therefore, energy loss is small for a cycle of magnetisation and demagnetisation.
(Permanent magnets are made by the materials such as steel, for which residual magnetism as well as coercivity should be high. Electromagnets are made by the materials such as soft iron for which residual magnetism is high, coercivity is low and hysteresis loss is low).
Important Points
- Magnetic length = 5 / 6 * geometric length of magnet.
- About 90% of magnetic moment is due to spin motion of electrons and remaining 10% of magnetic moment is due to the orbital motion of electrons.
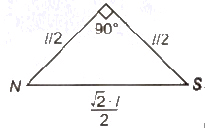
- When a magnet having magnetic moment M is cut into two equal parts
(i) Parallel to its length
M’ = m / 2 * l = M / 2

(ii) Perpendicular to its length
M’ = m * l / 2 = M / 2
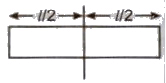
- When a magnet of length I, pole strength m and of magnetic moment M is turned into a semicircular arc then it new magnetic moment
M’ = m * 2R = m * 2 * 1 / π (πR = I)
= 2M / π (M = m * l)
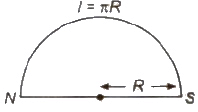
- A thin magnet of moment M is turned into an arc of 90°. Then new magnetic moment
M’ = 2√2M / π
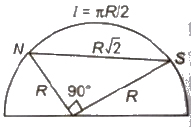
- A thin magnet of moment M is turned at mid point 90°.Then new magnet moment
M’ = M / √2
- A thin magnet of moment M is turned into an arc of 60°. Then new magnetic moment
M = 3M / π
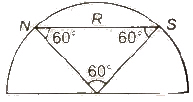
- A thin magnet of moment M is bent at mid point at angle 60°. Then new magnetic moment.
M’ = M / 2
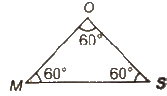
- Original magnet MOS is bent at O, the mid point at 60°.All sidesare equal
- The mutual interaction force between two small magnets of moments M1 and M2 is given by
F = K 6M1M2 / d4 in end- on position.
Here,d denotes the separation between magnets.
- Magnetic length = 5 / 6 * geometric length of magnet.
- Cause of diamagnetism is orbital motion and cause of paramagnetism is spin motion of electrons. Cause of ferromagnetism lies in formation of domains.
- The perpendicular bisector of magnetic axis is known as neutral axis of magnet. Magnetism at neutral axis is zero and at poles is maximum.
- For steel coercivity is large. However, retentivity is comparatively smaller in case of steel. So, steel is used to make permanent magnets.
- For soft iron, coercivity is very small and area of hysteresis loop is small. So, soft iron is an ideal material for making electromagnets.
|
263 videos|277 docs|238 tests
|
FAQs on Permanent Magnets & Electromagnets - Physics for JAMB
| 1. What is the difference between a permanent magnet and an electromagnet? |  |
| 2. Can a permanent magnet be turned into an electromagnet? |  |
| 3. What are some common applications of permanent magnets? |  |
| 4. How can an electromagnet be made stronger? |  |
| 5. Can an electromagnet be turned off? |  |
















