NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Wastewater story | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Which of the following is wastewater?
(a) Water trickling from a damaged tap.
(b) Water coming out of a shower.
(c) Water flowing in a river.
(d) Water coming out of laundry.
Ans: d
Explanation:
Water discharged during after routine works like washing clothes, flushing toilet, cleaning utensils makes the water dirty. This water is called as wastewater. Water coming out of the damaged tap, water coming out of shower and water flowing in a river are not dirty hence water coming out of a laundry is the right answer.
Q.2. Sewage is mainly a
(a) liquid waste.
(b) solid waste.
(c) gaseous waste.
(d) mixture of solid and gas.
Ans: a
Explanation:
Sewage water is the wastewater that includes domestic and industrial liquid wastes. It contains various suspended solids and harmful microorganisms.
Q.3. Which of the following is/are products of wastewater treatment?
(a) Biogas
(b) Sludge
(c) Both biogas and sludge
(d) Aerator
Ans: c
Explanation:
During wastewater, treatment water is allowed to settle in a large tank which is sloped towards the middle. Solids like faeces settle at the bottom and are removed with a scraper. This is the sludge. A skimmer removes the floatable solids like oil and grease. Water so cleared is called clarified water. The sludge is transferred to a separate tank where it is decomposed by the anaerobic bacteria. The biogas produced in the process can be used as fuel or can be used to produce electricity.
Q.4. An open-drain system is a breeding place for which of the following.
(a) Flies
(b) Mosquitoes
(c) Organisms which cause diseases
(d) All of these
Ans: d
Explanation:
The opening draining system causes problems with the foul smell. The open drainage system is the breeding sources for mosquitos and flies. The open drainage system also helps the growth of disease-causing organisms.
Q.5. Water polluted by various human activities causes a number of water-borne diseases. Which of the following is not a waterborne disease?
(a) Cholera
(b) Typhoid
(c) Asthma
(d) Dysentry
Ans: c
Explanation:
Asthma is airborne disease whereas Cholera, Typhoid and dysentery are spread by contaminated water and food.
Q.6. Pick from the following one chemical used to disinfect water.
(a) Chlorine
(b) Washing soda
(c) Silica
(d) Coal
Ans: a
Explanation:
Chorine is used to killing harmful organisms and the process of adding chlorine is called as chlorination.
Q.7. The system of a network of pipes used for taking away wastewater from homes or public buildings to the treatment plant is known as
(a) sewers.
(b) sewerage.
(c) transport system.
(d) treatment plant.
Ans: b
Q.8. Which of the following is a part of inorganic impurities of the sewage?
(a) Pesticides
(b) Urea
(c) Phosphates
(d) Vegetable waste
Ans: c
Explanation:
Pesticides, urea and vegetable waste ate the organic waste that acts as impurities in sewage water whereas phosphates are the inorganic impurities present in sewage.
Q.9. In a filtration, plant water is filtered using layers of
(a) sand and clay.
(b) clay and fine gravel.
(c) sand and fine gravel.
(d) sand, fine gravel and medium gravel.
Ans: d
Explanation:
During wastewater treatment wastewater is allowed to enter a grit of sand, fine gravel and medium gravel. Here the speed of wastewater is slowed down to allow sand, fine gravel and medium gravel to settle down.
Q.10. Which of the following is not a source of wastewater?
(a) Sewers
(b) Homes
(c) Industries
(d) Hospitals
Ans: a
Explanation:
Sewers are a network of big and small pipes that carries sewage from the point of being produced to the point of disposal, i.e. treatment plant.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Why are open drains a concern?
Ans: Because it creates unhygienic and unsanitary conditions because of which it leads to the spread of disease.
Q.2. State whether the following statements are True or False. In case a statement is false, write the correct statement.
(a) Sewage is a solid waste which causes water pollution and soil pollution.
(b) Used water is wastewater.
(c) Wastewater could be reused.
(d) Where underground sewerage systems and refuse disposal systems are not available, the high-cost on-site sanitation system can be adopted.
Ans:
a) False- Sewage is a liquid waste which causes water pollution and soil pollution
b) True
c) True
d) False- Where underground sewerage systems and refuse disposal systems are not available, the low-cost on-site sanitation system can be adopted.
Q.3. How are open drains harmful to human health?
Ans: The opening draining system causes problems with the foul smell. An open drainage system is the breeding sources for mosquitos and flies. The open drainage system also helps the growth of disease-causing organisms. Hence drains are harmful to human health.
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Name two inorganic impurities present in sewage.
Ans: Nitrates, Phosphates
Q.2. Animal waste, oil and urea are some of the organic impurities present in sewage. Name two more organic impurities present in sewage.
Ans: Fruits, Vegetables
Q.3. Name two alternative arrangements for sewage disposal where there is no sewerage system.
Ans: (i) Septic tanks (ii) Composting pits
Q.4. A man travelling in a train threw an empty packet of food on the platform. Do you think this is a proper waste disposal method? Elaborate.
Ans: No, what man does is not a proper disposal method. One must always put the waste in a nearby dustbin or carry it until a proper place to dispose of food packet is found.
Q.5. Why should we not throw
(a) used tea leaves into the sink?
(b) cooking oil and fats down the drain?
Ans:
a) Used tea leaves may block the sink.
b) Cooking oil and fats gets harden and block the sink.
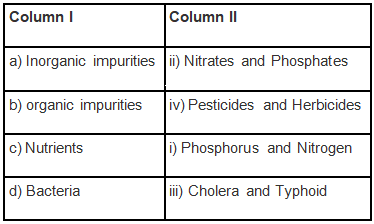
Q.6. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II with reference to sewage.
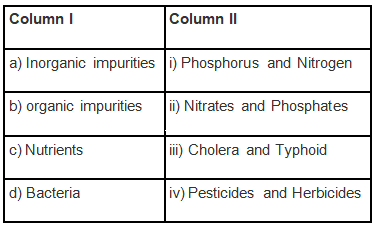
Ans:
Q.7. Given below is a jumbled sequence of the processes involved in a wastewater treatment plant. Arrange them in their correct sequence.
(a) Sludge is scraped out and skimmer removes the floating grease.
(b) Water is made to settle in a large tank with a slope in the middle.
(c) Large objects like plastic bags are removed by passing wastewater through bar screens.
(d) Sand, grit and pebbles are made to settle by decreasing the speed of incoming wastewater.
(e) Wastewater enters a grit and sand removal tank.
Ans:
(c) Large objects like plastic bags are removed by passing wastewater through bar screens.
(e) Wastewater enters a grit and sand removal tank.
(d) Sand, grit and pebbles are made to settle by decreasing the speed of incoming wastewater.
(b) Water is made to settle in a large tank with a slope in the middle.
(a) Sludge is scraped out and skimmer removes the floating grease.
Q.8. Three statements are provided here which define the terms –
(a) sludge
(b) sewage and
(c) wastewater.
Pick out the correct definition for each of these terms.
(a) The settled solids that are removed in wastewater treatment with a scraper.
(b) Water from the kitchen used for washing dishes.
(c) Wastewater released from homes, industries, hospitals and other public buildings.
Ans:
- Sludge
- Wastewater
- Sewage
Q.9. A mixture (x) in water contains suspended solids, organic impurities, inorganic impurities (a), nutrients (b), disease-causing bacteria and other microbes. Give names for (x), (a) and (b)?
Ans:
(x) sewage
(a) nitrates, phosphates and metal
(b) phosphorus and nitrogen
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. What are the different types of inorganic and organic impurities generally present in sewage?
Ans:
(i) Inorganic impurities – nitrates, phosphates and metals.
(ii) Organic impurities – fruit and vegetable wastes, oil, urea, human faeces, animal waste, pesticides and herbicides.
Q.2. The terms sewage, sewers and sewerage are interlinked with each other. Can you explain, how?
Ans: The terms ‘sewage, ‘sewers’ and ‘sewerage are interlinked with each other because sewage is a mixture of wastewater coming out of homes and other places. Sewers are pipes which carry sewage and sewerage is a network of sewage carrying pipes.
Q.3. Fill in the blanks in the following statements using words given in the box.
air, handpumps, cholera, water, large, ground
A very _________ number of our people defecate in the open. It may cause _________ pollution and soil pollution. Both the surface water and _________ water get polluted. _________ water is the source for wells, tubewells and _________. Thus it becomes the most common route for _________ borne diseases like _________, dysentery, etc.
Ans:
A very large number of our people defecate in the open. It may cause water pollution and soil pollution. Both the surface water and ground water get polluted. Ground water is the source for wells, tube-wells and handpumps. Thus it becomes the most common route for water borne diseases like cholera, dysentery, etc.
Q.4. Describe various steps of cleaning wastewater in a wastewater treatment plant.
Ans: Treatment of wastewater involves physical, chemical, and biological processes, which remove physical, chemical and biological matter that contaminates the wastewater.
- Wastewater is passed through bar screens. Large objects like rags, sticks, cans, plastic packets, napkins are removed.
- Water then goes to a grit and sand removal tank. The speed of the incoming wastewater is decreased to allow sand, grit and pebbles to settle down
- The water is then allowed to settle in a large tank which is sloped towards the middle. Solids like faeces settle at the bottom and are removed with a scraper. This is the sludge. A skimmer removes the floatable solids like oil and grease. Water so cleared is called clarified water. The sludge is transferred to a separate tank where it is decomposed by the anaerobic bacteria. The biogas produced in the process can be used as fuel or can be used to produce electricity.
- Air is pumped into the clarified water to help aerobic bacteria to grow. Bacteria consume human waste, food waste, soaps and other unwanted matter still remaining in clarified water.
After several hours, the suspended microbes settle at the bottom of the tank as activated sludge. The water is then removed from the top. The activated sludge is about 97% water. The water is removed by sand drying beds or machines. Dried sludge is used as manure, returning organic matter and nutrients to the soil. The treated water has a very low level of organic material and suspended matter. It is discharged into a sea, a river or into the ground. Nature cleans it up further. Sometimes it may be necessary to disinfect water with chemicals like chlorine and ozone before releasing it into the distribution system.
Q.5. Think and suggest some ways to minimise waste and pollutants at their source, taking your home as an example.
Ans:
- Do not throw used tea leaves, solid food remains, etc. in the drain. Throw them in the dustbin.
- Chemicals like medicines, paints, insecticides, etc. should not be thrown in the drain, as they increase the pollution load of the sewage.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Wastewater story - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is the wastewater story? |  |
| 2. Why is wastewater treatment important? |  |
| 3. How is wastewater treated? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of wastewater recycling? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to wastewater management? |  |





















