NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Synthetic Fibres & Plastics | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Pick the synthetic fibre out of the following?
(a) Cotton
(b) Nylon
(c) Jute
(d) Wool
Ans: b
Explanation:
Cotton and Jute are from plant sources, Wool is of animal source whereas Nylon is a synthetic fibre.
Q.2. Which of the following is a source of rayon?
(a) Wool
(b) PET
(c) Wood pulp
(d) Silk
Ans: c
Explanation:
Rayon is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp.
Q.3. Polycot is obtained by mixing
(a) nylon and wool
(b) polyester and wool
(c) nylon and cotton
(d) polyester and cotton
Ans: d
 Polycot Fabric
Polycot Fabric
Q.4. Which is a thermosetting plastic?
(a) Melamine
(b) Polythene
(c) PVC
(d) Nylon
Ans: a
Explanation:
Thermosetting plastics when moulded once can not be softened by heating. Examples are bakelite and melamine.
Q.5. The material similar to silk in appearance is
(a) Nylon
(b) Rayon
(c) Polyester
(d) Terylene
Ans: b
Explanation:
Rayon is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp. Rayon is cheaper than silk and can be woven like silk.
Q.6. The most suitable material for the preparation of handles of cooking utensils is
(a) Polythene
(b) PVC
(c) Nylon
(d) Bakelite
Ans: d
Explanation:
Bakelite is a bad conductor of heat and it does not get soft on heating hence Bakelite is used to prepare handles of cooking utensils.
Q.7. Which of the following is not a common property of plastics?
(a) Non-reactive
(b) Light in weight
(c) Durable
(d) Good conductor of electricity
Ans: d
Explanation:
Plastic is a bad conductor of electricity.
Q.8. Which of the following represents the correct match for items in Column A with those in Column B.
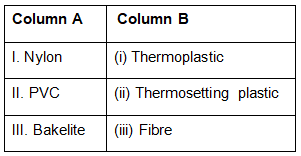
choose the option
(a) I-(ii), II-(iii), III-(i)
(b) I-(iii), II-(i), III-(ii)
(c) I-(ii), II-(i), III-(iii)
(d) I-(iii), II-(ii), III-(i)
Ans: c
Q.9. Which of the following groups contain all synthetic substances?
(a) Nylon, Terylene, Wool
(b) Cotton, Polycot, Rayon
(c) PVC, Polythene, Bakelite
(d) Acrylic, Silk, Wool
Ans: c
Explanation:
In option a) and c) there is wool which is extracted from an animal source.
In option b) there is cotton which is from a plant source.
Hence the answer is (c) PVC, Polythene, Bakelite.
Q.10. The material which is commonly used for making kitchen containers is
(a) PVC
(b) Acrylic
(c) Teflon
(d) PET
Ans: d
Explanation:
PET or Polyethylene tetra thalate is lightweight and it is used in making kitchen containers.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Cotton is a natural polymer. What is its chemical name?
Ans: The chemical name of cotton is cellulose.
Q.2. A synthetic fibre which looks like silk is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp. It is, therefore, known as artificial silk. What is its common name?
Ans: Rayon is known as artificial silk.
Q.3. Terrycot is made by mixing two types of fibres. Write the names of the fibres.
Ans: Terrycot is prepared by mixing terylene and cotton.
 Terrycot Fabric
Terrycot Fabric
Q.4. Plastic articles are available in all possible shapes and sizes. Can you tell why?
Ans: It is very easy to make moulds from plastic hence it is available in all possible shapes and sizes.
Q.5. Plastic is used for making a large variety of articles of daily use and these articles are very attractive. But it is advised to avoid the use of plastic as far as possible. Why?
Ans: Plastic is not bio-degradable and disposing of plastic waste is a major issue. Hence it is advised to avoid the use of plastic as far as possible.
Q.6. Why is it not advisable to burn plastic and synthetic fabrics?
Ans: Burning of plastic releases toxic gases which pollutes the air. Hence it not advisable to burn plastic and synthetic fabrics.
Q.7. Select the articles from the following list which are biodegradable.
(a) Paper
(b) Woollen clothes
(c) Wood
(d) Aluminium can
(e) Plastic bag
(f) Peels of vegetables
Ans:
a. Paper
b. Woollen clothes
c. Wood
d. Peels of vegetables
Q.8. A bucket made of plastic does not rust like a bucket made of iron. Why?
Ans: Plastic is a non-reactive material. To form rust it should react with water and oxygen. Hence plastic does not form rust.
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Rohit took with him some nylon ropes when he was going for rock climbing. Can you tell why he selected nylon ropes instead of ropes made of cotton or jute?
Ans: Because Nylon ropes are strong, flexible and elastic when compared to jute and cotton ropes.
Acrylic blankets are cheap, light in weight, more durable and are available in a variety of colours and designs. They can be easily washed at home.
Q.2. A lady went to the market to buy a blanket. The shopkeeper showed her blankets made of acrylic fibres as well as made of wool. She preferred to buy an acrylic blanket. Can you guess why?
Ans: Lady prefers acrylic blanket over wool blankets because acrylic blankets are cheap, light in weight, more durable and are available in a variety of colours and designs. They can be easily washed at home.
Q.3. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a thermoplastic and is used for making toys, chappals, etc. Bakelite is a thermosetting plastic and is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc. Can you write the major difference between these two types of plastics?
Ans: On heating, Thermoplastics get deformed and they can be easily bent. Whereas Thermosetting plastics cannot be softened by heating.
Q.4. Fill in the blanks.
(i) A polymer is a chain of many small units joined together which are called ______.
(ii) The synthetic fibres are also known as ______ fibres.
(iii) The first fully synthetic fibre was ______.
(iv) A fibre similar to wool is ______.
(v) A plastic used for making crockery is ______.
Ans:
(i) A polymer is a chain of many small units joined together which are called monomers.
(ii) The synthetic fibres are also known as man-made fibres.
(iii) The first fully synthetic fibre was Nylon.
(iv) A fibre similar to wool is acrylic.
(v) A plastic used for making crockery is melamine.
Q.5. Match items in List A with the items of list B.
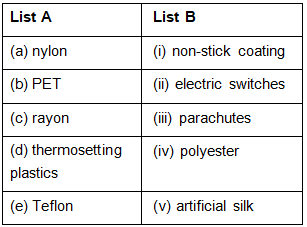
Ans:
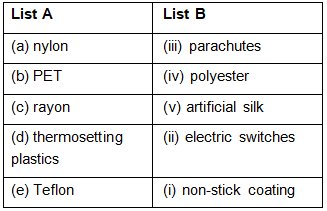
Q.6. Unscramble the jumbled words given below, related to synthetic materials.
(a) anory
(b) lopmery
(c) relyteen
(d) laspict
(e) yespolter
(f) felton
Ans:
(a) rayon
(b) polymer
(c) terylene
(d) plastic
(e) polyester
(f) Teflon
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Indicate whether the following statements are True or False. Also, write false statements in their correct form.
(i) The fabric terry wool is obtained by mixing terylene and wool.
(ii) Synthetic fibres do not melt on heating.
(iii) It is risky to wear synthetic clothes while working in the kitchen.
(iv) Most of the plastics are biodegradable.
Ans:
i) True
ii) False- Synthetic fibres melt on heating.
iii) True because synthetic clothes melt on exposure to heat
iv) False- Plastics are non-biodegradable
Q.2. Write the importance of synthetic polymers in our life.
Ans: Following are the points to justify the importance of synthetic polymers in our life.
- Nylon It is used for making ropes for rock climbing, fishing nets, raincoats, parachutes and tyre cords, etc.
- Acrylic It is used for sweaters, tracksuits, linings for boots and gloves and In furnishing fabrics and carpets.
- Terylene It is used in the textile industry to make clothes like sarees, tapestry and dress material. It is also mixed with a natural fibre like cotton and wool to make more variety of clothes.
- Plastics It is used to store food item, water, milk, pickles, dry food, etc. Plastic containers seem most convenient. This is because of lightweight, low price, good strength and easy handling as compared to metals. Plastics are used in cars, air crafts and spacecraft.
Q.3. Despite being very useful it is advised to restrict the use of plastic. Why is it so? Can you suggest some methods to limit its consumption?
Ans: Plastic is a non-biodegradable material which poses a serious threat to nature. Disposing of plastic waste is the biggest problem we face to regret the use of plastics. Plastics cause soil pollution and air pollution on burning.
Usage of plastic should be reduced and used plastic should be recycled and reused to reduce its consumption.
Q.4. Write an activity to show that synthetic fibres are stronger than the cotton fibres.
Ans: Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm length. Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it as shown in Figure below. At the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed in it. Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the thread. This weight indicates the strength of the fibre. Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, polyester, silk and nylon.
 An iron stand with a thread hanging from the clamp
An iron stand with a thread hanging from the clamp
Q.5. Complete the crossword given below with the help of clues

Ans: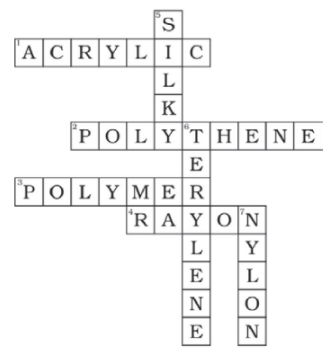
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Synthetic Fibres & Plastics - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7
| 1. What are synthetic fibres? |  |
| 2. How are synthetic fibres different from natural fibres? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using synthetic fibres? |  |
| 4. What are the disadvantages of using synthetic fibres? |  |
| 5. How are plastics related to synthetic fibres? |  |
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|


















