Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Microorganisms : Friend or Foe
Q.1. Explain how microbes are useful to us in our day-to-day life.
Ans.
- Microorganisms are beneficial to us in various ways; they not only prepare curd, bread, cake, wine and medicines for us but are also used to increase soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Thus we called them friendly.
- Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill the dough (a mixture of atta or maida and some sugar and water) and increase its volume. This is the basis of using yeast in the baking industry.
- Fermentation is the process of food processing in which sugar is converted into alcohol by the action of microorganisms. This process is used to produce alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer, and cider. For this purpose, yeast is grown on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juices, etc.
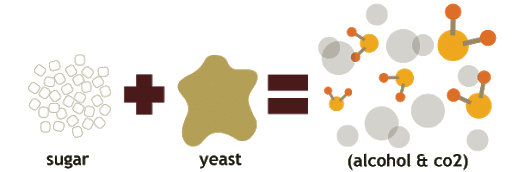 Fermentation
Fermentation - Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms and they are prepared from microorganisms.
Example: streptomycin, tetracycline and penicillin are some of the antibiotics prepared from microorganisms like fungi and bacteria.
Q.2. Explain how microbes are harmful to us.
Ans.
- Microorganisms are harmful in many ways. Some microorganisms cause diseases in human beings, plants and animals. Such disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.
- Some microorganisms spoil food, clothing and leather. Some of the common communicable diseases caused by microorganisms affecting humans are cholera, common cold, chickenpox and tuberculosis.
- Many microorganisms not only cause diseases in humans and plants but also in animals anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
- Disease-causing microorganisms in plants like wheat, rice, potato, sugarcane, orange, apple, and others reduce the yield of crops. Food poisoning is caused due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
Q.3. What are the major precautions one should follow while taking antibiotics?
Ans. The following precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics:
- Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. And one must finish the course prescribed by the doctor.
- Antibiotics must be avoided when not needed or in the wrong doses.
- Antibiotics taken unnecessarily may kill beneficial bacteria in the body.
Q.4. What are the major groups of microorganisms explain each group with their harmful and useful effects in our lives.
Ans. Microorganisms are broadly divided into five major groups:
(i) Bacteria
- Bacteria are single-celled microscopic organisms. They can survive in all types of environments, ranging from ice-cold climates to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.
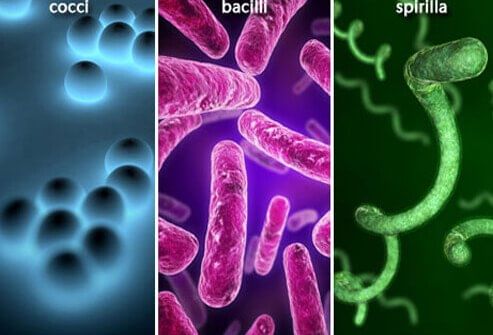 Bacteria
Bacteria - Bacteria always live in colonies. They are of spiral shape or rod shape. Bacteria play an important role in our lives; some bacteria are useful, whereas others are harmful and cause diseases.
- Bacteria are involved in the making of cheese and pickles. Lactobacillus bacteria promote the formation of curd. Antibiotics are also made from bacteria.
- Apart from these diseases like tuberculosis and typhoid are caused due to bacteria.
(ii) Virus
- Viruses are a microscopic infectious agent that acts as non-living outside the host cell and inside the host cell becomes living, and show reproduction.
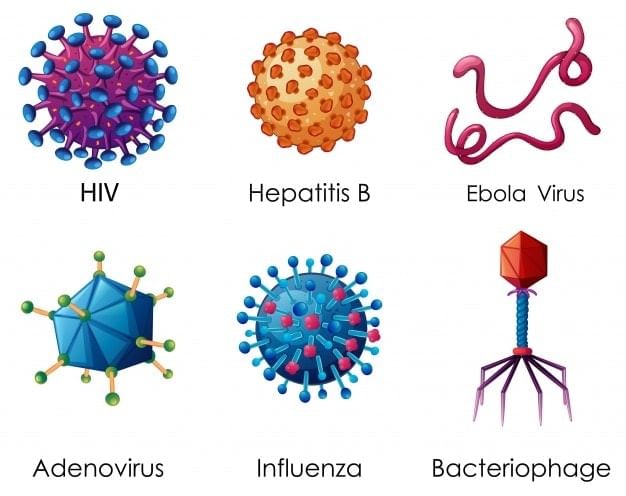 Virus
Virus - It can affect all kinds of organisms, including animals, plants, and bacteria. Common ailments like colds, coughs, and influenza (flu) are caused by viruses; serious diseases like chickenpox and polio are also caused by viruses.
(iii) Protozoa
- Protozoa had been defined as unicellular protists with animal-like behavior like movement. They move around with whip-like tails called flagella, and hair-like structures called cilia.
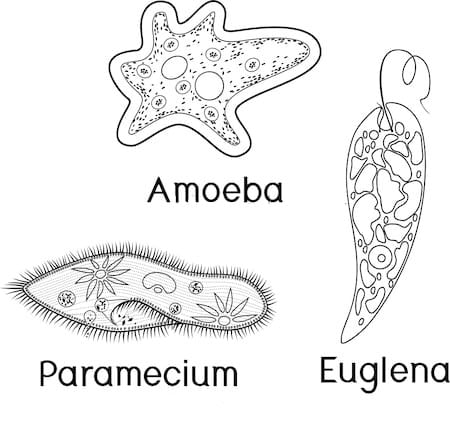 Protozoa
Protozoa - It is responsible for causing diseases like dysentery and malaria in human beings.
(iv) Algae
- Algae are a very large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms.
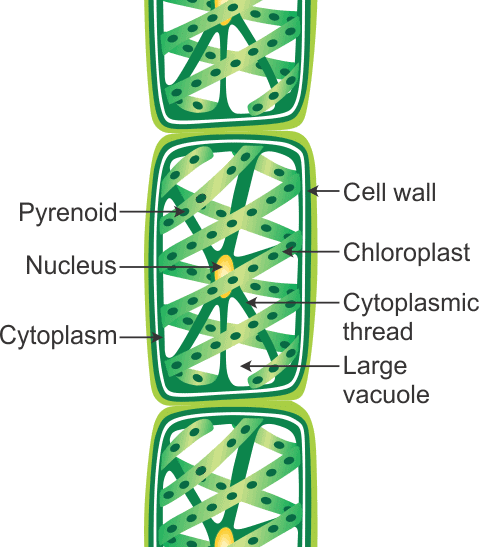 Spyrogyra
Spyrogyra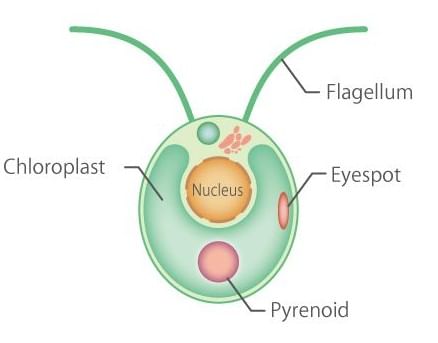 Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas - Most are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into many distinct organs found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine forms are called seaweeds.
(v) Fungi
- Fungi are non-green plants. They cannot synthesize their own food.
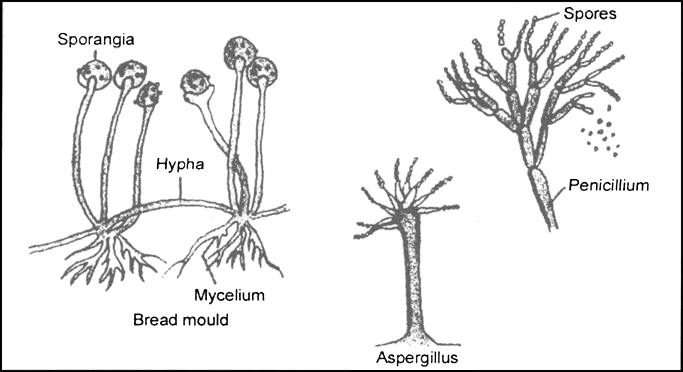 Fungi
Fungi - They have to depend for their food on others. Most fungi take their food from dead organic matter. Some live on other organisms as parasites.
Q.5. What are carriers of disease-causing microbes? Explain with the help of two examples.
Ans. There are some insects and animals that carry disease-causing microorganisms like a housefly and mosquitoes. Such insects and animals are called carriers of disease-causing microbes.
Examples:
(i) Housefly: The housefly is a carrier of microorganisms. They sit on the garbage and animal excreta. The pathogens stick to their bodies. When these flies sit on uncovered food, they may transfer the pathogens. Whoever eats the contaminated food is likely to get sick. So, we should not consume uncovered food.
(ii) Female Anopheles Mosquito: It is the carrier of the parasite of malaria. Female Aedes mosquito acts as a carrier of the dengue virus. We can control malaria by keeping the surroundings clean and dry.  Female Anopheles MosquitoQ.6. Explain causative microorganisms, mode of transmission, and preventive measures of human diseases like Tuberculosis, Measles, Chickenpox, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid, Hepatitis B Malaria etc.
Female Anopheles MosquitoQ.6. Explain causative microorganisms, mode of transmission, and preventive measures of human diseases like Tuberculosis, Measles, Chickenpox, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid, Hepatitis B Malaria etc.
Ans. Some of the common diseases affecting humans, their mode of transmission, and few general methods of prevention are given in the following table: 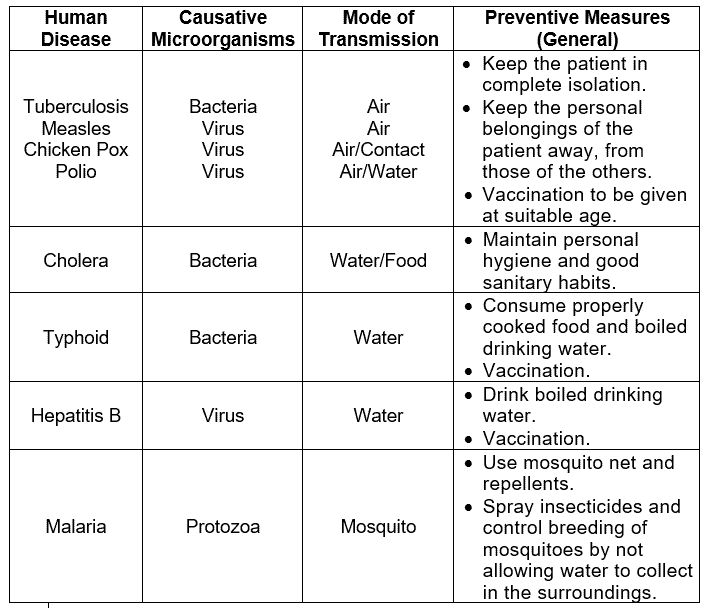 Q.7. Name some common plant diseases, their causative microorganisms, and mode of transmission with the help of the figures.
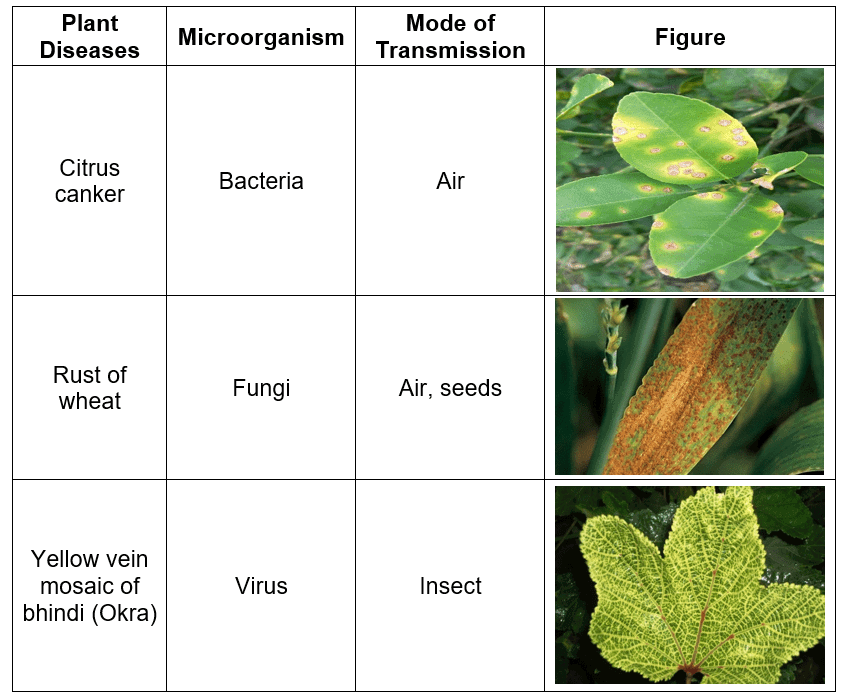
Q.7. Name some common plant diseases, their causative microorganisms, and mode of transmission with the help of the figures.
Ans.
Table: Some common plant diseases caused by microorganisms.
Q.8. What are food preservatives? Explain some common food preservatives.
Ans. The chemical substances that are used to check or stop the growth of harmful microorganisms in food are called food preservatives. These food preservatives keep the edible food materials protected from the invasion of microorganisms, which can spoil the food.
Some common food preservatives are:
- Salt: Common salt is used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes and tamarind etc.
- Sugar: Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved by sugar. Sugar reduces the moisture content, which inhibits the growth of bacteria that spoil food.
- Oil: Edible oils are used as preservatives in vegetables and pickles. Oil does not allow the moisture to surface, thus preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Vinegar: It is used to preserve fruits, vegetables, fish, meat and pickles.
Q.9. Explain the nitrogen cycle with a schematic diagram.
Ans.
- Certain bacteria and blue-green algae present in the soil fix the atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into compounds of nitrogen. These can be utilised by plants by taking them from the soil through their root system.
- Nitrogen is then used for the synthesis of plant proteins and other compounds. Animals use these proteins and other nitrogen compounds as food.
- When animals and plants die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert these nitrogenous waste into usable nitrogen compounds which are used by plants again.
- Some other bacteria convert some part of them to free nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As a result percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains constant.
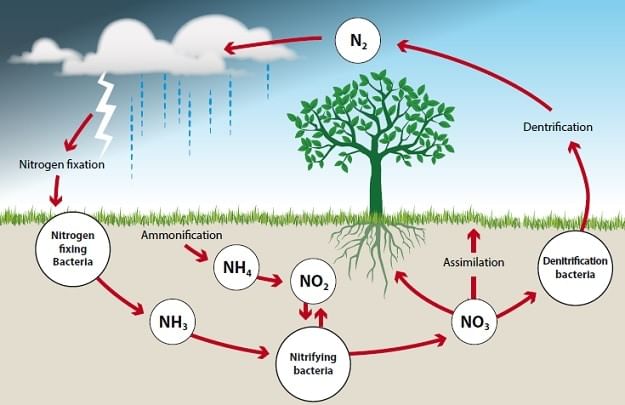 Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
Q.10. Explain the uses of Bacteria, Fungi and Algae.
Ans.
Uses of Bacteria
- They are used to increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
- Some bacteria are used to produce antibiotics.
- Lactobacillus bacteria convert milk into curd. It also helps in the digestion of food.
- Some bacteria help in many functions of our body.
Uses of Fungi
- Yeast is used to prepare alcohol and vinegar by fermentation.
- Yeast is used to produce bread, cheese, beer, wine etc.
- Mushrooms are eaten as food.
- Yeast is used to produce vitamin B.
- Penicillin is an antibiotic formed by a fungus called Penicillium.
Uses of Algae
- Algae are used to make jellies.
- They are used in soups, ice creams, jellies and jams as a thickening agent.
- Chlorella is used to obtain proteins.
- Silica from Diatoms is used in toothpaste.
Q.11. Explain some indications which help to detect the spoilage of food.
Ans.
Indications to detect spoilage of food:
- Odour: The unpleasant and foul smell indicates that food is spoiled.
- Discolouration: The presence of microorganisms in the food results in discolouration of food black. Some fungi and moulds cause a change in original color.
- Taste: Sometimes, the cooked food becomes sour. It is due to the production of acids by the action of certain bacteria.
- Sliminess: Sometimes, the food becomes slimy. It is also due to the action of certain bacteria, thread-like slims are also caused due to moulds.
- Gas formation: Due to the action of bacteria, gases like carbon dioxide are produced. They also spoil the food by making it swell or become spongy.
|
90 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Question Answers - Microorganisms : Friend or Foe
| 1. How do microorganisms benefit humans? |  |
| 2. Can all microorganisms be harmful to humans? |  |
| 3. How can we prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms? |  |
| 4. What are examples of harmful microorganisms? |  |
| 5. How do antibiotics work to combat harmful microorganisms? |  |

















