RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3I - Squares and Square Roots | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Q.1. Evaluate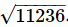
Ans. Using long division method: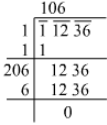
∴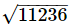 =106
=106
Q.2. Find the greatest number of five digits which is a perfect square. What is the square root of this number?
Ans. The greatest 5 digit number is 99999.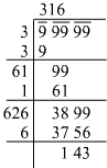
316 <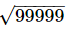 < 317
< 317
3162=99856
Thus, this is the greatest 5 digit number.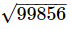 = 316
= 316
Q.3. Find the least number of four digits which is a perfect square. What is the square root of this number?
Ans. The least number of 4 digits is 1000.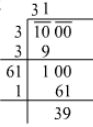
31< √100 < 32
322 = 1024
1024 is the least four digit perfect square and its square root is 32.
Q.4. Evaluate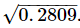
Ans.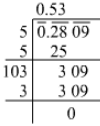
∴ 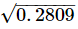 =0.53
=0.53
Q.5. Evaluate √3 correct up to two places of decimal.
Ans.
√3=1.732
Therefore, the value of √3 up to two places of decimal is 1.73.
Q.6. Evaluate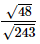
Ans.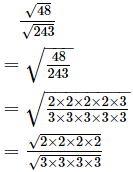
= (2×2)/(3×3)
=49
Q.7. Which of the following numbers is not a perfect square?
(a) 529
(b) 961
(c) 1024
(d) 1222
Ans. (d) 1222
A number ending in 2, 3, 7 or 8 is not a perfect square.
Q.8.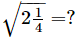
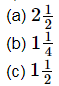
(d) none of these
Ans. (c)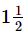
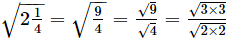
= 3/2
= 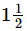
Q.9. Which of the following is the square of an even number?
(a) 529
(b) 961
(c) 1764
(d) 2809
Ans. (c) 1764
The square of an even number is always even.
Q.10. What least number must be added to 521 to make it a perfect square?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 8
Ans. (d) 8
521+8=529
√529=23
Q.11. What least number must be subtracted from 178 to make it a perfect square?
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 7
Ans. (c) 9
178−9=169
√169=13
Q.12. √72×√98=?
(a) 42
(b) 84
(c) 64
(d) 74
Ans. (b) 84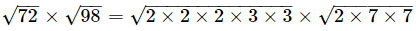
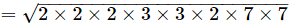
=2×2×3×7=84
Q.13. Fill in the blanks.
(i) 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + 13 = (.........)2.
(ii)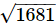 =.........
=.........
(iii) The smallest square number exactly divisible by 2, 4, 6 is .........
(iv) A given number is a perfect square having n digits, where n is odd. Then, its square root will have ......... digits.
Ans. (i) 1+3+5+7+9+11+13=(7)2
(ii)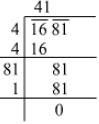
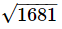 =41
=41
(iii) The smallest square number exactly divisible by 2, 4 and 6 is 36.
LCM of 2,4 and 6 is12.
Prime factorisation of 12 = 2×2×3
To make it a perfect square, we need to multiply it by 3.
∴ 12×3 = 36
(iv) A given number is a perfect square having n digits, where n is odd. then, its square root will have ((n+1)/2) digits.
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
















