Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Notes - Our Changing Earth
| Table of contents |

|
| What are the Lithosphere and Lithospheric Plates? |

|
| Earth's Movements and Their Causes |

|
| Effects of Earthquakes & Earthquake Preparedness |

|
| Formation of Major Landforms |

|
These chapter notes of the chapter "Our Changing Earth" explore how our Earth is always changing, with natural forces like earthquakes, volcanoes, and erosion constantly reshaping the world around us.
What are the Lithosphere and Lithospheric Plates?
The lithosphere is the Earth's outer shell, divided into several large and small pieces called lithospheric plates.

- These plates are rigid and irregularly shaped, supporting both continents and ocean floors.
- The movement of these plates is extremely slow, often just a few millimeters per year, due to the circulation of molten magma beneath the Earth's crust.
- As molten magma moves in a circular pattern, it causes the plates to shift, leading to changes on the Earth's surface.
Earth's Movements and Their Causes
The Movements of Lithospheric Plates cause changes on the surface of earth.
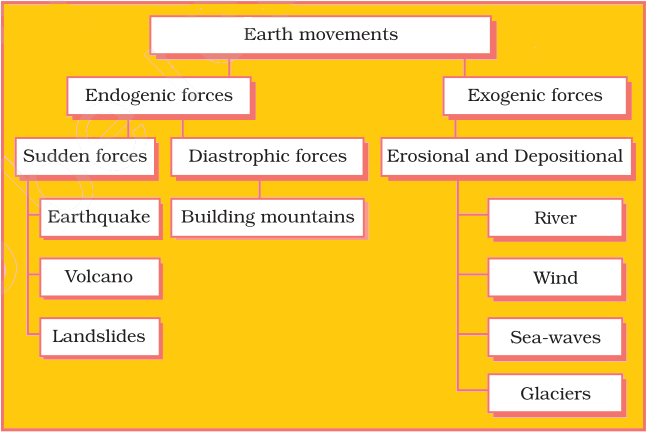 Earth Movements
Earth Movements
Endogenic Forces: These are forces originating within the Earth's interior. They can cause sudden movements, like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, or slow movements, like the formation of mountains.
Exogenic Forces: These are forces that act on the Earth's surface, like erosion and deposition, caused by agents such as wind, water, and ice. Exogenic forces shape the landscape over time.
Sudden Movements of the Earth
Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are examples of sudden movements that can cause significant destruction.
- A volcano is an opening in the Earth's crust through which molten material, gases, and rock fragments erupt, often forming a conical mountain.
 Volcano
Volcano - When tectonic plates shift, the Earth's surface vibrates, generating seismic waves that travel across the globe. The point where the movement begins is called the focus, and the point directly above it on the surface is the epicenter.
- There are three types of earthquake waves:
- P waves (Primary waves) or longitudinal waves: These waves are the fastest and travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
- S waves (Secondary waves) or transverse waves: These waves are slower and can only move through solids.
- L waves (Surface waves): These waves cause the most damage as they travel along the Earth's surface.
Effects of Earthquakes & Earthquake Preparedness
Earthquakes cause ground shaking, surface cracks, landslides, tsunamis, fires, and damage to buildings and roads.
 Effects of Earthquake
Effects of Earthquake
- The intensity of an earthquake is strongest at the epicenter; damage lessens as you move farther away.
- While earthquakes cannot be predicted with certainty, preparedness can help mitigate their effects. For example, unusual animal behavior, like pond fish becoming restless or snakes surfacing, can sometimes indicate an impending earthquake.
- Earthquakes are measured using a seismograph, and their magnitude is determined on the Richter scale. A magnitude of 7.0 or higher is considered a major earthquake.

Formation of Major Landforms
The Earth's surface is continuously shaped by two main processes: weathering and erosion.

- Weathering: The breaking down of rocks on the Earth's surface due to temperature changes, water, and other environmental factors.
- Erosion: The wearing away of the landscape by agents like water, wind, and ice.
Work of a River
- Waterfalls form when a river plunges over a cliff or rock formation.
- As the river flows into a plain, it winds and bends, creating large loops known as meanders.
- When a meander loop is cut off from the main river, it forms an oxbow lake.
- During floods, rivers deposit fine soil and sediments along their banks, creating fertile floodplains.
- Levees are raised banks formed by the accumulation of sediments along the river.
- At the river's mouth, sediments build up to form a delta.
Work of Sea Waves
The erosion and deposition by sea waves shape various coastal landforms:
- Sea caves: Hollow cavities formed in rocks due to wave action.
- Sea arches: Formed when sea caves grow larger and their roofs remain intact.
- Stacks: Vertical rock structures formed after the collapse of sea arches.
- Sea cliffs: Steep rocky coastlines that rise sharply above sea level.
Work of Ice
- Glaciers are slow-moving rivers of ice that erode the landscape by scraping and grinding rocks beneath them.
- The debris carried by glaciers, including rocks, sand, and silt, is deposited to form glacial moraines
Work of Wind
In deserts, wind is a powerful agent of erosion and deposition:
- Mushroom rocks are primarily shaped by a combination of water and wind erosion.
- Dunes are formed when wind-blown sand accumulates in low hills.
- Loess deposits occur when fine, light sand particles are carried by the wind over long distances and settle in large areas.
You can get a complete NCERT chapter explanation through this video:
While earthquakes cannot be predicted with certainty, preparedness can help mitigate their effects.
|
62 videos|336 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Notes - Our Changing Earth
| 1. What is the lithosphere and what are its main components? |  |
| 2. What are lithospheric plates and how do they move? |  |
| 3. What causes earthquakes, and how are they related to plate movements? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of earthquakes on the environment and human life? |  |
| 5. How can individuals and communities prepare for earthquakes? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|




















