NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Sound
Q1. Choose the correct answer:
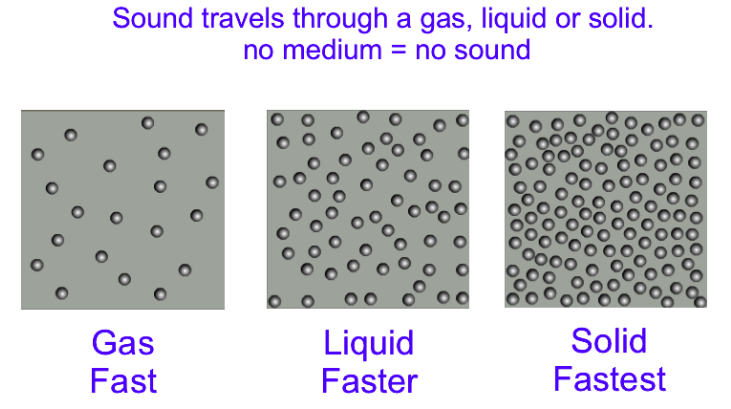
Sound can travel through
(a) Gases only
(b) Solids only
(c) Liquids only
(d) Solids, Liquids, and Gases.
Ans: (d) Solids, Liquids, and Gases.
Sound speed in various medium
Q2. Which of the following voices is likely to have a minimum frequency?
(a) Baby girl
(b) Baby boy
(c) A man
(d) A woman
Ans: (c) A man
The voice of a man generally has a lower frequency than that of women and children.
Q3. In the following statements, tick ‘T’ against those which are true, and ‘F’ against those which are false.
(a) Sound cannot travel in vacuum. (T/F)
Ans: True
- Sound needs a medium to travel.
- It cannot move through a vacuum.
(b) The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is called its time period. (T/F)
Ans: False
- The number of oscillations per second is called frequency. It is measured in hertz (Hz). In contrast:
- The time period is the time taken for one complete oscillation.
(c) If the amplitude of vibration is large, sound is feeble. (T/F)
Ans: False
A larger amplitude means:
- More energy in the sound wave
- Louder sound produced
(d) For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. (T/F)
Ans: True
The audible range for human ears is:
- From 20 Hz (low frequency)
- To 20,000 Hz (high frequency)
Frequencies outside this range are:
- Below 20 Hz: Inaudible sounds
- Above 20,000 Hz: Also inaudible
Some animals, like dogs, can hear sounds above this range, which is why they respond to high-frequency whistles that humans cannot hear.
(e) The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch. (T/F)
Ans: False
Here’s why:
- Lower frequencies produce lower pitches.
- Higher frequencies result in higher pitches.
For example:
- A drum has a low frequency, creating a low-pitched sound.
- A whistle has a high frequency, resulting in a high-pitched sound.
(f) Unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music. (T/F)
Ans: False
Noise is defined as any unwanted or unpleasant sound that can cause disturbance. It can arise from various sources, including:
- Construction activities
- Traffic and vehicle horns
- Explosions and loud machinery
Such sounds can lead to noise pollution, which may have negative effects on health, including:
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased stress and anxiety
- Potential hearing impairment
(g) Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment. (T/F)
Ans: True
- High levels of noise pollution can lead to hearing loss.
- It may also cause other health issues.
Q4. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called _____________
Ans: Time period
The time period is defined as the duration required for one complete cycle of motion in oscillatory systems.
(b) Loudness is determined by the _____________ of vibration.
Ans: Amplitude
Loudness is directly related to the amplitude of the sound wave; higher amplitude results in louder sounds.
(c) The unit of frequency is _____________
Ans: Hertz
Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz), which represents the number of oscillations per second.
(d) Unwanted sound is called _____________
Ans: Noise
Noise refers to any unwanted or unpleasant sound that can interfere with normal activities.
(e) Shrillness of a sound is determined by the _____________ of vibration.
Ans: Frequency and Amplitude
Higher frequency results in a shriller sound, while lower frequency produces deeper sounds.
Q5. A pendulum oscillates 40 times in 4 seconds. Find its time period and frequency.
Ans: Frequency is defined as the number of oscillations per second.

Since the time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation. It is the inverse of the frequency.
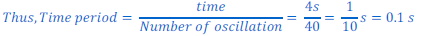
Q6. The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500 vibrations per second. What is the time period of the vibration?
Ans: Since the time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation.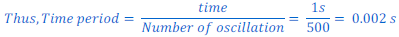
Q7. Identify the part which vibrates to produce sound in the following instruments:
(a) Dholak
(b) Sitar
(c) Flute Musical InstrumentsAns: (a) In Dholak, there is a stretched membrane at the top known as the head. When the head is beaten, the stretched membrane vibrates and thus the sound is produced.
Musical InstrumentsAns: (a) In Dholak, there is a stretched membrane at the top known as the head. When the head is beaten, the stretched membrane vibrates and thus the sound is produced.
(b) In Sitar, there are many stretched strings. When these strings are plucked, the string vibrates and thus the sound is produced.
(c) In Flute, there is a hollow pipe. When air is blown into it, the air inside it starts vibrating, and thus the sound is produced.
Q8. What is the difference between noise and music? Can music become noise sometimes?
Ans:
- The unwanted sound that is unpleasant to the ear is called noise. A pleasant sound is called music.
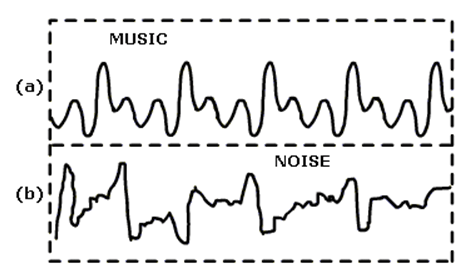
- Music can become noise in many instances. When someone tries to enjoy very loud music, it can be noise for someone else. When loud music is played during religious celebrations or marriages, it can be annoying for many people.
Q9. List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Ans: Following is the list of sources of noise pollution in my surroundings: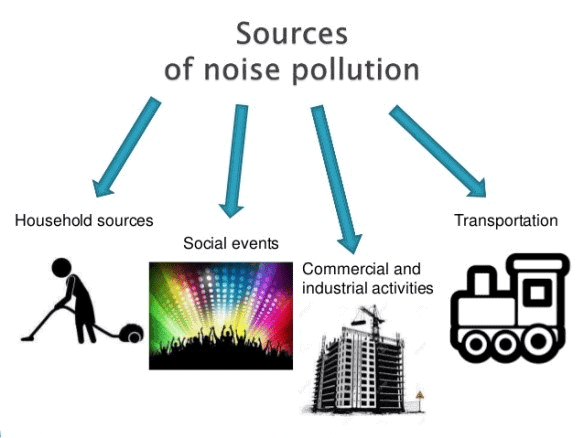
- Horns of vehicles.
- Bursting of crackers.
- Machines
- Loudspeakers
- Television and radio at high volumes.
- Kitchen appliances like mixer, etc.
- Air conditioners
Q10. Explain in what way noise pollution is harmful to humans.
Ans: Noise pollution can have several harmful effects on humans, including:
- Lack of sleep
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Temporary or permanent hearing impairment
- Headaches
- Increased stress
Q11. Your parents are going to buy a house. They have been offered one on the roadside and another three lanes away from the roadside. Which house would you suggest your parents should buy? Explain your answer.
Ans: I suggest my parents buy the house that is three lanes away from the roadside for the following reasons:
- The house on the roadside is likely to be noisy due to traffic.
- A house further away would provide a quieter living environment.
- Less noise can lead to a more peaceful home atmosphere.
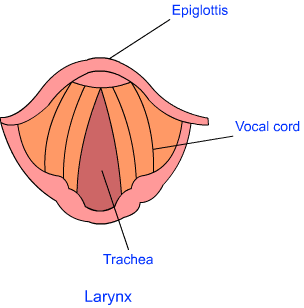
Q12. Sketch the larynx and explain its function in your own words.
Ans:
- The larynx is the part of the throat that is responsible for producing sound.
- Inside the larynx, there are two vocal cords, which are stretched across the voice box or larynx in such a way that it leaves a narrow slit between them for the passage of air.
- When we speak, the air is forced into this small gap by the lungs, which prompt vocal cords to vibrate.
- When the lungs force air through the slit, the vocal cords vibrate, producing sound.
Q13. Lightning and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and at the same distance from us. Lightning is seen earlier and thunder is heard later. Can you explain?
Ans: The phenomenon of lightning and thunder occurs simultaneously in the sky, but we perceive them at different times due to their differing speeds:
- The speed of light is approximately 3 x 108 m/s, allowing it to reach us almost instantly.
- In contrast, the speed of sound is about 330 m/s, which is significantly slower.
- As a result, we see the flash of lightning before we hear the rumble of thunder.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Sound
| 1. What is sound and how is it produced? |  |
| 2. How does the frequency of sound affect its pitch? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between loudness and intensity of sound? |  |
| 4. How do we measure the speed of sound in air? |  |
| 5. How do different materials affect the speed of sound? |  |






















