Mineral Resources Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Minerals? |

|
| Types of Minerals |

|
| Mining & Refining |

|
| Important Metals and Minerals |

|
| Mineral Conservation |

|
| Key Points |

|
What are Minerals?
Nature provides us with many resources, some on the Earth's surface and others buried deep underground. Underground resources, known as minerals, need to be extracted and refined for various uses.
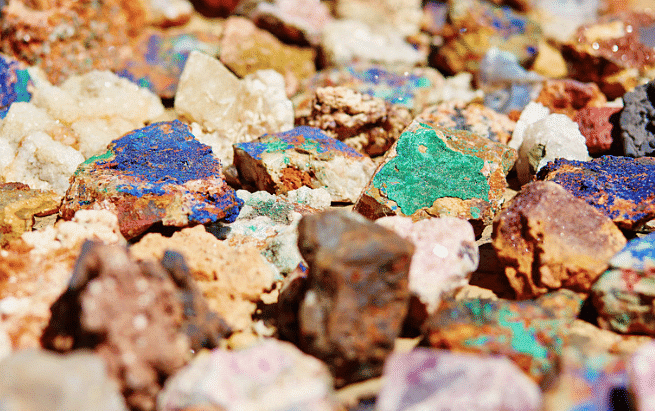 Various Minerals
Various Minerals
Minerals are naturally occurring substances found in the Earth's crust that have specific chemical compositions and physical properties.
Types of Minerals
- Metallic Minerals: These include iron, aluminium, gold, and copper. They are used to make tools, utensils, electrical wires, and even jewellery.
 Metallic Minerals
Metallic Minerals
- Non-Metallic Minerals: These include limestone, precious stones, salt, coal, and petroleum. Coal and petroleum are important as they are used as fuel (like for cooking or running vehicles).
 Non-Metallic Minerals
Non-Metallic Minerals
Mining & Refining
Mining: Mining is the process of extracting minerals from the Earth's crust. It involves locating mineral deposits, excavating them from the ground, and transporting them to processing facilities. Mining methods vary depending on the type of mineral and its location. Common mining techniques include surface mining (open-pit mining, quarrying) and underground mining (shaft mining, drift mining).
 Mining
Mining
Refining: Refining is the process of purifying and processing raw minerals or ores to obtain usable products. For metallic minerals like iron, copper, and gold, refining involves smelting, where the ore is heated to high temperatures to extract the metal. Non-metallic minerals like salt, coal, and petroleum undergo refining processes such as purification, distillation, and chemical treatments to remove impurities and obtain usable forms.
Important Metals and Minerals
- Iron: Iron is a vital metal used to make things like buildings, bridges, vehicles, and tools. It's strong and can be shaped into different forms, making it essential for construction and manufacturing.
 Iron
Iron
- Copper: Copper is another important metal used in wiring, plumbing, electronics, and machinery. It conducts electricity well, making it valuable for various technological and industrial applications.
 Copper
Copper
- Aluminium: Aluminium is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it ideal for making airplanes, cars, cans, and household items. It's also used in construction for windows, doors, and building materials.
 Aluminium
Aluminium
- Coal: Coal is a fossil fuel used for generating electricity, heating homes, and powering industries. It's obtained from underground mines and is a crucial energy resource globally.
 Coal
Coal
- Petroleum: Petroleum, also known as crude oil, is another fossil fuel used for making gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and plastics. It's extracted from beneath the Earth's surface and is essential for transportation, energy production, and manufacturing.
 Petrol
Petrol
These metals and minerals play essential roles in modern life, from infrastructure and technology to energy production and everyday products.
Steel Plants and Major Mining Areas
- Iron Ore Mining Areas: India has large quantities of iron ore, especially in states like Odisha, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh. Iron ore is a raw material used to make steel.
- Steel Plants in India: Steel plants are set up in strategic locations close to iron ore mining areas. Some prominent steel plants in India are located in Jamshedpur (Tatanagar), Bhilai, Rourkela, and Durgapur.
These steel plants use iron ore as a primary raw material to produce steel through a process called smelting and refining.
Steel Production Process
- Iron ore is first extracted from mines and transported to steel plants.
- At the steel plants, iron ore is smelted in blast furnaces to extract molten iron.
- The molten iron is then refined and processed to remove impurities and alloyed with other metals to produce different types of steel with varying properties.
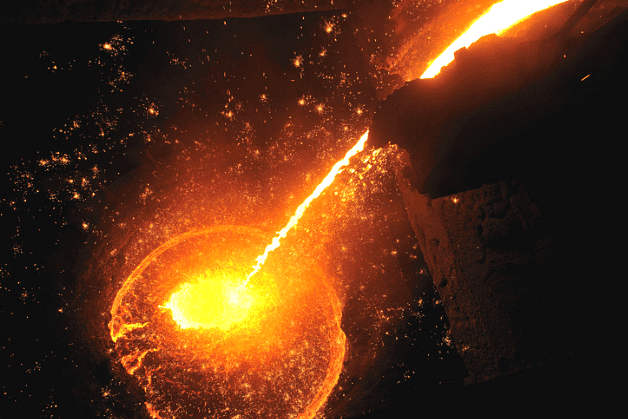 Molten iron
Molten iron
Other Minerals in India
- Manganese: Manganese is found in India and is used in steelmaking to improve the strength and hardness of steel alloys.
- Mica: India is a major producer of mica, which is used in electrical insulation, electronic devices, paints, and cosmetics.
- Gold: Gold mining occurs in places like Kolar, Karnataka, where gold deposits are extracted and processed for various purposes, including jewelry making and investment.
Coal and Petroleum Usage
- Coal Usage: Coal is a primary source of energy in India and is used in various sectors, including steel plants, thermal power stations for electricity generation, and as a domestic fuel for cooking and heating.
 Coal & petrol Usage
Coal & petrol Usage
- Petroleum Usage: Petroleum is a fossil fuel refined to produce various products like kerosene oil (for lamps and stoves), petrol (for vehicles), diesel oil (for vehicles and generators), grease (for lubrication), and paraffin wax (for candles and cosmetics).
Mineral Conservation
Mineral conservation refers to the responsible and sustainable use of mineral resources to ensure their availability for future generations. It involves strategies such as efficient utilization, recycling, reducing wastage, and adopting environmentally friendly mining practices.
Importance of Using Minerals Carefully
- Mineral reserves on Earth are limited and can't last forever once used up.
- We need to use minerals carefully and wisely to ensure they last longer for future generations.
Alternative Energy Sources
 Wind & Solar energy
Wind & Solar energy
- Wind power and solar energy are renewable alternatives to fossil fuels, but they are currently expensive to convert into electricity.
- Scientists are working to make these alternatives more affordable by improving technology and reducing costs.
Key Points
Definition of Minerals: Minerals are naturally occurring substances found in the Earth's crust with specific chemical compositions and physical properties.
Types of Minerals: Minerals are categorized into metallic (e.g., iron, copper, gold) and non-metallic (e.g., coal, petroleum, salt).
Mining: Mining is the process of extracting minerals from the Earth, using various methods depending on the type and location of the mineral.
Refining: Refining involves purifying raw minerals or ores to obtain usable products, such as smelting for metals or distillation for petroleum.
Importance of Metals: Key metals like iron, copper, and aluminium are crucial for construction, technology, and manufacturing.
Energy Resources: Coal and petroleum are vital energy resources used for electricity generation, transportation, and industry.
Mineral Conservation: It's important to use minerals responsibly to ensure their availability for future generations, involving strategies like recycling and reducing waste.
Renewable Alternatives: Wind and solar energy are renewable alternatives to fossil fuels, and ongoing research aims to make them more cost-effective and widely usable.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Mineral Resources Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What are mineral resources? |  |
| 2. How are mineral resources formed? |  |
| 3. Why are mineral resources important? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of mineral resources? |  |
| 5. How are mineral resources extracted? |  |















