Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Stars and the Solar System- 3 | Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur Solutions: Class 8 Science PDF Download
Q.71. What is a meteor? What is the other name of a meteor?
Meteor is seen as a bright streak of light coming down the night sky. A meteor is usually a small object that occasionally enters the Earth’s atmosphere with very high speed. The friction due to the atmosphere heats it up and it glows and evaporates quickly. As a result, the bright streak lasts for a very short time. These are commonly known as shooting stars.
Q.72. What is the difference between a star and a shooting star?
Stars are celestial bodies that emit light of their own. Our sun is also a star. The stars appear to move from east to west. A star which rises in the east in the evening, sets in the west in the early morning. Meteors are commonly known as shooting stars. Meteor is seen as a bright streak of light coming down the night sky. It is usually a small object that occasionally enters the Earth’s atmosphere with very high speed.
Q.73. What are meteorites?
Meteorites are the large meteors which can reach the Earth before they evaporate completely. Meteorites help scientists in investigating the nature of the material from which the solar system was formed.
Q.74. What is the difference between a meteor and a meteorite?
Meteor is seen as a bright streak of light coming down the night sky. A meteor is usually a small object that occasionally enters the Earth’s atmosphere with very high speed. The friction due to the atmosphere heats it up and it glows and evaporates quickly. As a result, the bright streak lasts for a very short time. These are commonly known as shooting stars. Meteorites are the large meteors which can reach the Earth before they evaporate completely. Meteorites help scientists in investigating the nature of the material from which the solar system was formed.
Q.75. What are meteoroids? Which of two is really a member of the Solar System: Meteoroid or Meteor?
A meteoroid is a small chunk of rock or iron that travels through space. When it enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it makes a bright trail and is called a meteor. Meteor is seen as a bright streak of light coming down the night sky. A meteor is usually a small object that occasionally enters the Earth’s atmosphere with very high speed. The friction due to the atmosphere heats it up and it glows and evaporates quickly. As a result, the bright streak lasts for a very short time. These are commonly known as shooting stars. Meteors are the part of the Solar System.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.76.
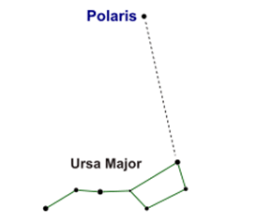
(A) What is the number of prominent stars in the Ursa Major?
Ursa Major is the constellation which reminds us of a large ladle or a question mark in the night sky. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark.
(B) Draw a diagram of Ursa Major constellation to show the position of main stars in it.
Following is the diagram of Ursa Major constellation:
Q.77.
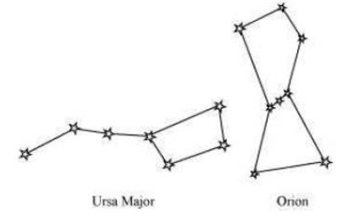
(A) What is the number of prominent stars in the Orion?
The constellation Orion is visible during winter in the late evenings. It also has seven or eight bright stars. It is also called the Hunter. The three middle stars represent the belt of the hunter. The four bright stars appear to be arranged in the form of a quadrilateral.
(B) Draw a diagram of the Orion constellation to show the position of prominent stars in it.
Following is the diagram of Orion and Ursa Major:
Q.78.
(A) What is the number of main stars in the Cassiopeia constellation? Draw a diagram of Cassiopeia constellation to show the position of main stars in it.
Cassiopeia is another prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter W or M.
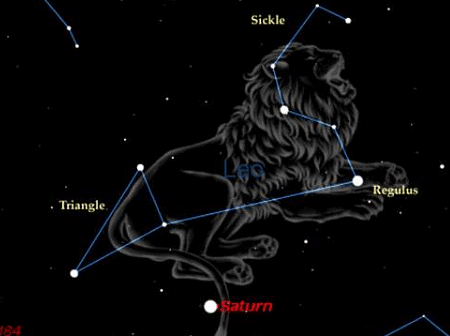
(B) What is the number of main stars in Leo Major constellation? Draw a diagram to show the position of main stars in Leo Major constellation.
Leo Major appears to have the shape of a big lion. It is visible in the northern hemisphere around the spring. It is easily identifiable through may. Its brightest star is Regulus. Its most prominent pattern of stars is a backwards question mark called the Sickle
Q.79.
(A) Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major constellation.
Ursa Major has seven prominent stars. Pole star can be located with the help of Ursa Major. It is located by drawing an imaginary line passing through the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. This imaginary line is extended towards the North direction, which is about five times the distance between the two lines. This line will lead to a star which is not too bright. This star is Pole star.
(B) Explain how the position of Sirius Star can be located in the night sky with the help of Orion constellation.
Sirius is the brightest star in the sky. It is located close to the Orion constellation. An imaginary line is drawn passing through the three middle stars of Orion. By looking along this line towards the east, will lead to a very bright star. This bright star is Sirius.
Q.80.
(A) What is the difference between a full Moon and a new Moon? After how many days a full Moon changes into a new Moon?
There is a change in the shape of moon every day. There are days when the shape of moon appears perfectly round. Also, there are days when the moon cannot be seen at all even if the sky is clear. The day on which the whole disc of the moon is visible is called the full Moon day. Every night, the size of the bright part of the moon appears to become thinner and thinner. On the fifteenth day, the moon is not visible. This day is called the new Moon day. The next day, only a small portion of the moon appears in the sky. This is known as the crescent moon. Then again, the moon grows larger every day. On the fifteenth day once again we get a full view of the moon. After fifteen days, the full moon changes into a new Moon.
(B) What is meant by the phases of the Moon? What causes the phases of the Moon?
The different shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called the phases of the moon. Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. It revolves around the Earth. It completes one rotation on its axis as it completes one revolution around the Earth. The moon does not have light of its own. We are able to see the moon because the sunlight falling on its surface gets reflected towards us. We, therefore, see only that part of the moon, from which the light of the Sun is reflected towards us. The size of the illuminated part of the moon visible from the Earth increases each day after the new moon day. After the full moon day, the sunlit part of the moon visible from the Earth decreases in size every day. This process leads to the phases of the Moon.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.81. Which of the following is not a planet of the Sun?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Sirius is the brightest star in the sky. It is located close to the Orion constellation.
Q.82. Ursa Major is a:
(a) star
(b) planet
(c) constellation
(d) satellite
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Ursa Major is the constellation which reminds us of a large ladle or a question mark in the night sky. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi.
Q.83. Which of the following is not a member of the Solar System?
(a) Asteroids
(b) Morning Star
(c) Satellites
(d) Constellations
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The stars forming a group that has a recognizsable shape is called a constellation. For example, Ursa Major is a constellation.
Q.84. Which of the following is not a planet?
(a) Mercury
(b) Saturn
(c) Mars
(d) Moon
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. It revolves around the Earth.
Q.85. Phases of the Moon occur because:
(a) we can see only that part of the Moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the Moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the Moon’s surface.
(d) the thickness of the Moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The size of the illuminated part of the moon visible from the Earth increases each day after the new moon day. After the full moon day, the sunlit part of the moon visible from the Earth decreases in size every day. This process leads to the phases of the Moon.
Q.86. Which of the following is not a member of the Solar System?
(a) an asteroid
(b) a satellite
(c) a constellation
(d) earth
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The stars forming a group that has a recognisable shape is called a constellation. For example, Ursa Major is a constellation.
Q.87. After the Sun, the next nearest star to the Earth is :
(a) Alpha Centauri
(b) Polestar
(c) Sirius
(d) Proxima Centauri
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The next nearest star to Earth is ‘Proxima Centauri’. It is 4.24 light years from the Sun. Its light will take 4.24 years to reach us.
Q.88. The distances between the various celestial objects are usually expressed in the unit of:
(a) kilometres
(b) light minutes
(c) light years
(d) light seconds
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Light year is the unit used to express distance between the various celestial bodies. Light year is the distance travelled by light in one year.
Q.89. Which of the following constellations can be seen in the night sky during the winter season?
(i) Orion
(ii) Ursa Major
(iii) Leo Major
(iv) Cassiopeia
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iv
(d) ii and iv
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The constellation Orion is visible during winter in the late evenings. It also has seven or eight bright stars. It is also called the Hunter. Cassiopeia is another prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night.
Q.90. The brightest star in the night sky called Sirius is located close to one of the following constellations. This constellation is:
(a) Great Bear
(b) Leo Major
(c) Cassiopeia
(d) Orion
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Sirius is the brightest star in the sky. It is located close to the Orion constellation.
Q.91. Asteroids revolve around the Sun between the orbits of the planets:
(a) Mars and Earth
(b) Venus and Mars
(c) Jupiter and Mars
(d) Mars and Saturn
Correct Answer is Option (c)
There is a large gap in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. This gap is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the Sun. These are called asteroids.
Q.92. The biggest planet of the solar system is:
(a) Mars
(b) Saturn
(c) Mercury
(d) Jupiter
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Jupiter is the biggest planet of the Solar system. It is so large that about 1300 earths can be placed inside this giant planet.
Q.93. The planet with a system of well-developed rings encircling it is:
(a) Jupiter
(b) Venus
(c) Saturn
(d) Neptune
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Saturn is the planet having a well-developed system of rings around it. These rings are not visible with the naked eye. They can be observed with a small telescope.
Q.94. The two pointer stars the line passing through which points to the direction of pole star are a part of the constellation called:
(a) Ursa Major
(b) Orion
(c) Cassiopeia
(d) Leo Major
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Ursa Major is the constellation which reminds us of a large ladle or a question mark in the night sky.
Q.95. The smallest planet of the solar system is:
(a) Earth
(b) Mars
(c) Mercury
(d) Saturn
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Mercury is the smallest planet of the Solar system. It is nearest to the Sun.
Q.96. Which of the following are non-luminous objects?
(i) Orion
(ii) Morning Star
(iii) Moon
(iv) Pole star
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) only iii
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The moon does not have light of its own. We are able to see the moon because the sunlight falling on its surface gets reflected towards us.
Q.97. Which of the following planets show phases like the moon?
(i) Venus
(ii) Mercury
(iii) Jupiter
(iv) Mars
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) iii and iv
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Mercury and Venus shows phases like the Moon. They have the orbits which are smaller than the Earth and exhibit the full range of phases like the moon.
Q.98. Which of the following is the hottest planet in the Solar System?
(a) Earth
(b) Mercury
(c) Venus
(d) Mars
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Venus is the hottest planet of the solar system. It is the second planet from the Sun and has a temperature that is maintained at 462 degrees Celsius.
Q.99. Which of the following constellations are visible in the summer season?
(i) Cassiopeia
(ii) Orion
(iii) Leo Major
(iv) Big Bear
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) iii and iv
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Ursa Major can be seen during summer time in the early part of the night. It has seven prominent stars. Leo Major is visible in the northern hemisphere around the spring. It is easily identifiable through may.
Q.100. The agency responsible for the development of space science programmes in India is :
(a) INSAT
(b) B. ORS
(c) IRS
(d) ISRO
Correct Answer is Option (d)
ISRO is also known as Indian Space Research Organisation is the agency responsible for the development of space science programs in India.
The Indian Space Research Organisation is the space agency of the Government of India headquartered in the city of Bengaluru
High Order Thinking Skills
Q.101. X is a group of stars which is visible during the summer season in the early part of the night. It can be seen clearly in the month of April in the northern part of the sky. It resembles a bowl with a handle. It also resembles a big kite with a tail.
(a) What is the general name of groups of stars like X?
(b) Write any two names of X.
(c) Is it a part of our Solar System?
(d) How many bright stars are usually observed in X?
(e) Which famous star can be located in the sky with the help of X?
(a) The general name for the group of stars like X is a constellation. The stars forming a group that has a recognisable shape is called a constellation. We can easily identify them in the night sky. Ursa Major and Orion are the examples of the constellations.
(b) X is the Ursa Major constellation. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark. There are three stars in the handle of the ladle and four in its bowl.
(c) Constellations is a group of stars forming a group that has a recognizable shape. Yes, Ursa Major is a part of our Solar System.
(d) There are seven prominent stars in the Ursa Major constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark. There are three stars in the handle of the ladle and four in its bowl.
(e) Pole star can be located with the help of Ursa Major. It is located by drawing an imaginary line passing through the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. This imaginary line is extended towards the North direction, which is about five times the distance between the two lines. This line will lead to a star which is not too bright. This star is Pole star.
Q.102.
(A) In which direction do stars appear to move in the sky?
The stars appears to move from east to the west direction in the sky.
(B) Why do they appear to move in this direction?
The stars appear to move in the sky. It appears because of the motion of the Earth. Earth is spinning around its own axis and also moves around the Sun. As a result, the stars also appear to move from east to west. A star which rises in the east in the evening, sets in the west in the early morning. All the stars do not appear to move. For example, pole star does not appear to move because it is situated in the direction of earth’s axis.
Q.103. The number of main stars in constellation A is 5, in constellation B is 7 in constellation C can be 7 or 8, whereas in constellation D is usually 9. Name the constellations A, B, C and D.
The constellation A is Cassiopeia. It is the prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter W or M.
The constellation B is Ursa Major. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark. There are three stars in the handle of the ladle and four in its bowl.
The constellation C is Orion. The constellation Orion is visible during winter in the late evenings. It also has seven or eight bright stars. It is also called the Hunter. The three middle stars represent the belt of the hunter. The four bright stars appear to be arranged in the form of a quadrilateral.
The constellation D is Leo Major. Leo Major appears to have the shape of a big lion. It is visible in the northern hemisphere around the spring. It is easily identifiable through may. Its brightest star is Regulus.
Q.104. Which star in the night sky can be located with the help of:
(a) Orion constellation?
(b) Ursa Major Constellation
(a) The constellation Orion is visible during winter in the late evenings. It also has seven or eight bright stars. It is also called the Hunter. Sirius is the brightest star in the sky. It is located close to the Orion constellation. An imaginary line is drawn passing through the three middle stars of Orion. By looking along this line towards the east, will lead to a very bright star. This bright star is Sirius.
(b) The constellation Ursa Major is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark. Pole star can be located with the help of Ursa Major. It is located by drawing an imaginary line passing through the two stars at the end of Ursa Major. This imaginary line is extended towards the North direction, which is about five times the distance between the two lines. This line will lead to a star which is not too bright. This star is Pole star.
Q.105. Match items in column A with one or more items in column B:
Column A
(i) Inner planets
(ii) Outer planets
(iii) Constellation
(iv) Satellite of the Earth
Column B
(a) Saturn
(b) Pole Star
(c)Great Bear
(d) Moon
(e) Earth
(f) Orion
(g) Mars
(i) Inner planets – (e) Earth and (g) Mars
There are eight planets in the Solar System. The first four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are much nearer the Sun than the other four planets. They are called the inner planets. The inner planets have very few moons.
(ii) Outer planets – (a) Saturn
The planets outside the orbit of Mars, namely Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are much farther off than the inner planets. They are called the outer planets. They have a ring system around them. The outer planets have large number of moons. The outer planets can be seen only with the help of large telescopes.
(iii) Constellation – (c) Great Bear and (f) Orion
The stars forming a group that has a recognisable shape is called a constellation. We can easily identify them in the night sky. Ursa Major and Orion are the examples of the constellations.
(iv) Satellite of the Earth – (d) Moon
Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. It revolves around the Earth.