Chapter 10 - Direct and Inverse Variations (Part - 2), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 10.12:
Question 1:
In which of the following tables x and y vary inversely:
(i)
| x | 4 | 3 | 12 | 1 |
| y | 6 | 8 | 2 | 24 |
(ii)
| x | 5 | 20 | 10 | 4 |
| y | 20 | 5 | 10 | 25 |
(iii)
| x | 4 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
| y | 9 | 12 | 8 | 36 |
(iv)
| x | 9 | 24 | 15 | 3 |
| y | 8 | 3 | 4 | 25 |
ANSWER:
(i) Since x and y vary inversely, we have:
y = k/x
⇒ xy = k
∴ The product of x and y is constant.In all cases, the product xy is constant (i.e., 24).
Thus, in this case, x and y vary inversely.
(ii) In all cases, the product xy is constant for any two pairs of values for x and y.
Here, xy = 100 for all cases
Thus, in this case, x and y vary inversely.
(iii) If x and y vary inversely, the product xy should be constant.
Here, in one case, product = 6 × 8 = 48 and in the rest, product = 36
Thus, in this case, x and y do not vary inversely.
(iv) If x and y vary inversely, the product xy should be constant.Here, product is different for all cases.
Thus, in this case, x and y do not vary inversely.
PAGE NO 10.12:
Question 2:
It x and y vary inversely, fill in the following blanks:
(i)
| x | 12 | 16 | ... | 8 | ... |
| y | ... | 6 | 4 | ... | 0.25 |
(ii)
| x | 16 | 32 | 8 | 128 |
| y | 4 | ... | ... | 0.25 |
(iii)
| x | 9 | ... | 81 | 243 |
| y | 27 | 9 | ... | 1 |
ANSWER:
(i) Since x and y vary inversely,
we have:
xy = k
For x = 16 and y = 6,
we have:16 × 6 = k
⇒ k = 96
For x = 12 and k = 96,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 12y = 96
⇒ y = 96/12
= 8
For y = 4 and k = 96,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 4x = 96
⇒ x = 96/4
= 24
For x = 8 and k = 96,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 8y = 96
⇒ y = 96/8
= 12
For y = 0.25 and k = 96,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 0.25x = 96
⇒ x = 96/0.25
= 384
(ii) Since x and y vary inversely, we have:
xy = k
For x = 16 and y = 4,
we have:16 × 4 = k
⇒ k = 64
For x = 32 and k = 64,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 32y = 64
⇒ y = 64/32
= 2
For x = 8 and k = 64
xy = k
⇒ 8y = 64
⇒ y = 64/8
= 8
(iii) Since x and y vary inversely,
we have:
xy = k
For x = 9 and y = 279 × 27 = k
⇒ k = 243
For y = 9 and k = 243,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 9x = 243
⇒ y = 243/9
= 27
For x = 81 and k = 243,
we have:
xy = k
⇒ 81y = 243
⇒ y = 243/81= 3
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 3:
Which of the following quantities vary inversely as each other?
(i) The number of x men hired to construct a wall and the time y taken to finish the job.
(ii) The length x of a journey by bus and price y of the ticket.
(iii) Journey (x km) undertaken by a car and the petrol (y litres) consumed by it.
ANSWER:
(i) If the number of men is more, the time taken to construct a wall will be less. Therefore, it is in inverse variation.
(ii) If the length of a journey is more, the price of the ticket will also be more. Therefore, it is not in inverse variation.
(iii) If the length of the journey is more, the amount of petrol consumed by the car will also be more. Therefore, it is not in inverse variation.
Thus, only (i) is in inverse variation.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 4:
It is known that for a given mass of gas, the volume v varies inversely as the pressure p. Fill in the missing entries in the following table:
| v (in cm3) | ... | 48 | 60 | ... | 100 | ... | 200 |
| p (in atmospheres) | 2 | ... | 3/2 | 1 | ... | 1/2 | ... |
ANSWER:
Since the volume and pressure for the given mass vary inversely,
we have:
vp = k
For v = 60 and p = 3/2,
we have:k = 60 × 3/2
= 90
For p = 2 and k = 90,
we have:
2v = 90
⇒ v = 90/2= 45
For v = 48 and k = 90,
we have:
48p = 90
⇒ p = 90/48
= 15/8
For p = 1 and k = 90,
we have:
1v = 90
⇒ v = 90/1
= 90
For v = 100 and k = 90,
we have:
100p = 90
⇒ v = 90/100
= 9/10
For p = 12 and k = 90,
we have:
12v = 90
⇒ v = 90 × 2
= 180
For v = 200 and k = 90,
we have:
200p = 90
⇒ p = 90/200
= 9/20
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 5:
If 36 men can do a piece of work in 25 days, in how many days will 15 men do it?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of days in which 15 men can do a piece of work.
| Number of men | 36 | 15 |
| Number of days | 25 | x |
Since the number of men hired and the number of days taken to do a piece of work are in inverse variation, we have:
36 × 25 = x × 15
⇒ x = 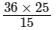
= 900/15
= 60
Thus, the required number of days is 60.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 6:
A work force of 50 men with a contractor can finish a piece of work in 5 months. In how many months the same work can be completed by 125 men?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number days required to complete a piece of work by 125 men.
| Number of men | 50 | 125 |
| Months | 5 | x |
Since the number of men engaged and the number of days taken to do a piece of work are in inverse variation, we have:
50 × 5 = 125x
⇒ x = 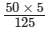
= 2
Thus, the required number of months is 2.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 7:
A work-force of 420 men with a contractor can finish a certain piece of work in 9 months. How many extra men must he employ to complete the job in 7 months?
ANSWER:
Let x be the extra number of men employed to complete the job in 7 months.
| Number of men | 420 | x |
| Months | 9 | 7 |
Since the number of men hired and the time required to finish the piece of work are in inverse variation, we have:
420 × 9 = 7x
⇒ x =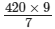
= 540
Thus, the number of extra men required to complete the job in 7 months = 540 − 420 = 120
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 8:
1200 men can finish a stock of food in 35 days. How many more men should join them so that the same stock may last for 25 days?
ANSWER:
| Number of men | 1200 | x |
| Days | 35 | 25 |
Let x be the number of additional men required to finish the stock in 25 days.
Since the number of men and the time taken to finish a stock are in inverse variation,
we have:
1200 × 35 = 25x
⇒ x = 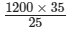
= 1680
∴ Required number of men = 1680 − 1200
= 480
Thus, an additional 480 men should join the existing 1200 men to finish the stock in 25 days.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 9:
In a hostel of 50 girls, there are food provisions for 40 days. If 30 more girls join the hostel, how long will these provisions last?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of days with food provisions for 80 (i.e., 50+30) girls.
Let x be the number of days with food provisions for 80 (i.e., 50+30) girls.
| Number of girls | 50 | 80 |
| Number of days | 40 | x |
Since the number of girls and the number of days with food provisions are in inverse variation,
we have:
50 × 40 = 80x
⇒ x = 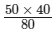
= 2000/80
= 25
Thus, the required number of days is 25.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 10:
A car can finish a certain journey in 10 hours at the speed of 48 km/hr. By how much should its speed be increased so that it may take only 8 hours to cover the same distance?
ANSWER:
Let the increased speed be x km/h.
| Time (in h) | 10 | 8 |
| Speed (km/h) | 48 | x+48 |
Since speed and time taken are in inverse variation, we get:
10 × 48 = 8(x + 48)
⇒ 480 = 8x + 384
⇒ 8x = 480 − 384
⇒ 8x = 96
= 12
Thus, the speed should be increased by 12km/h.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 11:
1200 soldiers in a fort had enough food for 28 days. After 4 days, some soldiers were transferred to another fort and thus the food lasted now for 32 more days. How many soldiers left the fort?
ANSWER:
It is given that after 4 days, out of 28 days, the fort had enough food for 1200 soldiers for (28 − 4 = 24) days.
Let x be the number of soldiers who left the fort
| Number of soldiers | 1200 | 1200-x |
| Number of days for which food lasts | 24 | 32 |
Since the number of soldiers and the number of days for which the food lasts are in inverse variation, we have:
1200 × 24 = (1200 − x) × 32
⇒ 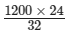 = 1200 − x
= 1200 − x
⇒ 900 = 1200 − x
⇒ x = 1200 − 900
= 300
Thus, 300 soldiers left the fort.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 12:
Three spraying machines working together can finish painting a house in 60 minutes. How long will it take for 5 machines of the same capacity to do the same job?
ANSWER:
Let the time taken by 5 spraying machines to finish a painting job be x minutes.
| Number of machines | 3 | 5 |
| Time (in minutes) | 60 | x |
Since the number of spraying machines and the time taken by them to finish a painting job are in inverse variation, we have:
3 × 60 = 5 × x
⇒ 180 = 5x
⇒ x = 180/5
= 36
Thus, the required time will be 36 minutes.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 13:
A group of 3 friends staying together, consume 54 kg of wheat every month. Some more friends join this group and they find that the same amount of wheat lasts for 18 days. How many new members are there in this group now?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of new members in the group.
| Number of members | 3 | x |
| Number of days | 30 | 18 |
Since more members can finish the wheat in less number of days, it is a case of inverse variation.Therefore,
we get:
3 × 30 = x × 18
⇒ 90 = 18x
⇒ x = 90/18
Thus, the number of new members in the group = 5 − 3 = 2
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 14:
55 cows can graze a field in 16 days. How many cows will graze the same field in 10 days?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of cows that can graze the field in 10 days .
| Number of days | 16 | 10 |
| Number of cows | 55 | x |
Since the number of cows and the number of days taken by them to graze the field are in inverse variation,
we have:
16 × 55 = 10 × x
⇒ x = 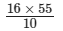
= 88
∴ The required number of cows is 88
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 15:
18 men can reap a field in 35 days. For reaping the same field in 15 days, how many men are required?
ANSWER:
Let the number of men required to reap the field in 15 days be x.
| Number of days | 35 | 15 |
| Number of men | 18 | x |
Since the number of days and the number of men required ro reap the field are in inverse variation,
we have: 35 × 18 = 15 × x
⇒ x = 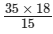
= 42
Thus, the required number of men is 42.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 16:
A person has money to buy 25 cycles worth Rs 500 each. How many cycles he will be able to buy if each cycle is costing Rs 125 more?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of cycles bought if each cycle costs Rs 125 more.
| Cost of a cycle (in Rs) | 500 | 625 |
| Number of cycles | 25 | x |
It is in inverse variation. Therefore, we get:
500 × 25 = 625 × x
⇒ x = 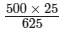
= 20
∴ The required number of cycles is 20.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 17:
Raghu has enough money to buy 75 machines worth Rs 200 each. How many machines can he buy if he gets a discount of Rs 50 on each machine?
ANSWER:
Let x be the number of machines he can buy if a discount of Rs. 50 is offered on each machine.
| Number of machines | 75 | x |
| Price of each machine (in Rs) | 200 | 150 |
Since Raghu is getting a discount of Rs 50 on each machine, the cost of each machine will get decreased by Rs 50.If the price of a machine is less, he can buy more number of machines.It is a case of inverse variation.
Therefore, we have:
75 × 200 = x × 150
⇒ x = 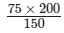
= 15000/150
= 100
∴ The number of machines he can buy is 100.
PAGE NO 10.13:
Question 18:
If x and y vary inversely as each other and
(i) x = 3 when y = 8, find y when x = 4
(ii) x = 5 when y = 15, find x when y = 12
(iii) x = 30, find y when constant of variation = 900.
(iv) y = 35, find x when constant of variation = 7.
ANSWER:
(i) Since x and y vary inversely, we have:
xy = k
For x = 3 and y = 8, we have:
3 × 8 = k
⇒ k = 24
For x = 4,
we have:
4y = 24
⇒ y = 24/4= 6
∴ y = 6
(ii) Since x and y vary inversely, we have:
xy = k
For x = 5 and y = 15,
we have:5 × 15 = k
⇒ k = 75
For y = 12,
we have:
12x = 75
⇒ x = 75/12
= 25/4
∴ x = 25/4
(iii) Given:x = 30 and k = 900
∴ xy = k
⇒ 30y = 900
⇒ y = 900/30= 30
∴ y = 30
(iv) Given:y = 35 and k = 7
Now, xy = k
⇒ 35x = 7
⇒ x = 7/35 = 1/5
∴ x = 1/5
FAQs on Chapter 10 - Direct and Inverse Variations (Part - 2), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is direct variation in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What is inverse variation in mathematics? |  |
| 3. How do you determine if a relationship is direct or inverse variation? |  |
| 4. How do you find the constant of variation in direct and inverse variation? |  |
| 5. Can there be a situation where there is both direct and inverse variation? |  |
















