Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - Tissues
Q1: The tissues given below are called as:
(a) meristematic tissues
(b) permanent tissues
(c) complex tissues
(d) all of these
Ans: (c)
The given tissues are complex tissues.
Q2: Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
1. There is no demarcation of dividing and nondividing regions in animals.
2. Animals consume less energy as compared to plants.
3. Most of the tissues that plants contain are living.
4. Structural organization of organs and organ systems are more specialized animals than even in very complex plants.
5. Growth of animals is indefinite.
(a) 2, 3 and 5
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 1 and 5
Ans : (c)
Animals consume more energy as compared to plants. They move around in search of food, mates and shelter and hence require more energy for their activities. Most of the plant tissues are dead. Since plants are stationary or fixed, their tissues require to be supportive which provide them structural strength. Dead cells provide mechanical strength as easily as live ones, and need less maintenance.
Q3: Parenchyma cells containing air cavities are called
(a) aerenchyma
(b) sclerenchyma
(c) chlorenchyma
(d) prosenchyma
Ans: (a)
In aquatic plants (hydrophytes) large air cavities are present in the parenchymatous tissue. These cavities store gases and provide buoyancy to aquatic plants to help them float. Such parenchyma are called aerenchyma.
Q4: Find the living cells that provides mechanical strength to the plant.
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Sclerotic cells
Ans: (b)
Collenchyma is the living cell that gives mechanical strength to the plant.
Q5: Which of these types of cells is most likely to divide?
(a) Epidermis
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Meristem
(d) Xylem
Ans : (c)
Meristems are the sites or regions within the plant body where formation of new meristematic cells takes place. For example, root and shoot tips.
Q6: What is chlorenchyma?
(a) It is a simple permanent tissue
(b) It is a parenchymatic tissue of green leaves and stems
(c) It is a photosynthetic in nature
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Parenchyma (simple permanent tissue) cells of green leaves and stems containing chloroplasts are called as chlorenchyma.
Q7: Tracheids, vessels, wood fibres and parenchymatous tissues are found in
(a) xylem
(b) cambium
(c) cortex
(d) phloem
Ans: (a)
Xylem (wood) is a complex permanent tissue forming a part of vascular bundle. It is primarily responsible for the conduction of water and solutes from the roots up to the top of the plant. It is composed of cellular structures, such as tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
Q8: Identify the features of striated muscles.
(a) Cylindrical, striped, skeletal and voluntary
(b) Spindle, unbranched and uninucleated
(c) Cylindrical, unstriped and without nucleus
(d) Cylindrical, striped and branched
Ans: (a)
Straited muscles are cylindrical, striped, skeletal, voluntary unbranched and multinucleated.
Q9: There are specific regions of plant body that constantly remain in the state of division. What are they?
(a) Perisperm
(b) Endosperm
(c) Meristem
(d) Stele
Ans: (c)
A meristem is a tissue in plants consisting of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells). It is found in specific regions of a plant body where constant cell division takes place.
Q10: Muscles, which are immune to fatigue are
(a) unstriped muscles
(b) cardiac muscles
(c) jaw muscles
(d) skeleton muscles
Ans: (b)
Cardiac muscle contracts and relaxes rapidly and continuously with a rhythm, but it never gets fatigued.
Q11: Which of the following helps in increasing the width and the girth of the plants?
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Lateral meristem
(c) Intercalary
(d) Permanent tissue
Ans: (b)
Lateral meristem brings about the outward growth of plant by increasing its width and girth. Outward growth result in thickness of the plant.
Q12. Which of these features is associated with plasma membrane?
(a) Permeable
(b) Impermeable
(c) Selectively permeable
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans : (c)
The plasma membrane allows the entry and exit of certain materials, in and out of the cell. It also prevents the movement of some other materials. Some substances like carbon-di-oxide or oxygen move across the cell membrane by process called diffusion. On the other hand, substances like water moves across the cell membrane through the process called osmosis. Therefore, the cell membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Q13. Which of the following meristems helps to increase girth of the stem?
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Lateral meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) Vertical meristem
Ans: (b)
Lateral meristem consists of initials which divide mainly in one plane and cause the organ to increase in diameter and girth. The lateral meristem usually occurs on the sides both in stem and root.
Q14: Read the given statements.
1. Many nerve cells bound together by connective tissue make up a nerve.
2. Areolar connective tissue fills the space inside the organs and helps in repair of tissues.
3. Glandular epithelium is formed by infolding of epithelial tissue.
4. Smooth muscle fibres show characteristic of both striated and unstriated muscles.
5. Skin epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat through which absorption and secretion occur.
Select the incorrect statements.
(a) 4 and 5
(b) 1, 3 and 5
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Cartilage is a soft connective tissue that forms the articular surfaces at joints of long bones, tracheal rings, nasal septum, ear and larynx.
Q15: Identify the tissue that is present in leaf stalks below the epidermis.
(a) Collenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Parenchyma
(d) Xylem
Ans: (a)
Collenchyma tissue forms continuous cylindrical strands beneath the epidermis of stem or leaf.
Q16: Which of the following tissues provides flexibility and mechanical support to the plant organs?
(a) Collenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Parenchyma
(d) Chlorenchyma
Ans: (a)
Collenchyma is a living tissue of primary body. The cells are thin-walled but possess thickenings of cellulose and pectic substances at the corners where number of cells join together. The tissue provides flexibility to soft aerial parts (e.g., leaves, young stems) of plant so that they can bend without breaking. The cells are compact and the inter-cellular spaces are absent.
Fill in the blanks.
Q17: Though cardiac muscle resembles the striated muscle but it is an .......... muscle.
Ans : Involuntary muscle
Despite the similarities between cardiac muscle and striated muscle, the cardiac muscle is categorized as an "Involuntary muscle". This means that it functions without the need for conscious control or effort. It operates automatically, maintaining the rhythmic contraction and relaxation necessary for the heart to pump blood throughout the body.
Q18: Meristematic tissue is found in the growing tips of .......... and ..........
Ans : Root, stem
Meristematic tissue is found in the growing tips of "Roots and Stems". This tissue contains cells that have the ability to divide and contribute to the growth of the plant. It is essential for the lengthening of the roots and stems, helping the plant grow taller and deeper into the soil
Q19: .......... muscles are present in Iris of the eye, in uterus and bronchi of lungs.
Ans : Smooth or involuntary
The "Smooth or Involuntary muscles" are present in the Iris of the eye, in the uterus and bronchi of lungs. These muscles are not under our conscious control and they perform functions like contraction and relaxation automatically. For example, the iris controls the amount of light entering the eye and the bronchi control the air flow into our lungs.
Q20: A group of cells alike in form, function and origin are called ..........
Ans : Tissue
The term "Tissue" refers to a group of cells that are alike in form, function and origin. This means that the cells in a tissue have a similar structure, perform a specific function, and originate from the same type of precursor cells. For example, muscle tissue consists of muscle cells that help in movement and originate from the mesoderm layer of the embryo.
Q21: Muscles present in our limbs are .......... muscles.
Ans : Skeletal muscles or voluntary muscles
The muscles present in our limbs are called "Skeletal muscles or Voluntary muscles". These muscles are attached to the bones (hence the name 'skeletal') and are under our conscious control (hence 'voluntary'). They allow us to move our limbs at will, enabling actions such as walking, running, lifting, etc.
True/False
Q22: A large central vacuole is present in permanent tissues.
Ans: True
A large central vacuole is indeed present in permanent tissues. Permanent tissues are mature tissues that have lost the ability to divide. They have a unique set of characteristics and a specific function. In plant cells, the large central vacuole is primarily involved in storing water and other substances.
Q23: Cork cells have suberin deposits.
Ans: True
Cork cells, or phellem, are dead cells that provide protection to plants. These cells are filled with a fatty substance known as suberin, which makes them waterproof. The presence of suberin prevents the loss of water, thereby helping plants to survive in dry conditions.
Q24: Collenchyma tissue is a strong, flexible, living mechanical tissue.
Ans: True
Collenchyma tissue, a type of simple permanent tissue, is a living mechanical tissue in plants. It provides strength and flexibility to the plant parts that are continuously growing, such as stems and leaves. The cells of collenchyma tissue are thickened at the corners due to the deposition of cellulose and pectin.
Q25: The cytoplasm of a muscle cell is called sarcoplasm.
Ans: True
The cytoplasm of a muscle cell is indeed known as sarcoplasm. This is specific to muscle cells. The sarcoplasm contains large amounts of stored glycogen that provides energy for muscle contraction. It also contains myoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen for use in muscular activity.
Q26: Tendons connect muscles to bones.
Ans: True
Tendons function to connect muscles to bones. They are tough, flexible bands of fibrous tissue that can withstand tension. When muscles contract, tendons transmit the forces to the bone, enabling movement. Thus, they play a crucial role in our locomotion and other physical activities.
Matching Questions
Direction: Each question contains statements given in two columns which have to be matched. Statements (A, B, C, D) in column-I have to be matched with statements (p, q, r, s) in column II.
Q27: 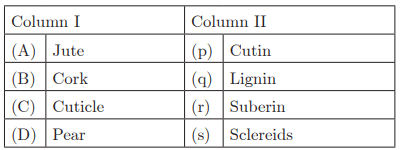
Ans : (b) A-q, B-r, C-p, D-s
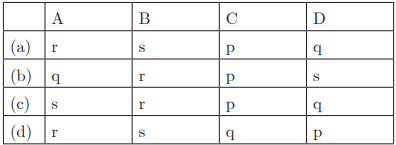
Q28: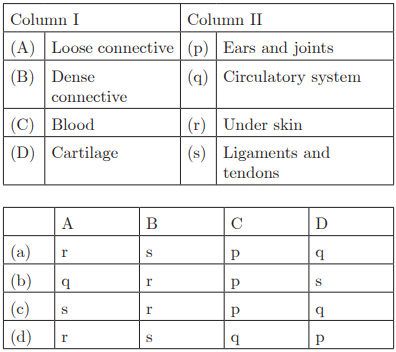 Ans : (d) A-r, B-s, C-q, D-p
Ans : (d) A-r, B-s, C-q, D-p
Q29: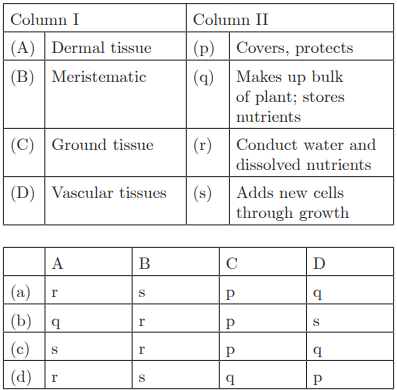 Ans : (c) A-r, B-s, C-q, D-p
Ans : (c) A-r, B-s, C-q, D-p
Q30: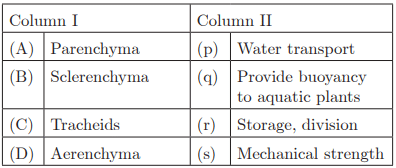
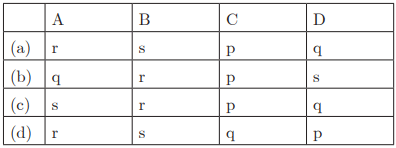
Ans : (a) A-r, B-s, C-p, D-q
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|





















